How Effective Is Retrieval Practice?
Why is this question important? Determining which tools are most effective in enhancing student performance is an important area of educational research. With the increased emphasis on school and teacher accountability, it is important that teachers use methods that maximize students’ abilities to demonstrate competency in skills they will need to be successful in life as well skills that will be examined on high-stakes tests.
See further discussion below.
Source(s): Retrieval Practice Produces More Learning Than Elaborative Studying With Concept Mapping
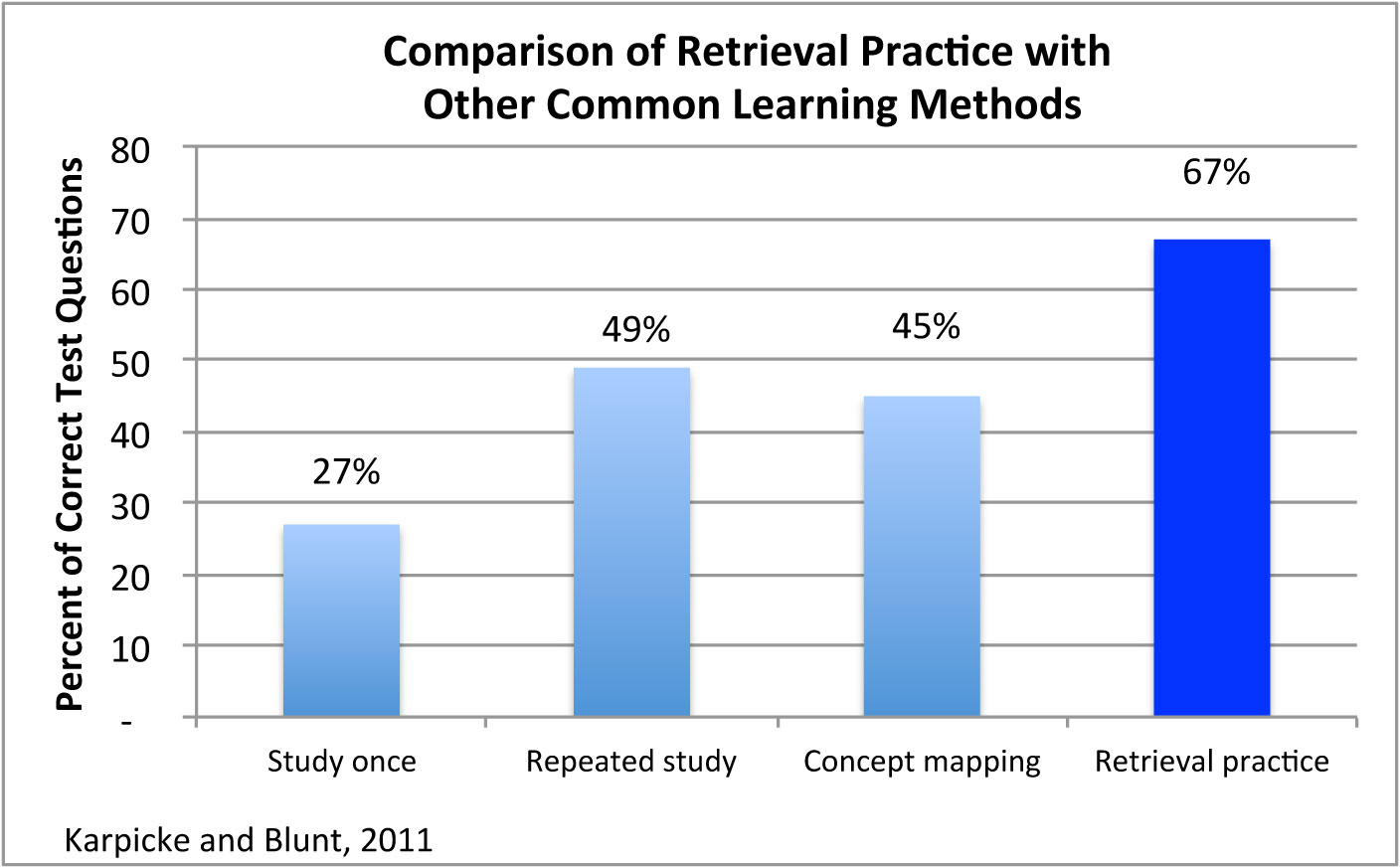
Result(s): The study found that students using the retrieval practice technique scored significantly higher than students using the study once, repeated study, and concept mapping techniques. The average percentage of correct test questions for each group was 67% for retrieval practice, 27% for study once, 49% for repeated study, and 45% for concept mapping.
Implication(s): Teacher preparation programs should incorporate practices such as retrieval practice into the course work for new teachers. Engaging students in study activities that have the potential to significantly improve student performance should be included as an integral part of every teacher’s teaching routine.
Author(s): J. D. Karpicke and J. R. Blunt
Publisher(s): American Association for the Advancement of Science
Study Description: The study attempted to compare the effectiveness of retrieval practices with that of three other common learning activities. In a randomized controlled trial, 80 undergraduate students were assigned to one of the following four groups, each employing a different method of studying:
- Study once group
- Repeated study group
- Concept mapping group
- Retrieval practice group
All study participants began by reading a 276-word passage on sea otters for 5 minutes. One week after the training, the students were given a test of the material covered in the training.
Definition(s):
Study once group: Students read the passage once, only during the first 5-minute reading period.
Repeated study group: Students read the same material during three additional 5-minute sessions, with 1-minute breaks between sessions.
Concept mapping group: Students spent 25 minutes after the reading period mapping out the text’s main concepts on paper.
Retrieval practice: Students spent 10 minutes after reading listing any information they remembered from the readings in a response box on a computer screen. The students then reread the text for an additional 5 minutes and again listed the information they recalled.
Citation: Karpicke, J. D., & Blunt, J. R. (2011). Retrieval practice produces more learning than elaborative studying with concept mapping. Science, 331, 772–775.
