What impact does a principal's leadership have on student outcomes?
Why is this question important? Decision makers and educators in the United States have placed school principals front and center in school reform efforts. Beginning with accountability measures in No Child Left Behind and subsequently with School Improvement Grants (SIG), policy makers have emphasized the importance of strong school leadership. SIG mandates four options to turn around a school's performance. It is notable that all four require changing the school principal. If we are to place such a high value on leadership, it is important that we find out if the evidence supports this heavy investment in school principals to leverage school improvement efforts.
See further discussion below.
Source: Robinson, V. M. (2007). School leadership and student outcomes: Identifying what works and why (Vol. 41). Winmalee, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Leaders
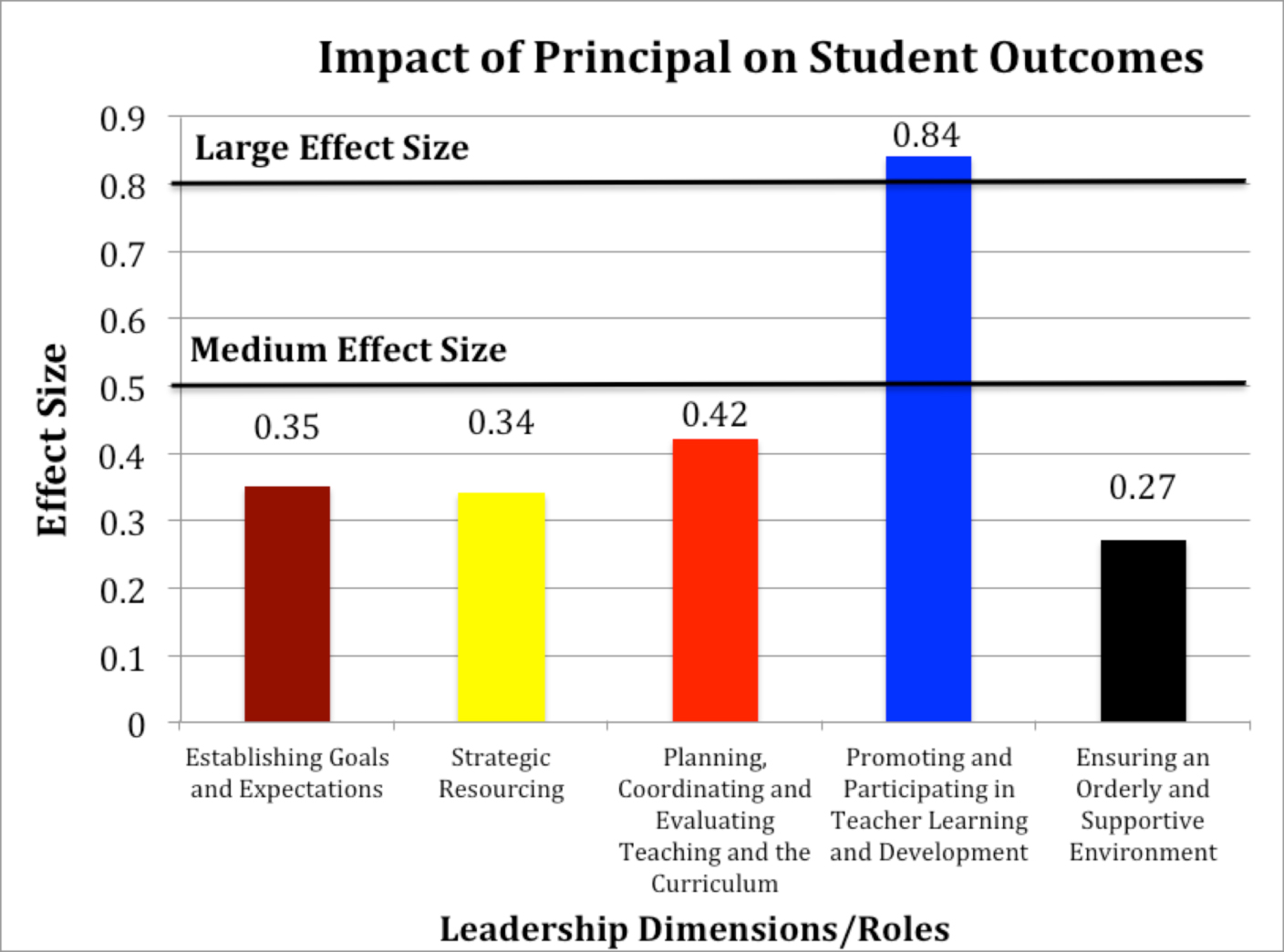
Results: This paper identifies five dimensions of a principal's leadership that result in improved student performance, along with the average effect size for each category. The five dimensions are:
- Establishing goals and expectations – 0.35 effect size
- Strategic resourcing – 0.34 effect size
- Planning, coordinating, and evaluating teaching and the curriculum – 0.42 effect size
- Promoting and participating in teacher learning and development – 0.84 effect size
- Ensuring an orderly and supportive environment – 0.27 effect size
This study differs from past work conducted by Leithwood, Louis, Anderson, and Wahlstrom, who organized their analysis into three categories: setting direction, developing people, and redesigning the organization. Robinson focuses on the goals and activities that make for an effective principal whereas previous research has been directed at the impact of relationships on leadership.
Implications: This paper offers categories of goals and activities that principals can use to improve their own performance in order to have a positive impact on teachers and students. It is important to recognize that promoting and participating in teacher learning and development has the most significant impact on student achievement. This research shows that it is approximately twice as powerful as the other four dimensions.
Study Description: This meta-analysis examines 26 studies on school leadership to develop the main findings on the magnitude of direct and indirect effects of leadership on teacher and student performance. Only 11 studies met the inclusion criteria to evaluate each leadership dimension and its impact on student outcomes.
Definitions: Establishing goals and expectations: Set, communicate, and monitor learning goals, standards, and expectations. Obtain the involvement of staff and others in the process so that there is clarity and consensus about goals.
Strategic resourcing: Align resource selection and allocation (including staff recruitment) with teaching goals.
Planning, coordinating, and evaluating teaching and the curriculum: Become directly involved in the support and evaluation of classroom instruction through regular classroom visits and the use of formative and summative feedback. Directly oversee schoolwide coordination of curriculum across classes and grades that are aligned with school goals.
Promoting and participating in teacher learning and development: Promote and directly participate with teachers in professional learning.
Ensuring an orderly and supportive environment: Ensure adequate time for instruction and learning by reducing external pressures and interruptions and by establishing an orderly and supportive environment both inside and outside classrooms.
