What behavior management factors reduce disruptive behavior?
Why is this question important? When surveyed, principals and teachers cited classroom management and student conduct near the top of the list of issues impeding the effective running of a classroom. Hattie (2009) ranked classroom management fifth among school issues affecting student performance. Classroom conduct problems have a debilitating effect on schools, impacting staff morale as well as contributing to lower student achievement (Marzano, Marzano, & Pickering, 2003). What classroom management practices does the research show have the greatest impact on reducing disruptive behavior?
See further discussion below.
Source(s): Classroom Management That Works: Research-Based Strategies for Every Teacher
Result(s): The overall impact on student achievement in this study was an effect size of 0.521. This effective size is for all components of behavior management including but not limited to the factors listed below. The study reported a 20% increase in achievement when systematic rules and procedures were implemented.
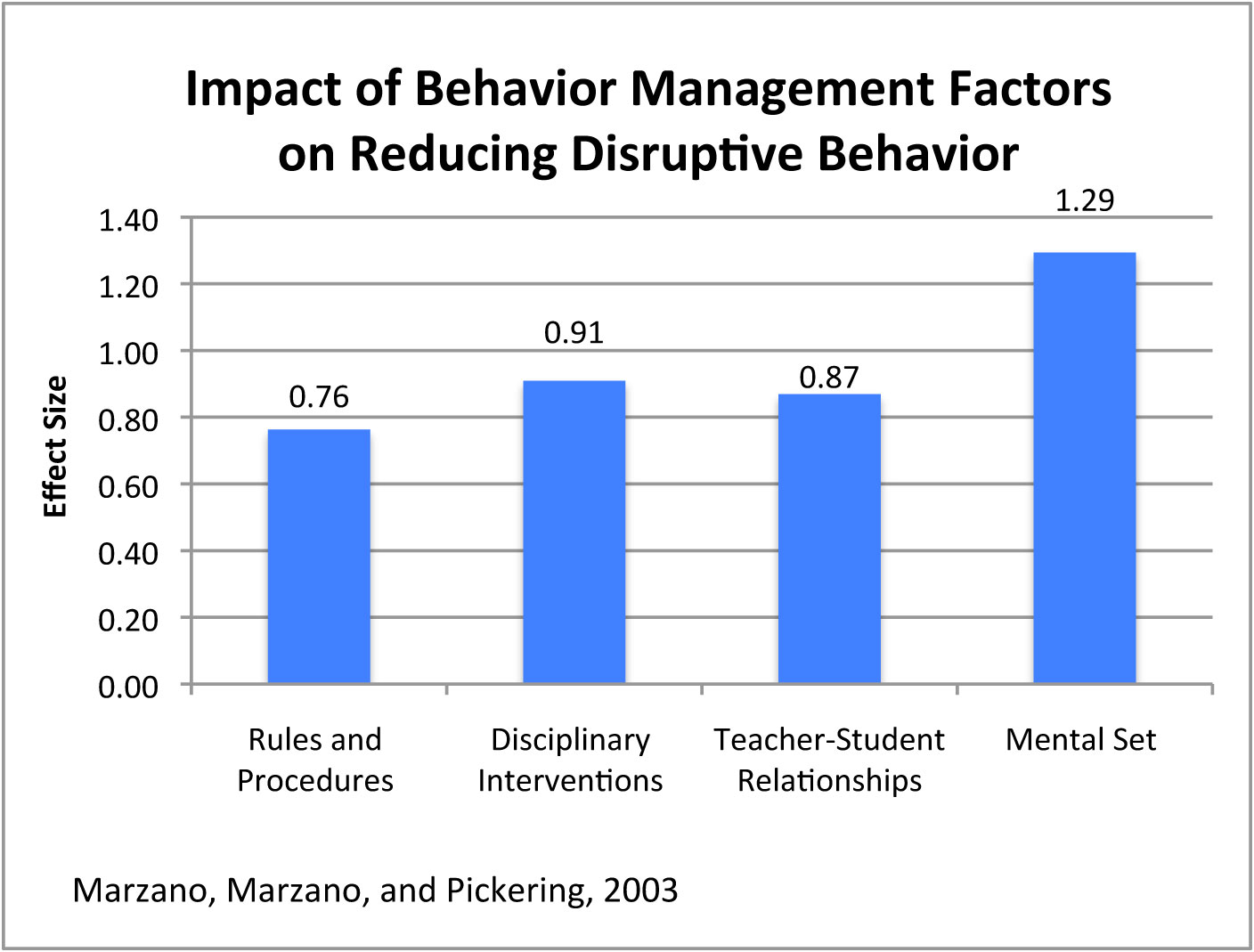
Factors That Reduce Disruptive Behavior
| Factors | Effect Size |
| Rules and Procedures | 0.76 |
| Disciplinary Interventions | 0.91 |
| Teacher-Student Relationships | 0.87 |
| Mental Set | 1.29 |
In the original report, the effect sizes were reported as negative numbers because the measures were a reduction of behavior problems relative to comparison conditions. For ease of understanding, the effect sizes here are reported as positives to more clearly communicate the benefits of effective classroom practices. The values remain the same.
Implication(s): Poor classroom management can have a significant impact on staff morale, leading to teacher burnout and turnover. It can also negatively impact student performance. Knowing what classroom management strategies work and what don’t is critical in building effective and productive schools.
Author(s): R.J. Marzano, J.S. Marzano, and D.J. Pickering
Publisher(s): Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Study Description: Marzano, Marzano, and Pickering conducted a meta-analysis that included 134 effect sizes derived from 100 studies on the topic of behavior management. This meta-analysis provided effect sizes for core components of effective classroom management.
| Factors | # of Studies |
| Rules and Procedures | 10 |
| Disciplinary Interventions | 68 |
| Teacher-Student Relationships | 4 |
| Mental Set | 5 |
Definition(s):
- Rules and procedures: Stated expectations regarding student behavior. Rules identify general expectations or standards, and procedures communicate expectations for specific behavior or performance.
- Disciplinary interventions: Strategies and actions that school personnel use when students do not follow rules and procedures. They are implemented schoolwide as well as at the classroom level.
- Teacher-student relationships: Characteristics comprising the interactions between teachers and their students. Most noteworthy is the ability of teachers to provide guidance while attending to the needs and concerns of the students.
- Mental set: A teacher’s keen awareness of disruptive or potentially disruptive behavior and his or her immediate attention and response to it.
Citation:
Hattie, J., (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses related to achievement. New York: Routledge.
Marzano, R.J., Marzano, J.S., & Pickering, D.J. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum. Development
