Do teacher working conditions correlate with student learning conditions?
Why is this question important? It is critical to identify variables that most impact student learning. All schools have cultures (deliberately planned or not) that create teacher working conditions. The degree to which these working conditions affect student performance is critical as limited resources are allocated. It is also critical to examine these findings across different grade levels.
See further discussion below.
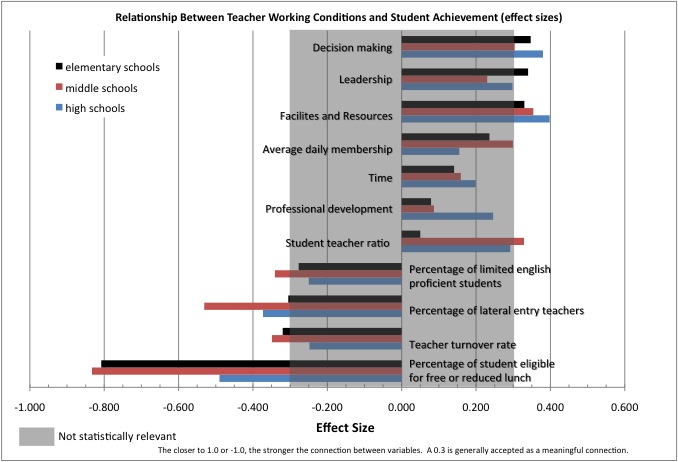
Source:North Carolina Teacher Working Conditions Survey Brief: Teacher Working Conditions Are Student Learning Conditions
Results: While there was variation between elementary, middle, and high schools, the data did show a high correlation between decision making, leadership, time, facilities, and resources and student achievement. The strongest correlations was student characteristics, in particular poverty. The next highest were factors related to teacher turnover.
Implications: The data suggests that teacher working conditions are an important piece of the puzzle for building effective student learning environments.
Author(s): Eric Hirsch, New Teacher Center and Keri Church, LEARN INC
Publisher: New Teacher Center, University of California, Santa Cruz 2009
Study Description: North Carolina’s Professional Teaching Standards Commission and State Board of Education have conduced Teacher Working Condition Surveys since 2001. The above data represents the responses of over 104,000 North Carolina educators (87%) from a survey completed in 2008. The New Teacher Center analyzed the relationship between survey responses aggregated to the school-level and student performance as measured by the student performance composite.
Citation:
Hirsch, E. & Church, K. (2009). North Carolina Teacher Working Conditions Survey Brief: Teacher Working Conditions Are Student Learning Conditions (Research Brief #09-06). Retrieved from North Carolina’s Teacher Working Conditions Initiative: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED498770
