Education Drivers
Introduction
Evaluating the evidence base for an educational practice involves synthesizing the results of multiple studies. As locating and evaluating the results of multiple primary sources is a time-consuming endeavor for educators, review articles play a critical role in this synthesis for practitioners. Review articles are publications that summarize and discuss research on a specific topic. While the term “review article” generally implies a discussion of multiple experimental studies, a systematic review is a review with explicit, replicable search and coding methods that addresses a specific question (Page et al., 2021). Systematic reviews can focus on one type of study (group designs, single case designs, qualitative research) or include multiple types of studies, although it can be difficult to combine results across types of studies. Moreover, a meta-analysis involves aggregating data across multiple studies and conducting statistical analyses of synthesized effects. A meta-analysis may coincide with a systematic review if it includes the features of that kind of review, but may also be conducted outside the context of a systematic review, perhaps on a limited number of data sets (Page et al., 2021).
Quality Indicators of Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews can vary widely in quality and rigor. Consumers must consider various quality indicators when evaluating the findings of a systematic review (Maggin et al., 2017):
- Research question. The research question of a systematic review should provide clear boundaries for inclusion and exclusion of studies. For example, Alperin et al. (2021) “...systematically review[ed] the school-based literature on behavior interventions and supports implemented with middle school students (grades 6 to 8) exhibiting disruptive behaviors” (p. 3). This statement specifies the setting of the research, the target demographic, and the presenting problem.
- Eligibility criteria. The criteria, including participant information, research design, and publication date range, should align with the research question. That is, for Alperin et al., the eligibility criteria included empirical studies that took place in school settings for students in grades 6 to 8 where disruptive behavior was measured.
- Search procedures. Experimental studies clearly describe their methods and procedures so that another researcher could replicate the work. Similarly, systematic reviews are distinguished from other types of reviews by their clearly defined search criteria, or how the included articles are identified. This includes:
- Databases or registries searched
- Keywords used in searches
- The date when a search was conducted
- Language criteria (e.g., include only articles published in English)
King et al. (2020) described additional considerations for search and selection factors. Although database searches are comprehensive and easy to replicate, other types of searches can also be conducted. Hand searches involve manually searching through a specific journal. Ancestral searches involve consulting the reference lists of relevant articles and locating the citations.
Another critical factor when selecting articles to review is publication status. Published work refers to articles published in peer-reviewed journals. Unpublished work consists of doctoral dissertations or master’s theses—empirical work that is not published in a peer-reviewed journal and that may or may not be available in library databases. Many systematic reviews do not include unpublished work because it is difficult to locate and may be of poor quality. Yet omitting unpublished work could contribute to publication bias. That is, studies showing that an intervention is successful are more likely to be published.
- Retrieval and screening procedures. After implementing the search procedures, the systematic review should report the total citations returned, any screening procedures, the total articles excluded, and the total articles reported in the review. Articles may be screened out if they do not meet the inclusion criteria laid out in the research question (e.g., participant demographics do not align with the population of interest) or based on study quality. When a large volume of studies on a topic exists, researchers may omit poor-quality studies from systematic reviews. However, when there is limited research on a topic, eliminations may not be appropriate (King et al., 2020). If quality-based inclusion criteria are modified to include a larger number of studies, researchers should identify this limitation and caution readers about making strong conclusions.
- Coding. Once the sample of articles to be included in the review has been finalized, each article must be coded for analysis. Articles may be coded by characteristics of participants, interventions, measures, or methodological quality. In addition, a proportion of the articles should be double coded (i.e., by two independent researchers) to check for agreement and reliability. There may also be a procedure for resolving any disagreements and addressing missing information.
- Research personnel. Who are the individuals searching for and coding articles? The systematic review may describe the qualifications of the researchers (e.g., academic degrees, years of research experience). If others, such as graduate students or research assistants, aid in searching for or coding articles, the systematic review should also report how these individuals were trained.
- Data analysis plan. The data analysis plan for a systematic review should address the specific research questions. Data should be aggregated and displayed in table or with graphs. If conducting a meta-analysis, statistical tests are also reported (Maggin et al., 2017).
Clearly describing the procedures for article search and selection are critical for readers to evaluate consistency across reviews. King et al. (2020) described search and selection procedures of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in 38 special education journals between 2004 and 2016. The authors analyzed more than 1,100 articles, classifying each article by type of review, search procedures, and search criteria.
Most of the articles in the study (88%) searched multiple databases and reported the search terms used (90%). More than half (57%) identified range of years included in the review, while only 14% reported the date the literature search took place. Only 27% of the articles reported assessing the quality of the reviewed studies, and 17% used poor study quality as an exclusionary factor; the authors also reported a trend toward assessing quality over the past 12 years. For experimental designs, 25% of the articles included only group-design studies, 21% included only single-case design studies, and the remaining included studies of varied designs. Lastly, 31% of the articles restricted their searches by participant age range, specific intervention, or population of interest.
As systematic reviews increasingly use study quality as an exclusionary factor, it is vital to examine how study quality is assessed. Maggin et al. (2014) compared the features of the following seven evaluation tools (rubrics) for evaluating single-case research:
- Evaluative Method for Assessing Single-Case Research (Reichow et al., 2008)
- Scientific Merit Rating Scale (National Autism Center, 2008)
- National Professional Development Center on Autism Spectrum Disorders (NPDC-ASD)
- Protocol for Assessing Single-Subject Research Quality (PASS-RQ; Maggin & Chafouleas, 2010)
- Single-Case Experimental Design Scale (SCEDS; Tate et al., 2008)
- Single-Subject Research Design Quality Rating (SSRDQ; Logan et al., 2008)
- What Works Clearinghouse Single-Case Design Standards (Kratochwill et al., 2010)
Maggin et al. found that all seven rubrics included items related to experimental control and reliability of the dependent variable. Other criteria, however, varied widely. Some of the rubrics included criteria as shown below (the number of rubrics from the list of seven, above, that address each criterion is noted in the parenthetical).
- visual analysis (5/7)
- treatment integrity (3/7)
- baseline description (3/7)
- operational definition of dependent variable (4/7)
- description of independent variable (4/7)
- description of participants (5/7)
- description of setting (2/7)
Overall, the overlap of criteria among rubrics ranged from 21% to 75% (average 48%). The researchers noted two types of scoring procedures across the rubrics. Some used an “inventory” approach, in which each criterion is assessed as met or not met, then assigning a percentage of criteria met. Others used a “gating” procedure; studies are assessed as meeting or not meeting a criterion, and only those that meet the criterion are assessed for the next criterion.
As an additional comparison, Maggin et al. (2014) evaluated a sample of 28 research articles using all seven rubrics and classified the evidence for the intervention of interest as strong, moderate, or no evidence. Across the seven rubrics, between 4 and 22 of the articles were found to have strong evidence, between 5 and 22 were found to have moderate evidence, and between 1 and 20 were found to have no evidence. For example, the Scientific Merit Rating Scale (National Autism Center, 2008) classified 22 of the 28 studies as having strong evidence, 5 of the 28 as having moderate evidence , and 1 of the 28 as having no evidence, whereas the What Works Clearinghouse Single-Case Design Standards (Kratochwill et al., 2010) classified 7 of the 28 studies as having strong evidence, 12 of the 28 as having moderate evidence, and 9 of the 28 as having no evidence.
Given the high level of variability across rubrics, Maggin et al. (2014) recommended that researchers use two or more evaluation tools, consider the strengths and weaknesses of each, and synthesize the results. The authors suggested using at least one rubric scored by the inventory method and one scored by the gating method could facilitate a more comprehensive assessment of the studies.
Effect Sizes
Some systematic reviews and most meta-analyses report effect sizes, or numerical values quantifying the effectiveness of the intervention of interest, for each study. Effect sizes are a critical tool for synthesizing results across studies, particularly when attempting to determine the evidence base for an educational practice. What Works Clearinghouse (2017) recommended calculating effect size with Hedge’s g or the Cox index for group design studies or a design-comparable effect size (D-CES) for single-case design studies (although it should be noted that there is not currently an agreed-upon effect size measure for single-case design). Effect sizes may be reported as a decimal point for Cohen’s d or Hedges g (e.g., 0.25) or a percentage for Cohen’s U3 (e.g., 60%). Table 1 is adapted from Cook et al. (2018), which provides a reference for interpreting effect sizes.
Table 1
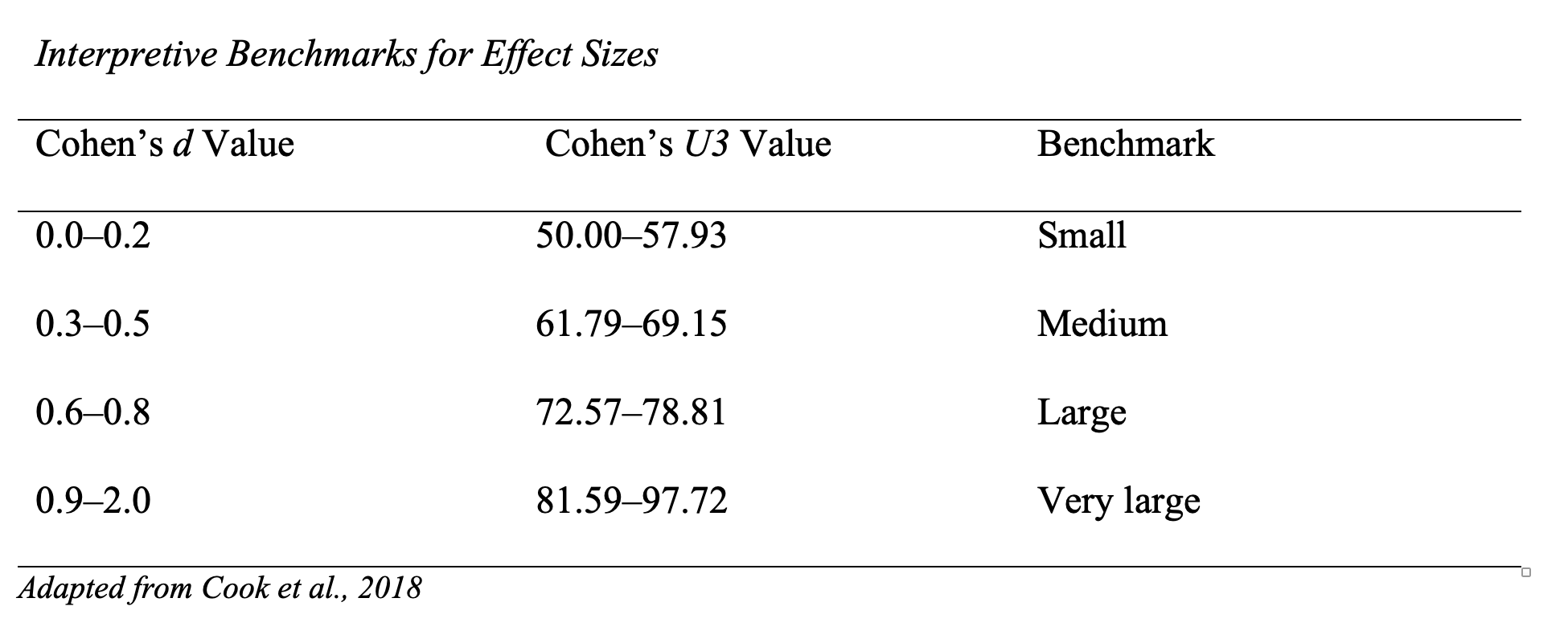
Once effect size has been determined, a study can be classified as having a positive, an indeterminate, or a negative effect. These categorizations can then be used to determine an overall rating of effectiveness for an intervention as a positive effect, a potentially positive effect, no discernible effect, a mixed effect, a potentially negative effect, or a negative effect (What Works Clearinghouse, 2017). Cook et al. (2018) also noted that considering contextual variables (see Contextual Fit) is critical when interpreting effect size. That is, an intervention found to have one effect size with typically developing students may have a different effect size among students with learning disabilities.
Replicating Systematic Reviews
A key feature of a systematic review is defined search criteria, which usually include a specified range of publication years or otherwise identify all the published research to date on a topic. As new research is constantly being published, systematic reviews must be replicated to include more recently published studies. The results of an updated systematic review or meta-analysis could strengthen the findings of the original or challenge them.
For example, Randolph (2007) conducted a meta-analysis of 18 studies on using response cards. A range of publication years was not provided in the search criteria; therefore, we assume that the review targeted all research to date on response cards. The studies measured four dependent variables: test achievement, quiz achievement, participation, and off-task behavior. Randolph analyzed the effect size for each of these measures separately and found moderate to strong effect sizes favoring response cards. For example, an average 48% increase in participation and an average 34% decrease in off-task behavior were observed across studies when response cards were implemented. Some studies used preprinted response cards while others used write-on response cards; no statistically significant differences were detected between the two types of cards.
More recently, Marsh et al. (2021) replicated and updated Randolph’s meta-analysis, adding 15 additional studies to the analysis. Across the same four dependent measures, moderate to strong effect sizes were also detected. For example, an average increase of 59 percentage points in participation and an average decrease of 26 percentage points in off-task behavior were observed across studies when response cards were implemented. The researchers also analyzed differences between students in general education and special education settings. Students in special education settings demonstrated greater gains in quiz (22%) and test (15%) scores than those in general education settings (quiz scores: 12%; test scores: 11%). Students in general education settings demonstrated greater increases in participation (63%) and greater decreases in off-task behavior (40%) than those in special education (participation: 57%; off-task behavior; 14%). By replicating Randolph’s meta-analysis, Marsh et al. strengthened the previous findings by adding more studies and provided further insight with additional analyses.
Conclusions
Systematic reviews summarize and evaluate the research base for a given educational practice, sometime with specific age ranges, settings, or populations. A systematic review includes a clear research question and replicable search and coding procedures. Increasingly, systematic reviews include exclusion criteria based on study quality (King et al., 2020). There are many established rubrics for assessing the quality of published studies. However, as agreement among these rubrics is highly variable, using multiple assessment methods and synthesizing the results are recommended (Maggin et al., 2014). Systematic reviews must be replicated regularly to include more recently published studies.
Citations
Alperin, A., Reddy, L. A., Glover, T. A., Bronstein, B., Wiggs, N. B., & Dudek, C. M. (2021). School-based interventions for middle school students with disruptive behaviors: A systematic review of components and methodology. School Psychology Review. https://doi.org/10.1080/2372966X.2021.1883996
Cook, B. G., Cook, L., & Therrien, W. J. (2018). Group-difference effect sizes: Gauging the practical importance of findings from group-experimental research. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 33(2), 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12167
King, S., Davidson, K., Chitiyo, A., & Apple, D. (2020). Evaluating article search and selection procedures in special education literature reviews. Remedial and Special Education, 41(1), 3–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932518813142
Kratochwill, T. R., Hitchcock, J., Horner, R. H., Levin, J. R., Odom, S. L., Rindskopf, D. M., & Shadish, W. R. (2010). Single-case design technical documentation. What Works Clearinghouse. https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/ReferenceResources/wwc_scd.pdf
Logan, L. R., Hickman, R. R., Harris, S. R., & Heriza, C. B. (2008). Single-subject research design: Recommendations for levels of evidence and quality rating. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 50(2), 99–103.
Maggin, D. M., & Chafouleas, S. M. (2010). PASS-RQ: Protocol for assessing single-subject research quality. Unpublished research instrument.
Maggin, D. M., Briesch, A. M., Chafouleas, S. M., Ferguson, T. D., & Clark, C. (2014). A comparison of rubrics for identifying empirically supported practices with single-case research. Journal of Behavioral Education, 23, 287–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-013-9187-z
Maggin, D. M., Talbott, E., Van Acker, E. Y., & Kumm, S. (2017). Quality indicators for systematic reviews in Behavioral Disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 42(2), 52–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/0198742916688653
Marsh, R. J., Cumming, T. M., Randolph, J. J., & Michaels, S. (2021). Updated meta-analysis of the research on response cards. Journal of Behavioral Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09463-0
National Autism Center. (2008). National standards project. https://nationalautismcenter.org/national-standards/
National Professional Development Center on Autism Spectrum Disorders. (2009). Evidence-based practices for children and youth with ASD. http://autismpdc.fpg.unc.edu/sites/autismpdc.fpg.unc.edu/files/EBP_Update_Reviewer_Training_printversion.pdf
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Boussuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M. Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. British Medical Journal, 372(71), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Randolph, J. J. (2007). Meta-analysis of the research on response cards: Effects on test achievement, quiz achievement, participation, and off-task behavior. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 9(2), 113–128. https://doi.org/10.1177/10983007070090020201
Reichow, B., Volkmar, F. R., & Cicchetti, D. V. (2008). Development of the evaluative method for evaluating and determining evidence-based practices in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(7), 1311–1319.
Tate, R. L., McDonald, S., Perdices, M., Togher, L., Schultz, R., & Savage, S. (2008). Rating the methodological quality of single-subject designs and n-of-1 trials: Introducing the Single-Case Experimental Design (SCED) Scale. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 18(4), 385–401.
What Works Clearinghouse. (2017). Procedures handbook (version 4.0). https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/ReferenceResources/wwc_procedures_handbook_v4_draft.pdf
Publications
Evidence-based, empirically-supported, and best practice are often used interchangeably. A case is made that for clarity each term should have a separate and distinct meaning.
Detrich, R. (2008). Evidence-Based, Empirically Supported, OR Best Practice?. Effective practices for children with autism, 1.
Increasing education’s reliance on evidence to guide decisions requires a significant change in the culture of districts and schools. This paper reviews the implications of moving toward evidence-based education.
Detrich, R., Keyworth, R., & States, J. (2007). A Roadmap to Evidence-based Education: Building an Evidence-based Culture. Journal of Evidence-based Practices for Schools, 8(1), 26-44.
This paper outlines the best practices for researchers and practitioners translating research to practice as well as recommendations for improving the process.
Shriver, M. D. (2007). Roles and responsibilities of researchers and practitioners for translating research to practice. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 8(1), 1-30.
Synopsis: Evidence-based practice is characterized as a framework for decision-making integrating best available evidence, clinical expertise, and client values and context. This paper reviews how these three dimensions interact to inform decisions.
Spencer, T. D., Detrich, R., & Slocum, T. A. (2012). Evidence-based practice: A framework for making effective decisions. Education and Treatment of Children, 35(2), 127-151.
This paper examines the types of research to consider when evaluating programs, how to know what “evidence’ to use, and continuums of evidence (quantity of the evidence, quality of the evidence, and program development).
Twyman, J. S., & Sota, M. (2008). Identifying research-based practices for response to intervention: Scientifically based instruction. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 9(2), 86-101.
Data Mining
This item provides information for practitioners on how to interpret effect sizes found in research papers.
States, J. (2010). How can I interpret the effect size from a study into the impact a practice might have if I implement the practice in my classroom or school? Retrieved from how-can-i-interpret.
Presentations
This paper outlines the best practices for researchers and practitioners translating research to practice as well as recommendations for improving the process.
Shriver, M. (2006). Roles and Responsibilities of Researchers and Practitioners Translating Research to Practice [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2006-wing-presentation-mark-shriver.
This paper offers an overview of issues practitioners must consider in selecting practices. Types of evidence, sources of evidence, and the role of professional judgment are discussed as cornerstones of effective evidenced-based decision-making.
States, J. (2010). What the Data Tell Us [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2010-capses-presentation-jack-states.
This paper examines the types of research to consider when evaluating programs, how to know what “evidence’ to use, and continuums of evidence (quantity of the evidence, quality of the evidence, and program development).
Twyman, J. (2007). Identifying Research-based Practices for RtI: Scientifically Based Reading [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2007-wing-presentation-janet-twyman.
This book is a very serious effort to apply behavioral psychology to culture change. The book begins with a technical discussion of the principles of reinforcement and then moves on to a discussion of how one changes cultural practices.
In this book, the authors point to the opportunities that exist for scientist-practitioners and attempt to prepare students to succeed in the era of managed care. The purpose is to describe in some detail methods of developing, administering, evaluating, and training in the delivery of behavioral health care and education services that will epitomize the role of the scientist-practitioner.
This book brings together 70 top researchers and scholars in the field to address the major foundational, assessment, characteristics, intervention, and methodological issues facing the field of emotional and behavioral disorders (EBD) of children and adolescents
The present paper makes the case for systematic assessment and evaluation in clinical practice. The purpose of systematic evaluation is to enhance client care and to improve the basis for drawing inferences about treatment and therapeutic change.
Kazdin, A. E. (1993). Evaluation in clinical practice: Clinically sensitive and systematic methods of treatment delivery. Behavior Therapy, 24(1), 11-45.
This book represents updates in the field over the last two decades. The book covers four major topics in field experimentation.
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference.
Two retarded boys exhibited abnormally low rates of smiling. In Exp. I, the frequency of a boy's smiling was first increased with candy reinforcement, but the frequency of the response did not decrease when candy reinforcement was terminated.
The purpose of the present study was to survey a large national sample of practitioners regarding their attitudes and beliefs about the role of psychotherapy treatment manuals in clinical practice.
Addis, M. E., & Krasnow, A. D. (2000). A national survey of practicing psychologists' attitudes toward psychotherapy treatment manuals. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 68(2), 331.
We analyze the relationship between inequality and economic growth from two directions. The first part of the survey examines the effect of inequality on growth. The second part analyzes several mechanisms whereby growth may increase wage inequality, both across and within education cohorts.
Aghion, P., Caroli, E., & Garcia-Penalosa, C. (1999). Inequality and economic growth: The perspective of the new growth theories. Journal of Economic literature, 37(4), 1615-1660.
The authors effectively cover the construction of psychological tests and the interpretation of test scores and scales; critically examine classical true-score theory; and explain theoretical assumptions and modern measurement models, controversies, and developments.
Allen, M. J., & Yen, W. M. (2001). Introduction to measurement theory. Waveland Press.
This paper reviews methods for deriving measures of effect for interrupted time-series (single case) designs.
Allison, D. B., & Gorman, B. S. (1993). Calculating effect sizes for meta-analysis: The case of the single case∗. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 31(6), 621-631.
The “Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing” were approved as APA policy by the APA Council of Representatives in August 2013.
American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, Joint Committee on Standards for Educational, Psychological Testing (US), & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1985). Standards for educational and psychological testing. American Educational Research Association.
This paper examines the benefits and challenges inherent in using randomized clinical trials and quasi-experimental designs in the field of education research.
Angrist, J. D. (2003). Randomized trials and quasi-experiments in education research. NBER Reporter Online, (Summer 2003), 11-14.
Evaluated the use of the N. S. Jacobson et al (see record 1985-00073-001) criteria for clinical significance in psychotherapy data analysis.
Ankuta, G. Y., & Abeles, N. (1993). Client satisfaction, clinical significance, and meaningful change in psychotherapy. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 24(1), 70-74.
Objective: To review alternative treatments (Tx) of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)those other than psychoactive medication and behavioral/psychosocial Tx-for the November, 1998 National Institute of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Conference on ADHD.
Arnold, L. E. (1999). Treatment alternatives for attention-deficit! hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Journal of attention disorders, 3(1), 30-48.
The authors use panel data from New York City to compare four ways in which teachers are new to assignment: new to teaching, new to district, new to school, or new to subject/grade.
Atteberry, A., Loeb, S., & Wyckoff, J. (2017). Teacher churning: Reassignment rates and implications for student achievement. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 39(1), 3-30.
The Condition of Education. This year’s report presents 49 indicators of important developments and trends in U.S. education.
Aud, S., Hussar, W., Johnson, F., Kena, G., Roth, E., Manning, E., ... & Zhang, J. (2012). The Condition of Education 2012. NCES 2012-045. National Center for Education Statistics.
The Condition of Education. This year's report presents 50 indicators of important developments and trends in U.S. education.
Aud, S., Hussar, W., Kena, G., Bianco, K., Frohlich, L., Kemp, J., & Tahan, K. (2011). The Condition of Education 2011. NCES 2011-033. National Center for Education Statistics.
There is growing evidence to support the use of trial-based functional analyses, particularly in classroom settings. However, there currently are no evaluations of this procedure with typically developing children. Furthermore, it is possible that refinements may be needed to adapt trial-based analyses to mainstream classrooms.
Austin, J. L., Groves, E. A., Reynish, L. C., & Francis, L. L. (2015). Validating trialâbased functional analyses in mainstream primary school classrooms. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 48(2), 274-288.
The Knowledge Utilization Society provides a home for researchers, scholars, and others who examine the processes of knowledge utilization and develop and test strategies for planned change in public and private institutions.
Backer, T. E. (1991). Knowledge utilization: The third wave. Knowledge, 12(3), 225-240.
This chapter reviews a set of behavioral science findings derived from the November 1993 NIDA Technical Review, “Reviewing the Behavioral Science Knowledge Base on Technology Transfer.” This is not intended to be a complete recapitulation of the arguments and conclusions drawn by the authors of the 14 papers presented in this monograph.
Backer, T. E., & David, S. L. (1995). Synthesis of behavioral science learnings about technology transfer. NIDA research monograph, 155, 262-279.
In 1980, a national conference (Ysseldyke & Weinberg, 1981) acknowledged a growing crisis of morale and mission in the discipline of school psychology. As part of that conference, Baer and Bushell (1981) described the accomplishments of behavior-analytic approaches to public education.
Baer, D. M. (1988). The Future of Behavior Analysis in Educational Settings. In Handbook of Behavior Therapy in Education (pp. 823-828). Springer, Boston, MA.
Analytic behavioral application is the process of applying sometimes tentative principles of behavior to the improvement2 of specific behaviors, and simultaneously evaluating whether or not any changes noted are indeed attributable to the process of application-and if so, to what parts of that process.
Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., & Risley, T. R. (1968). Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis 1. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 1(1), 91-97.
This book is a practical text that provides the beginning researcher with a clear description of how behavior analysts conduct applied research and submit it for publication. In a sequence of ten logical steps, the text covers the elements of single-case research design and the practices involved in organizing, implementing, and evaluating research studies.
Bailey, J. S., & Burch, M. R. (2017). Research methods in applied behavior analysis. Routledge.
This book has been raging for decades, raising many questions about the power of science. The book not only helps resolve many current debates about science, but it is also a major contribution to explaining science in terms of a powerful philosophical system.
Baldwin, J. D. (2015). Ending the science wars. Routledge.
This article reviews evidence suggesting that psychological interventions from a variety of theoretical perspectives have demonstrated effectiveness for a wide range of disorders—either alone or, in some cases, in combination with medications.
Barlow, D. H. (1994). Psychological interventions in the era of managed competition. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 1(2), 109-122.
The purpose of this book is to provide a comprehensive sourcebook on single case experimental designs with practical guidelines for their use in a range of research and clinical settings.
Barlow, D. H., Nock, M., & Hersen, M. (2009). Single case experimental designs: Strategies for studying behavior for change (No. Sirsi) i9780205474554).
In this paper, the concepts of decision reliability and validity, extensions of reliability and validity theory that encompass decision outcomes, are used to frame a general analysis of three alternative assessment strategies: multiple gating, template matching, and time-series methods.
Barnett, D. W., & Macmann, G. M. (1992). Decision reliability and validity: Contributions and limitations of alternative assessment strategies. The Journal of Special Education, 25(4), 431-452.
In this article, we attempt to distinguish between the properties of moderator and mediator variables at a number of levels.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of personality and social psychology, 51(6), 1173.
s. In this study, the authors used meta-analytic procedures to test one possible factor contributing to the attenuation of effects: structural inequalities between placebo and active treatments.
Baskin, T. W., Tierney, S. C., Minami, T., & Wampold, B. E. (2003). Establishing specificity in psychotherapy: a meta-analysis of structural equivalence of placebo controls. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 71(6), 973.
The conclusion of the Division 12 Task Force's report on empirically supported treatments raises 3 questions. It is concluded that the Task Force's selection of criteria, particularly as modified by D. L. Chambless and S. D. Hollon (1998), was a reasonable response to these pressures.
Beutler, L. E. (1998). Identifying empirically supported treatments: What if we didn't?. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 66(1), 113.
This article describes an $80-million project designed to test whether a continuum of mental health and substance abuse services for children and adolescents is more cost-effective than services delivered in the more typical fragmented system.
Bickman, L. (1996). A continuum of care: More is not always better. American Psychologist, 51(7), 689.
After reviewing relevant scientific literature, the author concludes that these are myths with little or no evidence to support them. The author suggests 4 ways to improve the quality and effectiveness of services.
Bickman, L. (1999). Practice makes perfect and other myths about mental health services. American Psychologist, 54(11), 965.
The present study considered outcomes at 5-year follow-up to examine long-term effects from the continuum of care.
Bickman, L., Lambert, E. W., Andrade, A. R., & Penaloza, R. V. (2000). The Fort Bragg continuum of care for children and adolescents: mental health outcomes over 5 years. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 68(4), 710.
This paper examines the strengths and weaknesses of the three main paradigms that guide prevention research: organicism, mechanism, and contextualism
Biglan, A. (1995). Choosing a paradigm to guide prevention research and practice. Drugs & Society, 8(3-4), 149-160.
The authors propose a version of contextualism as an alternative paradigm for the behavioral sciences. According to this paradigm, theories and research are evaluated in terms of their contribution to the prediction and influence of behavior.
Biglan, A., & Hayes, S. C. (1996). Should the behavioral sciences become more pragmatic? The case for functional contextualism in research on human behavior. Applied and Preventive Psychology, 5(1), 47-57.
the objective of this research is to evaluate a community intervention to mobilise positive reinforcement for not selling tobacco to young people.
Biglan, A., Henderson, J., Humphrey, D., Yasui, M., Whisman, R., Black, C., & James, L. (1995). Mobilising positive reinforcement to reduce youth access to tobacco. Tobacco Control, 4(1), 42.
This article describe recent developments in the integration of research-based practices into the prevention of youth problem behaviors.
Biglan, A., Mrazek, P. J., Carnine, D., & Flay, B. R. (2003). The integration of research and practice in the prevention of youth problem behaviors. American Psychologist, 58(6-7), 433.
The author discusses what he believes to be the promise of this approach, its influence on the role of the school psychologist, and what educators can do if they choose to pursue the leads offered by this group.
Bijou, S. W. (1970). What psychology has to offer education—now. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 3(1), 65.
It is the thesis of this paper that data from descriptive and experimental field studies can be interrelated at the level of data and empirical concepts if both sets are derived from frequency-of-occurrence measures.
Bijou, S. W., Peterson, R. F., & Ault, M. H. (1968). A METHOD TO INTEGRATE DESCRIPTIVE AND EXPERIMENTAL FIELD STUDIES AT THE LEVEL OF DATA AND EMPIRICAL CONCEPTS 1. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 1(2), 175-191.
Functional communication training incorporates a comprehensive assessment of the communicative functions of maladaptive behavior with procedures to teach alternative and incompatible responses.
Bird, F., Dores, P. A., Moniz, D., & Robinson, J. (1989). Reducing severe aggressive and self-injurious behaviors with functional communication training. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 94(1), 37-48.
In the present article, it is argued that rules and conventions for generalizing in group-statistical research are different from those applying to single-subject research.
Birnbrauer, J. S. (1981). External validity and experimental investigation of individual behaviour. Analysis and Intervention in Developmental Disabilities, 1(2), 117-132.
The generality of the mathematical principles of reinforcement (MPR) was tested with humans.
Bizo, L. A., Remington, B., D’Souza, L. S., Heighway, S. K., & Baston, C. (2002). Human variable ratio performance. Learning and motivation, 33(4), 411-432.
Explains how meta-analysis can be used to estimate the effectiveness of various teaching strategies in special education and related services.
Blum lM, F. S. K. K., & Lloyd, J. W. (1997). Megaanalysis of meta-analysis: what works in special education. Teaching Exceptional Children, 29(6), 4-9.
This research evaluated the outcomes of a school psychology training practicum by replicating intervention-based service delivery procedures established in prior research.
Bonner, M., & Barnett, D. W. (2004). Intervention-based school psychology services: Training for child-level accountability; preparing for program-level accountability. Journal of School Psychology, 42(1), 23-43.
Robert F Boruch's book untangles the complexities of randomized field experiments to enable researchers to evaluate better the impact of new programs.
Boruch, R. F. (1997). Randomized experiments for planning and evaluation: A practical guide (Vol. 44). Sage.
The purpose of this book is to provide a comprehensive sourcebook on single case experimental designs with practical guidelines for their use in a range of research and clinical settings.
Boyle, M. E. (1983). Single Case Experimental Designs: Strategies for Studying Behavior Change.
The OSEP conference brought together people with different perspectives on LD (parents, researchers, practitioners, and policymakers) and resulted in this book, which examines the research on nine key issues concerning the identification of children with learning disabilities.
Bradley, R., Danielson, L., & Hallahan, D. P. (2002). Identification of learning disabilities: Research to practice. Routledge.
An overview of the many types of studies that fall into the qualitative design genre is provided. Strategies that qualitative researchers use to establish the authors’ studies as credible and trustworthy are listed and defined
Brantlinger, E., Jimenez, R., Klingner, J., Pugach, M., & Richardson, V. (2005). Qualitative studies in special education. Exceptional children, 71(2), 195-207.
This book offers principles and strategies to use in motivating students to learn.
Brophy, J. (2013). Motivating students to learn. Routledge.
The authors conducted functional analyses of aberrant behavior with 4 children with developmental disabilities, then implemented functional communication training (FCT) by using different mands across two contexts.
Brown, K. A., Wacker, D. P., Derby, K. M., Peck, S. M., Richman, D. M., Sasso, G. M., ... & Harding, J. W. (2000). Evaluating the effects of functional communication training in the presence and absence of establishing operations. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 33(1), 53-71.
This article describes an evaluation of a prisoner-run delinquency prevention program at Hawaii's major prison.
Buckner, J. C., & Chesney-Lind, M. (1983). Dramatic cures for juvenile crime: An evaluation of a prisoner-run delinquency prevention program. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 10(2), 227-247.
This DataWatch explores the roles of human service sectors (mental health, education, health, child welfare, and juvenile justice) in providing mental health services for children.
Burns, B. J., Costello, E. J., Angold, A., Tweed, D., Stangl, D., Farmer, E. M., & Erkanli, A. (1995). Children's mental health service use across service sectors. Health affairs, 14(3), 147-159.
As pressure increases for the demonstration of effective treatment for children with mental disorders, it is essential that the field has an understanding of the evidence base. To address this aim, the authors searched the published literature for effective interventions for children and adolescents and organized this review
Burns, B. J., Hoagwood, K., & Mrazek, P. J. (1999). Effective treatment for mental disorders in children and adolescents. Clinical child and family psychology review, 2(4), 199-254.
Although prereferral intervention teams (PIT) are common in public schools, there is little and conflicting research to support them. The current article conducted an empirical meta-analysis of research on PITs by reviewing 72 articles.
Burns, M. K., & Symington, T. (2002). A meta-analysis of prereferral intervention teams: Student and systemic outcomes. Journal of School Psychology, 40(5), 437-447.
This book has three main goals: to take stock of progress in the development of data-analysis procedures for single-subject research; to clearly explain errors of application and consider them within the context of new theoretical and empirical information of the time; and to closely examine new developments in the analysis of data from single-subject or small n experiments.
Busk, P. L., Serlin, R. C., Kratochwill, T. R., & Levin, J. R. (1992). Single-case research design and analysis: New directions for psychology and education.
Many of the difficulties lie in the intransigence of the research setting and in the presence of recurrent seductive pitfalls of interpretation. The bulk of this article will be devoted to these problems.
Campbell, D. T. (1969). Reforms as experiments. American psychologist, 24(4), 409.
This paper examines the validity of 16 experimental designs against 12 common threats to valid inference. By experiment, we refer to that portion of research in which variables are manipulated and their effects upon other variables observed.
Campbell, D. T., & Stanley, J. C. (2015). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for research. Ravenio Books.
It is generally agreed that serious misbehavior in children should be replaced with socially appropriate behaviors, but few guidelines exist with respect to choosing replacement behaviors. The authors address this issue in two experiments.
Carr, E. G., & Durand, V. M. (1985). Reducing behavior problems through functional communication training. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 18(2), 111-126.
The relative effectiveness of group care (GC) and multidimensional treatment foster care (MTFC) was compared in terms of their impact on criminal offending, incarceration rates, and program completion outcomes for 79 male adolescents who had histories of chronic and serious juvenile delinquency.
Chamberlain, P., & Reid, J. B. (1998). Comparison of two community alternatives to incarceration for chronic juvenile offenders. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 66(4), 624.
The work of several such task forces and other groups reviewing empirically supported treatments (ESTs) in the United States, United Kingdom, and elsewhere is summarized here, along with the lists of treatments that have been identified as ESTs
Chambless, D. L., & Ollendick, T. H. (2001). Empirically supported psychological interventions: Controversies and evidence. Annual review of psychology, 52(1), 685-716.
This report provides the second update on our progress in developing a list of empirically supported psychological treatments for specific target populations.
Chambless, D. L., Baker, M. J., Baucom, D. H., Beutler, L. E., Calhoun, K. S., Crits-Christoph, P., ... & Johnson, S. B. (1998). Update on empirically validated therapies, II. The clinical psychologist, 51(1), 3-16.
Carroll and Nuro (this issue) outline a model for development of psychotherapy manuals that parallels the recently articulated stage model of psychotherapy research. The authors outline excellent considerations for treatment manuals in early, middle, and late stages of development.
Chorpita, B. F. (2002). Treatment manuals for the real world: Where do we build them?. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 9(4), 431-433.
This article details the context and findings of a review conducted by a state-established panel established to examine the efficacy and effectiveness of child treatments for Anxiety Disorders, Depression, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Conduct and Oppositional Disorders, and Autistic Disorder
Chorpita, B. F., Yim, L. M., Donkervoet, J. C., Arensdorf, A., Amundsen, M. J., McGee, C., ... & Morelli, P. (2002). Toward largeâscale implementation of empirically supported treatments for children: A review and observations by the Hawaii Empirical Basis to Services Task Force. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 9(2), 165-190.
The purpose of this study is to estimate the extent to which publication bias is present in education and special education journals. This paper shows that published studies were associated with significantly larger effect sizes than unpublished studies (d=0.64). The authors suggest that meta-analyses report effect sizes of published and unpublished separately in order to address issues of publication bias.
Chow, J. C., & Ekholm, E. (2018). Do Published Studies Yield Larger Effect Sizes than Unpublished Studies in Education and Special Education? A Meta-review.
Eight comprehensive chapters cover the common problems of disruptive behavior, anxiety, sleep disorders, nocturnal enuresis, encopresis, habit disorders (such as tics and thumbsucking), the treatment of pain and, finally, helping children adhere to medical regimens. The book describes diagnosis and treatment, with an emphasis on practicality.
Christophersen, E. R., & Mortweet, S. L. (2001). Treatments that work with children: Empirically supported strategies for managing childhood problems. Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association.
This guide presents the tools therapists need to incorporate outcomes measurement effectively and meaningfully into everyday clinical work.
Clement, P. W. (1999). Outcomes and incomes: How to evaluate, improve, and market your psychotherapy practice by measuring outcomes. Guilford Press.
This Guide is intended to serve as a user-friendly resource that the education practitioner can use to identify and implement evidence-based interventions, so as to improve educational and life outcomes for the children they serve.
Coalition for Evidence-Based Policy. (2003). Identifying and implementing educational practices supported by rigorous evidence: A user-friendly guide. US Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
In 1962, I published a survey of the articles in a volume of the Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology from the perspective of their power to detect operationally defined small, medium, and large effect sizes. This edition has the same approach and organization as its predecessors but has some major changes from the Revised Edition.
Cohen, J. (2013). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Routledge.
This book explicate four kinds of validity then describe and critically examine some quasi-experimental designs from the perspective of these four kinds of validity, especially internal validity.
Cook, T. D., Campbell, D. T., & Peracchio, L. (1990). Quasi experimentation.
This handbook is a comprehensive treatment of literature synthesis and provides practical advice for anyone deep in the throes of, just teetering on the brink of, or attempting to decipher a meta-analysis
Cooper, H., & Hedges, L. V. (Eds.). (1993). The handbook of research synthesis. Russell Sage Foundation.
The authors conducted a preliminary analysis of maintaining variables for children with conduct disorders in an outpatient clinic. The assessment focused on appropriate child behavior and was conducted to formulate hypotheses regarding maintaining contingencies.
Cooper, L. J., Wacker, D. P., Sasso, G. M., Reimers, T. M., & Donn, L. K. (1990). Using parents as therapists to evaluate appropriate behavior of their children: Application to a tertiary diagnostic clinic. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23(3), 285-296.
Cronbach discuss the past and future place within psychology of two historic streams of method, thought, and affiliation which run through the last century of our science. One stream is experimental psychology; the other, correlational psychology.
Cronbach, L. J. (1957). The two disciplines of scientific psychology. American psychologist, 12(11), 671.
This book offers many provocative arguments and analyses of basic conceptual frameworks for the study of human behavior.
Cronbach, L. J. (1986). Social inquiry by and for earthlings. Metatheory in social science: Pluralisms and subjectivities, 83-107.
Describes problems of assessing change with short time-series data: unreliability of visual inference and fact that current statistical procedures cannot control Type I error because they underestimate positive autocorrelation.
Crosbie, J. (1993). Interrupted time-series analysis with brief single-subject data. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61(6), 966.
This article provides an overview of the nonspecific/universal engagement strategies used by MST therapists, frequently observed barriers to achieving therapistâfamily engagement, and specific strategies to overcome a sampling of these barriers.
Cunningham, P. B., & Henggeler, S. W. (1999). Engaging multiproblem families in treatment: Lessons learned throughout the development of multisystemic therapy. Family Process, 38(3), 265-281.
The General Performance Standards are requirements for all Child and Adolescent Mental Health Division (CAMHD) services, and apply to each of the specific services. They are set forth to guide effective practices in the delivery of behavioral health supports and services for eligible youth in the State of Hawai’i.
Department of Health Child & Adolescent Mental Health Division (2012). Child and Adolescent Mental Health Performance Standards. Hawaii: Clinical Service Office and Performance Manage Office, Department of Health State of Hawaii
The effects of changes in depression-relevant cognition were examined in relation to subsequent change in depressive symptoms for outpatients with major depressive disorder randomly assigned to cognitive therapy (COT; n = 32) vs those assigned to pharmacotherapy only (NoCT; n = 32).
DeRubeis, R. J., Evans, M. D., Hollon, S. D., Garvey, M. J., Grove, W. M., & Tuason, V. B. (1990). How does cognitive therapy work? Cognitive change and symptom change in cognitive therapy and pharmacotherapy for depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58(6), 862-869.
Including cost-effectiveness data in the evaluation of programs is the next step in the evolution of evidence-based practice. Evidence-based practice is grounded in three complementary elements: best available evidence, professional judgment, and client values and context. To fully apply the cost-effectiveness data, school administrators will have to rely on all three of these elements. The function of cost-effectiveness data is to guide decisions about how limited financial resources should be spent to produce the best educational outcomes. To do so, it is necessary for decision makers to choose between options with known cost-effectiveness ratios while working within the budget constraints. In this article, I discuss some of the considerations that have to be addressed in the decision-making process and implications of including cost-effectiveness analyses in data-based decision making.
Detrich, R. (2020). Cost-effectiveness analysis: A component of evidence-based education. School Psychology Review, 1-8.
This article explored developmental and intervention evidence relevant to iatrogenic effects in peer-group interventions. Longitudinal research revealed that "deviancy training" within adolescent friendships predicts increases in delinquency, substance use, violence, and adult maladjustment.
Dishion, T. J., McCord, J., & Poulin, F. (1999). When interventions harm: Peer groups and problem behavior. American psychologist, 54(9), 755.
A common, yet questionable assumption underlying many evaluations of service intervention programs is that program clients uniformly receive the services purportedly available. The authors draw upon the experience of a randomized field experiment to point out the hazards of that assumption.
Dobson, D., & Cook, T. J. (1980). Avoiding type III error in program evaluation: Results from a field experiment. Evaluation and Program Planning, 3(4), 269-276.
This comprehensive textbook is an essential primer for all practitioners and students who are grappling with the new age of evidence-based practice. The contributors explore some of the complex challenges in implementing EBPs, and highlight the meaningful opportunities that are inherent in this paradigm shift.
Drake, R. E., Merrens, M. R., & Lynde, D. W. (Eds.). (2005). A Norton professional book. Evidence-based mental health practice: A textbook. New York, NY, US: W W Norton & Co.
This is a book about single-subject experiments. The goal is to detail the underlying rationale and logic of single-case designs and to present major design options.
Edgington, E. (1983). Response-guided experimentation. Psyccritiques, 28(1), 64-65.
This article discusses the use of randomized controlled trials as required by the Department of Education in evaluating the effectiveness of educational practices.
EDUC, A. R. O. (2005). Can randomized trials answer the question of what works?.
The authors argue that important evidence about best practice comes from case-based research, which builds knowledge in a clinically useful manner and complements what is achieved by multivariate research methods.
Edwards, D. J., Dattilio, F. M., & Bromley, D. B. (2004). Developing evidence-based practice: The role of case-based research. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 35(6), 589.
This year's surgeon general's report on smoking and health is the first such report to focus on young people. From extensive data that indicate that tobacco use is a pediatric epidemic, the report reached six major conclusions.
Elders, M. J., Perry, C. L., Eriksen, M. P., & Giovino, G. A. (1994). The report of the Surgeon General: preventing tobacco use among young people. American journal of public health, 84(4), 543-547.
The author research focuses on the development and application of time-series models to areas in economics and finance.
Enders, W. (2008). Applied econometric time series. John Wiley & Sons.
The purpose of this paper is to identify the forces that influence how developmental research is prioritized and evaluated and how these influences are changing as we enter the new millennium.
Fabes, R. A., Martin, C. L., Hanish, L. D., & Updegraff, K. A. (2000). Criteria for evaluating the significance of developmental research in the twentyâfirst century: Force and counterforce. Child development, 71(1), 212-221.
This chapter of Design and Analysis of Single-Case Research book describes Meta-analysis as a collection of methods designed to quantitatively summarize the results of separate studies.
Faith, A. (2014). Meta-analysis of single-case research. In Design and analysis of single-case research (pp. 267-300). Psychology Press.
Articulated in the Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion, this strategy emphasizes the importance of environmental influences on the behaviors associated with health promotion and injury prevention.
Fawcet, S. B., Paine, A. L., Francisco, V. T., & Vliet, M. (1993). Promoting Health Trough Community Development.
This book analyzes the findings of a treatment program which integrated antisocial and delinquent youths into prosocial peer groups in a suburban community center in St. Louis.
Feldman, R. A., Caplinger, T. E., & Wodarski, J. S. (1983). The St. Louis conundrum: The effective treatment of antisocial youths. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
The relationship between the clinical psychologist and the clinical researcher is often presented as an integrated model in which the researcher conceives and the clinician executes. We argue that this is an unworkable model because these are independent fields, each with its own problems and its own styles of thinking.
Fensterheim, H., & Raw, S. D. (1996). Psychotherapy research is not psychotherapy practice. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 3(2), 168-171.
The current investigation is part of an ongoing line of research designed to identify critical instructional components for training new staff members in the implementation of behavior-analytic procedures, with the goal of approximating the efficiency of
indirect instructional methods while retaining the effectiveness of more direct methods.
Fisher, W. W., Kelley, M. E., & Lomas, J. E. (2003). Visual aids and structured criteria for improving visual inspection and interpretation of singleâcase designs. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 36(3), 387-406.
In this paper we will review some of the examples from industrial innovation and dissemination, provide some data on replications of the Achievement Place/Teaching-Family Model over 20 years, and try to share some of the philosophical, practical, and technological guidelines we have come to accept.
Fixsen, D. L., & Blase, K. A. (1993). Creating new realities: Program development and dissemination. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 26(4), 597-615.
The standard reference in the field, this acclaimed work synthesizes findings from hundreds of carefully selected studies of mental health treatments for children and adolescents.
Fonagy, P., Cottrell, D., Phillips, J., Bevington, D., Glaser, D., & Allison, E. (2014). What works for whom?: a critical review of treatments for children and adolescents. Guilford Publications.
This paper reports the effects of the intervention on ordinances in TPOP communities, on cigarette purchase success by youth, and on adolescents' perceptions of availability and self-reported smoking behavior.
Forster, J. L., Murray, D. M., Wolfson, M., Blaine, T. M., Wagenaar, A. C., & Hennrikus, D. J. (1998). The effects of community policies to reduce youth access to tobacco. American Journal of Public Health, 88(8), 1193-1198.
This book focuses on one important aspect of psychological research -- the intensive study of people measured one or more at a time.
Franklin, R. D., Allison, D. B., & Gorman, B. S. (Eds.). (2014). Design and analysis of single-case research. Psychology Press.
The main enemies of large-scale reform are overload and extreme
fragmentation, Mr. Fullan points out. The three stories he outlines here serve
to lend coherence to an otherwise disjointed system.
Fullan, M. (2000). The three stories of education reform. Phi Delta Kappan, 81(8), 581-584.
This book is written for individuals at all levels of the educational system. All key players will find a chapter on their own roles, as well as chapters on other roles and agencies with whom they must interact.
Fullan, M. (2001). The new meaning of educational change. Routledge.
G. A. Kelly's personal construct theory of personality is examined. The status of the psychology of personality is reviewed by means of a contextual framework using the metaphors of formism, mechanism, contextualism, and organicism.
G. A. Kelly's personal construct theory of personality is examined. The status of the psychology of personality is reviewed by means of a contextual framework using the metaphors of formism, mechanism, contextualism, and organicism.
This text provides a comprehensive introduction to educational research. This textbook has been revised to reflect a balance of both quantitative and qualitative research methods
Gall, M. D., Borg, W. R., & Gall, J. P. (1996). Educational research: An introduction. Longman Publishing.
This report: (1) investigates the declining state of the educational system in America, as measured by high school student performance in the United States and other countries; (2) identifies specific problem areas; and (3) offers multiple recommendations for improvement
Gardner, D. P. (1983). A Nation At Risk: The Imperative For Educational Reform. An Open Letter to the American People. A Report to the Nation and the Secretary of Education.
This article is a response to the report of the Task Force on Promotion and Dissemination of Psychological Procedures of the Division of Clinical Psychology of the American Psychological Association (1995).
Garfield, S. L. (1996). Some problems associated with “validated” forms of psychotherapy. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 3(3), 218-229.
This paper discusses the effectiveness of researchâbased educational approaches on
classroom practice.
Gersten, R. (2001). Sorting out the roles of research in the improvement of practice. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 16(1), 45-50.
This article discusses critical issues related to conducting high-quality intervention research using experimental and quasi-experimental group designs.
Gersten, R., Baker, S., & Lloyd, J. W. (2000). Designing high-quality research in special education: Group experimental design. The Journal of Special Education, 34(1), 2-18.
This article reviews key findings from school-reform studies of the 1980s and explains their relevance to special education. It also highlights significant findings from more recent studies that help elucidate and flesh out the earlier findings.
Gersten, R., Chard, D., & Baker, S. (2000). Factors enhancing sustained use of research-based instructional practices. Journal of learning disabilities, 33(5), 445-456.
These papers provide up-to-date, informative summaries of current knowledge and a base from which further venture into the critical area of instructional intervention in special education can occur.
Gersten, R., Schiller, E. P., & Vaughn, S. R. (Eds.). (2000). Contemporary special education research: Syntheses of the knowledge base on critical instructional issues. Routledge.
Design and Analysis of Time Series Experiments develops a comprehensive set of models and methods for drawing causal inferences from time series.
Glass. G. V., Willson. V. L., & Grottman, J. M. (1975). Design and Analysis of Time Series Experiments. Boulder: University of Colorado Press
The primary hypothesis of COMMIT (Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation) was that a community-level, multi-channel, 4-year intervention would increase quit rates among cigarette smokers, with heavy smokers (≥25 cigarettes per day) of priority.
Glynn, T. J., Shopland, D. R., Manley, M., Lynn, W. R., Freedman, L. S., Green, S. B., ... & Chapelsky, D. A. (1995). Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation (COMMIT): I. Cohort results from a four-year community intervention. American journal of public health, 85(2), 183-192.
COMMIT (Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation) investigated whether a community-level multichannel intervention would decrease the prevalence of adult cigarette smoking and increase quitting with heavy smokers (≥25 cigarettes per day) receiving the highest priority.
Glynn, T. J., Shopland, D. R., Manley, M., Lynn, W. R., Freedman, L. S., Green, S. B., ... & Chapelsky, D. A. (1995). Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation (COMMIT): II. Changes in adult cigarette smoking prevalence. American Journal of Public Health, 85(2), 193-200.
The authors describe the policy and administrative-practice implications of implementing evidence-based services, particularly in public-sector settings. They review the observations of the contributors to the evidence-based practices series published throughout 2001 in Psychiatric Services.
Goldman, H. H., Ganju, V., Drake, R. E., Gorman, P., Hogan, M., Hyde, P. S., & Morgan, O. (2001). Policy implications for implementing evidence-based practices. Psychiatric Services, 52(12), 1591-1597.
Pew Research Center recently asked a national sample of adults to select among a list of 10 skills: “Regardless of whether or not you think these skills are good to have, which ones do you think are most important for children to get ahead in the world today?”
Goo, S. A. R. A. (2015). The skills Americans say kids need to succeed in life. Pew Research Center.
Examined the forecasting accuracy of 2 slope estimation procedures (ordinary-least-squares regression and split-middle trend lines) for reading curriculum-based measurement (CBM), a behavioral approach to the assessment of academic skills that emphasizes the direct measurement of academic behaviors.
Good, R. H., & Shinn, M. R. (1990). Forecasting accuracy of slope estimates for reading curriculum-based measurement: Empirical evidence. Behavioral Assessment.
This book is a comprehensive introduction to all the major time-series techniques, both time-domain and frequency-domain. It includes work on linear models that simplify the solution of univariate
Gottman, J. M. (1981). Time-series analysisa comprehensive introduction for social scientists (No. 519.55 G6).
This breakthrough book guides you through a series of self-tests designed to help you determine what kind of marriage you have, where your strengths and weaknesses are, and what specific actions you can take to help your marriage.
Gottman, J., Gottman, J. M., & Silver, N. (1995). Why marriages succeed or fail: And how you can make yours last. Simon and Schuster.
This book shows why a more accurate way of understanding our world (and the history of life) is to look at a given subject within its own context.
Gould, S. J. (1998). Full house: the spread of excellence from Plato to Darwin. Senior Managing Editor, 5(2), 68.
In this edition, Dr. Gould has written a substantial new introduction telling how and why he wrote the book and tracing the subsequent history of the controversy on innateness right through The Bell Curve.
Gould, S. J., & Gold, S. J. (1996). The mismeasure of man. WW Norton & Company.
The present paper explores employing s general transformation to avoid the model identification step. This approach permits the employments of time series analysis in a wider variety of situations as a result of relacing the requirement of a large number of points for model identification.
Grant, C. A. Time Series Analysis Without Model ldentification.
The purpose of the current study was to test theoretically derived hypotheses regarding the relationships between team efficacy, potency, and performance and to examine the moderating effects of level of analysis and interdependence on observed relationships.
Gully, S. M., Incalcaterra, K. A., Joshi, A., & Beaubien, J. M. (2002). A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships. Journal of applied psychology, 87(5), 819.
The author puts forth the case that using simple checklists prior to medical and surgical procedures can substantially improve outcomes.
Guwande, A. (2010). The checklist manifesto. New York: Picadur.
This article introduces a special section addressing these resource allocation issues in the context of prevalent disorders
Haaga, D. A. F. (2000). Introduction to the special section on stepped care models in psychotherapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(4), 547-548.
This study examines adoption and implementation of the US Department of Education's new policy, the `Principles of Effectiveness', from a diffusion of innovations theoretical framework. In this report, we evaluate adoption in relation to Principle 3: the requirement to select research-based programs.
Hallfors, D., & Godette, D. (2002). Will the “principles of effectiveness” improve prevention practice? Early findings from a diffusion study. Health Education Research, 17(4), 461–470.
The study finds that interest in instructional leadership among scholars and practitioners remained strong throughout the period of the review, the PIMRS has proven a reliable and valid data collection tool, and the use of research methodology has improved in several specific areas. Nonetheless, the results also suggest that the conceptual frameworks and methodologies used by these doctoral students were, on the whole, inadequate for the task of contributing to either the theoretical or the practical knowledge base in this field.
Hallinger, P. (2011). A review of three decades of doctoral studies using the principal instructional management rating scale: A lens on methodological progress in educational leadership. Educational Administration Quarterly, 47(2), 271-306.
The relative distribution provides a general integrated framework for analysis.
Handcock, M. S., & Morris, M. (2006). Relative distribution methods in the social sciences. Springer Science & Business Media.
Computer generated data representative of 26 ARIMA models was used to compare the results of interrupted time-series analysis using: (1) the known model identification, (2) an assumed (1, 0, 0) model, and (3) an assumed (3, 0, 0) model as an approximation to the General Transformation approach.
Harrop, J. W., & Velicer, W. F. (1985). A comparison of alternative approaches to the analysis of interrupted time-series. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 20(1), 27-44.
The Rise of Universities goes far beyond its central subject to offer a broad description of the social conditions in which universities took root and flourished.
Haskins, C. H. (2017). The rise of universities. Routledge.
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
This book aim to provide the reader, who is presumably not yet an expert on single-subject research, with the information necessary to understand the literature and develop a single-subject research study in general.
Hawkins, C. (2001). Single Subject Research: Applications in Educational and Clinical Settings. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 14(2), 155-157.
Contextualism is being looked to as a framework within which psychology may advance, stripped of needless mechanism and needless philosophical inconsistencies.
Hayes, S. C. (2015). Analytic goals and the varieties of scientific contextualism. In The Act in Context (pp. 126-142). Routledge.
This book explains the philosophy of evidence-based medicine (EBM) and demonstrating its application.
Haynes, R. B., Sackett, D. L., Richardson, W. S., Rosenberg, W., & Langley, G. R. (1997). Evidence-based medicine: How to practice & teach EBM. Canadian Medical Association. Journal, 157(6), 788.
This paper examines things that people often overlook in their data analysis, and ways people sometimes "bend the rules" of statistics to support their viewpoint. It discusses ways you can make sure your own statistics are clear and accurate.
Helberg, C., (1995). Pitfalls of Data Analysis (or How to Avoid Lies and Damned Lies). Third International Applied Statistics in Industry Conference in Dallas, TX, June 5-7, 1995.
The purpose of this chapter is to examine the existing time management literature.
Hellsten, L. M. (2012). What do we know about time management. A review of the literature and a psychometric critique of instruments assessing time management. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech, 21-22.
Many writers who are not scientists themselves are trading on the prestige of science and the authority of scientists. Reference to “peer-reviewed research” and to an alleged “scientific consensus” are regarded as veritable knock-out blows by many commentators.
Higgs, R. (2007). Peer review, publication in top journals, scientific consensus, and so forth. The Independent Institute, 7.
This book examines the use of randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies in education.
Hilton, M., & Towne, L. (Eds.). (2004). Implementing Randomized Field Trials in Education:: Report of a Workshop. National Academies Press.
In 1981, Maine passed a drunk driving law with mandatory penalties and a new civil charge to increase the conviction rate. One year later, Massachusetts increased drunk driving penalties, particularly for repeat offenders and intoxicated drivers involved in fatal crashes.
Hingson, R., Heeren, T., Kovenock, D., Mangione, T., Meyers, A., Morelock, S., Lederman, R., Scotch, N.A.. (1987). Effects of Maine's 1981 and Massachusetts' 1982 Driving-Under-the-Influence Legislation. American journal of public health. American Journal of Public Health. 77, 593-597.
Two ways of measuring the gap between two cumulative distribution functions (CDFs) are examined—vertical and horizontal distance.
Holland, P. W. (2002). Two measures of change in the gaps between the CDFs of test-score distributions. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 27(1), 3-17.
This research evaluated three nurse-assisted interventions designed to minimize physician burden and increase counseling in primary care settings
Hollis, J. F., Lichtenstein, E., Vogt, T. M., Stevens, V. J., & Biglan, A. (1993). Nurse-assisted counseling for smokers in primary care. Annals of internal medicine, 118(7), 521-525.
This document presents a set of criteria to be used in evaluating treatment guidelines that have been promulgated by health care organizations, government agencies, professional associations, or other entities.1 The purpose of treatment guidelines is to educate health care professionals2 and health care systems about the most effective treatments available
Hollon, D., Miller, I. J., & Robinson, E. (2002). Criteria for evaluating treatment guidelines. American Psychologist, 57(12), 1052-1059.
This book provides encouragement and strategies for researchers who routinely address research questions using data from small samples.
Hoyle, R. H. (Ed.). (1999). Statistical strategies for small sample research. Sage.
A statistics textbook appropriate for graduate students and researchers conducting quasi-experimental design and analysis.
Hyman, R. (1982). Quasi-experimentation: design and analysis issues for field settings (book). Journal of Personality Assessment, 46(1), 96-97.
This article examines the extent to which each study conforms to the guidelines set forth by the Task Force on Promotion and Dissemination of Psychological Procedures (1996) for well-established and probably efficacious interventions.
Kaslow, N. J., & Thompson, M. P. (1998). Applying the criteria for empirically supported treatments to studies of psychosocial interventions for child and adolescent depression. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 27(2), 146-155.
This paper is a review of primary research investigating the Feingold hypothesis which suggests diet modification as an efficacious treatment for hyperactivity.
Kavale, K. A., & Forness, S. R. (1983). Hyperactivity and diet treatment: A meta-analysis of the Feingold hypothesis. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 16(6), 324-330.
This chapter traces the history of behavior modification as a general movement. Individual conceptual approaches and techniques that comprise behavior modification are obviously important in tracing the history, but they are examined as part of the larger development rather than as ends in their own right.
Kazdin, A. E. (1982). History of behavior modification. In International handbook of behavior modification and therapy (pp. 3-32). Springer, Boston, MA.
in this article, the author discuss the relation between limited conceptualization of treatment and the methods of study and resulting knowledge about treatment.
Kazdin, A. E. (1995). Scope of child and adolescent psychotherapy research: Limited sampling of dysfunctions, treatments, and client characteristics. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 24(2), 125-140.
The previous articles in this special section make the case for the importance of evaluating the clinical significance of the therapeutic change, present key measures and innovative ways in which they are applied, and more generally provide important guidelines for evaluating therapeutic change.
Kazdin, A. E. (1999). The meanings and measurement of clinical significance.
The review by Sheldrick et al. evaluates treatments for children and adolescents with conduct disorder and whether they produce clinically significant change
Kazdin, A. E. (2001). Almost clinically significant (pClinical psychology: Science and practice, 8(4), 455-462.
The role, importance, and paucity of theory in child and adolescent psychotherapy research is described, underscored, and lamented, respectively, in these comments.
Kazdin, A. E. (2001). Bridging the enormous gaps of theory with therapy research and practice. Journal of clinical child psychology, 30(1), 59-66.
In this successful text, Kazdin describes research methods in psychology and provides criteria for conducting and evaluating clinical research.
Kazdin, A. E. (2003). Research design in clinical psychology.
The focus of this chapter is on psychotherapy research and a call for research on mechanisms of therapeutic change.
Kazdin, A. E. (2006). Mechanisms of Change in Psychotherapy: Advances, Breakthroughs, and Cutting-Edge Research (Do Not Yet Exist).
Single-case research has played an important role in developing and evaluating interventions that are designed to alter a particular facet of human functioning. In this edition, the author provides a notable contrast to the quantitative methodology approach that pervades the biological and social sciences.
Kazdin, A. E. (2011). Single-case research designs: Methods for clinical and applied settings. Oxford University Press.
Now thoroughly updated in its second edition, acclaimed author Alan Kazdin's Single-Case Research Designs provides a notable contrast to the quantitative methodology approach that pervades the biological and social sciences.
Kazdin, A. E. (2011). Single-case research designs: Methods for clinical and applied settings. Oxford University Press.
In this article, we discuss the importance of studying mechanisms, the logical and methodological requirements, and why almost no studies to date provide evidence for why or how treatment works.
Kazdin, A. E., & Nock, M. K. (2003). Delineating mechanisms of change in child and adolescent therapy: Methodological issues and research recommendations. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 44(8), 1116-1129.
An overview of teaching and classroom management techniques for learning for student paced learning from 1963.
Keller, F. S. (1968). Good-bye, teacher... Journal of applied behavior analysis, 1(1), 79.
In this study a psychosocial treatment for 47 Ss (aged 9–13 years) with anxiety disorders was investigated. A 16-session cognitive–behavioral treatment was compared with a wait-list condition.
Kendall, P. C. (1994). Treating anxiety disorders in children: results of a randomized clinical trial. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 62(1), 100.
This book provides up-to-date, in-depth information about the use of single-case experimental designs in educational research across a range of educational settings and students.
Kennedy, C. H. (2005). Single-case designs for educational research. Pearson/A & B.
More than 300 studies that appeared to address the efficacy of formative assessment in grades K-12 were reviewed. Many of the studies had severely flawed research designs yielding uninterpretable results.
Kingston, N., & Nash, B. (2011). Formative assessment: A metaâanalysis and a call for research. Educational measurement: Issues and practice, 30(4), 28-37.
This review chapter examines the literature on work team effectiveness. This paper consider their nature, define them, and identify four critical conceptual issues—context, workflow, levels, and time—that serve as review themes and discuss the multitude of forms that teams may assume.
Kozlowski, S. W., & Bell, B. S. (2003). Work groups and teams in organizations. Handbook of psychology, 333-375.
The authors developed a methodological basis for investigating how risk factors work together. Better methods are needed for understanding the etiology of disorders, such as psychiatric syndromes, that presumably are the result of complex causal chains.
Kraemer, H. C., Stice, E., Kazdin, A., Offord, D., & Kupfer, D. (2001). How do risk factors work together? Mediators, moderators, and independent, overlapping, and proxy risk factors. American journal of psychiatry, 158(6), 848-856.
This paper describes an analytic framework to identify and distinguish between moderators and mediators in RCTs when outcomes are measured dimensionally.
Kraemer, H. C., Wilson, G. T., Fairburn, C. G., & Agras, W. S. (2002). Mediators and moderators of treatment effects in randomized clinical trials. Archives of general psychiatry, 59(10), 877-883.
This book presents an overview of strategies used to evaluate change is single-subject research, a particular referring to time-series paradigms in which each subject is used repeatedly.
Kratochwill, T. R. (Ed.). (2013). Single subject research: Strategies for evaluating change. Academic Press.
the editors of this volume fulfill three main goals: to take stock of progress in the development of data-analysis procedures for single-subject research
Kratochwill, T. R., & Levin, J. R. (Eds.). (2015). Single-case research design and analysis (psychology revivals): new directions for psychology and education. Routledge.
This paper by a What Works Clearinghouse the panel provides an overview of singlr-subject designs (SCDs), specifies the types of questions that SCDs are designed to answer, and discusses the internal validity of SCDs. The panel then proposes standards to be implemented by the WWC.
Kratochwill, T. R., Hitchcock, J., Horner, R. H., Levin, J. R., Odom, S. L., Rindskopf, D. M., & Shadish, W. R. (2010). Single-case designs technical documentation. What Works Clearinghouse.
This book presents an overview of strategies used to evaluate change in single subject research, a particular approach referring to time-series paradigms in which each subject is used repeatedly.
Kratochwill, Thomas R., ed. Single subject research: Strategies for evaluating change. Academic Press, 2013.
The authors conducted a comprehensive review of research to identify the impact of coaching on changes in preservice and in-service teachers’ implementation of evidence-based practices.
Kretlow, A. G., & Bartholomew, C. C. (2010). Using coaching to improve the fidelity of evidence-based practices: A review of studies. Teacher Education and Special Education, 33(4), 279-299.
The present study attempted to examine the causal relationships among changes in automatic thoughts, dysfunctional attitudes, and depressive symptoms in a 12-week group cognitive behavior therapy (GCBT) program for depression.
Kwon, S. M., & Oei, T. P. (2003). Cognitive change processes in a group cognitive behavior therapy of depression. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 34(1), 73-85.
This editorial offers recommendations aimed at providing examples of a series of elements that may significantly contribute towards demonstrating the robustness of quantitative results. It is therefore not a methodological guide but instead a guide that acts as a reminder of some basic principles when reporting quantitative research.
López, X., Valenzuela, J., Nussbaum, M., & Tsai, C. C. (2015). Some recommendations for the reporting of quantitative studies. Computers & Education, 91(C), 106-110.
This bestselling resource presents authoritative thinking on the pressing questions, issues, and controversies in psychotherapy research and practice today.
Lambert, M. J., Garfield, S. L., & Bergin, A. E. (2004). Handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
In the present correlational study of 199 treated adolescents, the authors used a multitrait-multimethod analysis to examine psychometrically measured pathology change (pre- and postassessment of symptoms and functioning), consumer satisfaction, and perceived improvement reported by multiple informants.
Lambert, W., Salzer, M. S., & Bickman, L. (1998). Clinical outcome, consumer satisfaction, and ad hoc ratings of improvement in children's mental health. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66(2), 270-278.
Populations and study samples can change over time—sometimes dramatically so. We illustrate this important point by presenting data from 5 randomized control trials of the efficacy of Kindergarten Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies, a supplemental, peer-mediated reading program.
Lemons, C. J., Fuchs, D., Gilbert, J. K., & Fuchs, L. S. (2014). Evidence-based practices in a changing world: Reconsidering the counterfactual in education research. Educational Researcher, 43(5), 242-252.
The chapter focuses on the historically perceived poor methodological rigor and low scientific credibility of most educational/psychological intervention research.
Levin, J. R., & Kratochwill, T. R. (2012). Educational/psychological intervention research circa 2012. Handbook of Psychology, Second Edition, 7.
This edition of Forecasting and Time Series Analysis Using the SCA Statistical System initiates the replacement process of the document entitled The SCA Statistical System: Reference Manual for Forecasting and Time Series Analysis (May 1986).
Liu, L. M., Hudak, G. B., Box, G. E., Muller, M. E., & Tiao, G. C. (1992). Forecasting and time series analysis using the SCA statistical system (Vol. 1, No. 2). DeKalb, IL: Scientific Computing Associates.
This article reports the results of behavior modification treatment for two groups of similarly constituted, young autistic children.
Lovaas, O. I. (1987). Behavioral treatment and normal educational and intellectual functioning in young autistic children. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 55(1), 3.
Tallies were made of outcomes of all reasonably controlled comparisons of psychotherapies with each other and with other treatments. For comparisons of psychotherapy with each other, most studies found insignificant differences in proportions of patients who improved (though most patients benefited).
Luborsky, L., Singer, B., & Luborsky, L. (1975). Comparative studies of psychotherapies: is it true that everyone has won and all must have prizes?. Archives of general psychiatry, 32(8), 995-1008.
The objectives in the following series of experiments were to evaluate the effectiveness of the high-probability command sequence in increasing compliance to "do" and "don't" commands; to conduct preliminary investigations regarding the appropriateness of the behavioral momentum analogy; and to evaluate the generality of the procedure to reduce excessive compliance latency and task duration
Mace, F. C., Hock, M. L., Lalli, J. S., West, B. J., Belfiore, P., Pinter, E., & Brown, D. K. (1988). Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 21(2), 123-141.
Used metaâanalysis to examine the efficacy of bibliotherapy. Bibliotherapy treatments were compared to control groups and therapistâadministered treatments.
Marrs, R. W. (1995). A metaâanalysis of bibliotherapy studies. American journal of community psychology, 23(6), 843-870.
This book develops critical thinking skills about research and is designed to produce knowledgeable and informed critical research consumers.
Martella, R. C., Nelson, J. R., & Marchand-Martella, N. E. (1999). Research methods: Learning to become a critical research consumer. Allyn & Bacon.
The present paper is an attempt to formulate a positive theory of motivation which will satisfy these theoretical demands and at the same time conform to the known facts, clinical and observational as well as experimental. It derives most directly, however, from clinical experience.
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological review, 50(4), 370.
Jaime Escalante is an outstanding example of excellence and dedication. This is the story of his entire career, including the development of the teaching techniques that got such brilliant results from the desperate students of gang-ridden Garfield High in East Los Angeles.
Mathews, J. (1989) Escalante: The best teacher in America. New York:Henry Hold and Co
The literature assumes that visual analysts will be conservative judges. They show that previous research into visual analysis has not adequately examined false alarm and miss rates or the effect of serial dependence.
Matyas, T. A., & Greenwood, K. M. (1990). Visual analysis of singleâcase time series: Effects of variability, serial dependence, and magnitude of intervention effects. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23(3), 341-351.
Many scientists have searched for dynamics by calculating df/dt: the ratio of changes or differences d in a function f relative to changes in time t. This research use this dynamic equation, but here they examine multivariate psychological change data using the 20th century developments of latent variable structural equation modeling.
McArdle, J. J. (1988). Dynamic but structural equation modeling of repeated measures data. In Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology (pp. 561-614). Springer, Boston, MA.
The book reviews several available software packages for the analysis of time series data and the use of interactive software
McCleary, R., Hay, R. A., Meidinger, E. E., & McDowall, D. (1980). Applied time series analysis for the social sciences (p. 331). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publications.
In a large sample of children from the general population this research found no association between parent, teacher, and self-reports of ADDH behaviors and a history of allergic disorders (asthma, eczema, rhinitis, and urticaria) at ages 9 or 13 years.
McGee, R., Stanton, W. R., & Sears, M. R. (1993). Allergic disorders and attention deficit disorder in children. Journal of abnormal child psychology, 21(1), 79-88.
Developed a fidelity index of program implementation for assertive community treatment (ACT). In Study 1, 20 experts rated the importance of 73 elements proposed as critical ACT ingredients, also indicating ideal model specifications for elements.
McGrew, J. H., Bond, G. R., Dietzen, L., & Salyers, M. (1994). Measuring the fidelity of implementation of a mental health program model. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62(4), 670-678.
This paper examines school-based experimental studies with individuals 0 to 18 years between 1991 and 2005. Only 30% of the studies provided treatment integrity data. Nearly half of studies (45%) were judged to be at high risk for treatment inaccuracies.
McIntyre, L. L., Gresham, F. M., DiGennaro, F. D., & Reed, D. D. (2007). Treatment integrity of schoolâbased interventions with children in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 1991–2005. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 40(4), 659–672.
As a method for representing development, latent trait theory is presented in terms of a statistical model containing individual parameters and a structure on both the first and second moments of the random variables reflecting growth
Meredith, W., & Tisak, J. (1990). Latent curve analysis. Psychometrika, 55(1), 107-122.
The stability and validity of early adolescents' reports of 6 parenting constructs were examined: parent–child conflict, positive family relations, parental monitoring, parents' rule making, consistent enforcement of rules, and use of positive reinforcement.
Metzler, C. W., Biglan, A., Ary, D. V., & Li, F. (1998). The stability and validity of early adolescents' reports of parenting constructs. Journal of Family Psychology, 12(4), 600.
Mapping State Proficiency Standards Onto the NAEP Scales
MEXICO, N. (2011). Mapping State Proficiency Standards Onto the NAEP Scales: Variation and Change in State Standards for Reading and Mathematics, 2005-2009.
A variety of researches are examined from the standpoint of information theory. It is shown that the unaided observer is severely limited in terms of the amount of information he can receive, process, and remember. However, it is shown that by the use of various techniques, e.g., use of several stimulus dimensions, recoding, and various mnemonic devices, this informational bottleneck can be broken.
Miller, G. A. (1956). The magical number seven, plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychological review, 63(2), 81.
This book discusses major mental disorders in a question-and-answer format. It offers information about treatment decisions and the pros and cons of a particular treatment. This books helps people understand the issues involved when working with a mental health professional.
Nathan, P. E., Gorman, J. M., & Salkind, N. J. (1999). Treating mental disorders: A guide to what works. Oxford University Press.
To what extent does a student’s ethnicity, socio economic status, or location predict/impact their education performance. One of the most respected tools for answering this question is the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), as it disaggregates test data by student ethnicity, socio-economic status, and location of schools.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2019). Nation’s report card. National Assessment of Educational Progress.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2019). NAEP Data Explorer. National Assessment of Educational Progress.
This book describes the similarities and differences between scientific inquiry in education and scientific inquiry in other fields and disciplines and provides a number of examples to illustrate these ideas.
National Research Council. (2002). Scientific research in education. National Academies Press.
the Center for Education of the National Research Council (NRC) has undertaken a series of activities to address issues related to the quality of scientific education research.1 In 2002, the NRC released Scientific Research in Education (National Research Council, 2002), a report designed to articulate the nature of scientific education research and to guide efforts aimed at improving its quality.
National Research Council. (2004). Scientific research in education. National Academies Press.
the purpose of this book was to growing edges will find something to meet the author inaugurate a radical new outlook on experimental psychology.
Nesselroade, J. R., & Cattell, R. B. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology. Springer Science & Business Media.
This article covers current efforts by the National Institute of Mental Health to bridge this gap. Included are discussions of problems with the current research portfolio and new efforts in expanding the research portfolio, innovative methodological research, and expansion of training programs.
Norquist, G., Lebowitz, B., & Hyman, S. (1999). Expanding the frontier of treatment research. Prevention & Treatment, 2(1). Article ID 1a.
This text considers the measurement problems that arise in areas of psychology, education, and areas of business such as management and marketing.
Nunnally, J. C. (1994). Psychometric theory 3E. Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
This study has two separate but related purposes: (1) to delineate cross-sectional differences among U.S. high school seniors and young adults that may be due to variations in recent years in state-level minimum drinking age laws and (2) to examine the effects of recent changes in minimum drinking age laws on alcohol consumption and other relevant attitudes and behaviors.
O'Malley, P. M., & Wagenaar, A. C. (1991). Effects of minimum drinking age laws on alcohol use, related behaviors and traffic crash involvement among American youth: 1976-1987. Journal of studies on Alcohol, 52(5), 478-491.
This article reviews the impact of physician-delivered smoking interventions on smokers, physician attitudes toward intervention, and physicians' reported intervention practices.
Ockene, J. K. (1987). Physician-delivered interventions for smoking cessation: strategies for increasing effectiveness. Preventive medicine, 16(5), 723-737.
Education at a Glance: OECD Indicators 2011 ofers a rich, comparable and up-to-date array of indicators that relect a consensus among professionals on how to measure the current state of education internationally.
OECD (2011), Education at a Glance 2011: OECD Indicators, OECD Publishing. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/eag-2011-en
A report prepared by the board that governs the National Assessment of Educational Progress cautions that measuring an achievement gap does not come down to a single statistic.
Olson, L. (2002). Testing experts develop new method of presenting achievement gap data. Education Week, 21(26), 11
This chapter of Single-Case Research Design and Analysis (Psychology Revivals) describes Visual analysis as one of the oldest forms of data analysis.
Parsonson, B. S., & Baer, D. M. (2015). The visual analysis of data, and current research into the stimuli controlling it. In Single-Case Research Design and Analysis (Psychology Revivals) (pp. 27-52). Routledge.
The relationship of client satisfaction to outcome was investigated for adult outpatients (N = 152) from 3 urban community mental health centers. Clients completed a problem self-rating and the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) at intake, 10 weeks later, and 5 months later.
Pekarik, G., & Wolff, C. B. (1996). Relationship of satisfaction to symptom change, follow-up adjustment, and clinical significance. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 27(2), 202-208.
Project Northland is an efficacy trial with the goal of preventing or reducing alcohol use among young adolescents by using a multilevel, communitywide approach.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Toomey, T. L., Komro, K. A., Anstine, P. S., ... & Wolfson, M. (1996). Project Northland: outcomes of a communitywide alcohol use prevention program during early adolescence. American Journal of Public Health, 86(7), 956-965.
It is argued that the design of contemporary psychotherapy outcome studies is conceptually incompatible with the models of psychotherapy evaluated in those studies.
Persons, J. B. (1991). Psychotherapy outcome studies do not accurately represent current models of psychotherapy: A proposed remedy. American psychologist, 46(2), 99.
A discussion of this chapter entitled "Dissemination of What, and to Whom?" by B. S. Kohlenberg follows this chapter.
Persons, J. B. (1995). Why practicing psychologists are slow to adopt empirically-validated treatments. In S. C. Hayes, V. M. Follette, R. M. Dawes, & K. E. Grady (Eds.), Scientific standards of psychological practice: Issues and recommendations (pp. 141-157). Reno, NV, US: Context Press
Two clinicians provided opposite answers to the title question: Persons argued that information from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is vital to clinicians, and Silberschatz argued that information from RCTs is irrelevant to clinicians.
Persons, J. B., & Silberschatz, G. (1998). Are results of randomized controlled trials useful to psychotherapists?. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 66(1), 126.
This award-winning twelve-volume reference covers every aspect of the ever-fascinating discipline of psychology and represents the most current knowledge in the field. This ten-year revision now covers discoveries based in neuroscience, clinical psychology's new interest in evidence-based practice and mindfulness, and new findings in social, developmental, and forensic psychology.
Pianta, R. C., Hamre, B., Stuhlman, M., Reynolds, W. M., & Miller, G. E. (2003). Handbook of psychology: Educational psychology.
In this provocative and persuasive new book, the author asserts that the secret to high performance and satisfaction-at work, at school, and at home—is the deeply human need to direct our own lives, to learn and create new things, and to do better by ourselves and our world.
Pink, D. H. (2011). Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us. Penguin.
This article shows some common type of misused or unhelpful NAEP analyses to look out for and avoid. This article also give some warning to avoid misuse of the NAEP data.
Polikoff, M.S. (2015). Friends don’t let friends misuse NAEP data. Retrieved from https://morganpolikoff.com/2015/10/6/friends-dont-let-friends-misuse-naep-data/
Teacher turnover occurs during and at the end of the school year, although documentation of within-year turnover currently rests on anecdotal evidence.
Redding, C., & Henry, G. T. (2018). New evidence on the frequency of teacher turnover: Accounting for within-year turnover. Educational Researcher, 47(9), 577-593.
The authors report on descriptive evidence of growing differences in the characteristics of alternatively and traditionally certified teachers and the schools in which they teach.
Redding, C., & Smith, T. M. (2016). Easy in, easy out: Are alternatively certified teachers turning over at increased rates?. American Educational Research Journal, 53(4), 1086-1125.
This chapter describe and contrast different paradigms for the design and delivery of school psychological services, analyze problems in the traditional delivery system, and review major policy and reform statements. The chapter concludes with a discussion of the knowledge base, underlying principles, and strategies that form the basis for psychological services that emphasize problem solving, functional assessment, and educational accountability.
Reschly, D. J., & Ysseldyke, J. E. (2002). Paradigm shift: The past is not the future.
The criteria for empirically supported treatments, as described by Lonigan, Elbert, and Johnson (this issue), were applied to reports of eight treatment efficacy studies published in peer-reviewed journals.
Rogers, S. J. (1998). Empirically supported comprehensive treatments for young children with autism. Journal of clinical child psychology, 27(2), 168-179.
Describes treatment of autism, a severe, chronic developmental disorder that results in significant lifelong disability for most persons, with few persons ever functioning in an independent and typical lifestyle.
Rogers, S. J. (1998). Empirically supported comprehensive treatments for young children with autism. Journal of clinical child psychology, 27(2), 168-179.
Current systems for listing empirically supported therapies (ESTs) provide recognition to treatment packages, many of them proprietary and trademarked, without regard to the principles of change believed to account for their effectiveness.
Rosen, G. M., & Davison, G. C. (2003). Psychology should list empirically supported principles of change (ESPs) and not credential trademarked therapies or other treatment packages. Behavior modification, 27(3), 300-312.
The British Road Safety Act of 1967, which introduces scientific tests to determine and define the crime of drinking and driving, has been the subject of much interest among American lawyers and social scientists.
Ross, H. L. (1973). Law, science, and accidents: the British Road Safety Act of 1967. The Journal of Legal Studies, 2(1), 1-78.
Casting a wide net through history and culture, Sagan examines and authoritatively debunks such celebrated fallacies of the past as witchcraft, faith healing, demons, and UFOs. And yet, disturbingly, in today's so-called information age, pseudoscience is burgeoning with stories of alien abduction, channeling past lives, and communal hallucinations commanding growing attention and respect.
Sagan, C. (2011). The demon-haunted world: Science as a candle in the dark. Ballantine Books.
Two messages are conveyed in the report: Mental health is fundamental to health, and mental disorders are real health conditions. The surgeon general's report summarizes the Office's detailed review of more than 3,000 research articles, plus 1st-person accounts from individuals who have been afflicted with mental disorders.
Satcher, D. (2000). Mental health: A report of the Surgeon General--Executive summary. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 31(1), 5-13.
This article suggests the routine use of replications in field studies.
Schafer, W. D. (2001). Replication: A design principle for field research. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 7(15), 1-7.
The challenges of specifying a complex and individualized treatment model and measuring fidelity thereto are described, using multisystemic therapy (MST) as an example.
Schoenwald, S. K., Henggeler, S. W., Brondino, M. J., & Rowland, M. D. (2000). Multisystemic therapy: Monitoring treatment fidelity. Family Process, 39(1), 83-103.
Written by one of the leaders in evaluation, Evaluation Thesaurus, Fourth Edition, provides readers with a quick analysis of the leading concepts, positions, acronyms, processes, techniques, and checklists in the field of evaluation.
Scriven, M. (1991). Evaluation thesaurus. Sage.
The leadership stories in the book demonstrate the many ways that the core ideas in The Fifth Discipline, many of which seemed radical when first published in 1990, have become deeply integrated into people's ways of seeing the world and their managerial practices.
Senge, P. M. (2006). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization. Broadway Business.
This study evaluated the impact of intensive behavioral treatment on the development of young autistic children.
Sheinkopf, S. J., & Siegel, B. (1998). Home-based behavioral treatment of young children with autism. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 28(1), 15-23.
This paper outlines the best practices for researchers and practitioners translating research to practice as well as recommendations for improving the process.
Shriver, M. D. (2007). Roles and responsibilities of researchers and practitioners for translating research to practice. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 8(1), 1-30.
the purpose of this chapter is to review the science of teams and their effectiveness, extrapolate critical lessons learned, and highlight several future challenges critical for military psychology to address in order to prepare future military teams for success.
Shuffler, M. L., Pavlas, D., & Salas, E. (2012). Teams in the military: A review and emerging challenges. In J. H. Laurence & M. D. Matthews (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of military psychology(pp. 282–310). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Discussing the major themes of replication, variability, and experimental design, Sidman describes the step-by-step planning of experiments, the need for constant attention to trends of incoming data, and the alteration of plan, method, or design that those trends sometimes make necessary
Sidman, M. (1960). Tactics of Scientific Research: Evaluating Experimental Data in Psychology. Boston: Authors Cooperative.
Discussing the major themes of replication, variability, and experimental design, Sidman describes the step-by-step planning of experiments, the need for constant attention to trends of incoming data, and the alteration of plan, method, or design that those trends sometimes make necessary.
Sidman, M. (1960). Tactics of scientific research; evaluating experimental data in psychology. New York: basic Books
In this article, alternative analytical procedures are developed for cross-sectional time-series in which the sample size is large and the number of observations per case is relatively small.
Simonton, D. K. (1977). Cross-sectional time-series experiments: Some suggested statistical analyses. Psychological Bulletin, 84(3), 489.
In this article, alternative analytical procedures are developed for cross-sectional time-series in which the sample size is large and the number of observations per case is relatively small.
Simonton, D. K. (1977). Erratum to Simonton.
Did you know that plants and plant products can be used to improve people’s cognitive, physical, psychological, and social functioning? Well, they can, and Horticulture as Therapy is the book to show you how!
Simson, S., & Straus, M. (1997). Horticulture as therapy: Principles and practice. CRC Press.
The case history in scientific method cited is autobiographical; Skinner relates certain relevant experiences in the development of some of his scientific contributions.
Skinner, B. F. (1956). A case history in scientific method. American Psychologist, 11(5), 221.
The psychology classic—a detailed study of scientific theories of human nature and the possible ways in which human behavior can be predicted and controlled.
Skinner, B. F. (1965). Science and human behavior (No. 92904). Simon and Schuster.
Recent analyses of American schools and proposals for school reform have missed an essential point: Most current problems could be solved if students learned twice as much in the same time and with the same effort.
Skinner, B. F. (1984). The shame of American education. American Psychologist, 39(9), 947.
This paper contrasts effect sizes in What Works Clearinghouse and Best Evidence Encyclopedia reading and math reviews to explore the degree to which these measures produce different estimates.
Slavin, R. E., & Madden, N. A. (2008). Understanding bias due to measures inherent to treatments in systematic reviews in education. In annual meeting of the Society for Research on Effective Education, Crystal City, VA.
This study uses data from the elementary and secondary mathematics explores the effects of sample size on effect size in program evaluations in education.
Slavin, R.E., & Smith, D. (2009). The relationship between sample sizes and effect sizes in systematic reviews in education. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 31 (4), 500-506.
A commentary on: Retrieval practice protects memory against acute stress
Smith, A. M., Floerke, V. A., & Thomas, A. K. (2016). Retrieval practice protects memory against acute stress. Science, 354(6315), 1046-1048.
Since 1980, 12 peer-reviewed outcome studies (nine on behavior analytic programs, one on Project TEACCH, and two on Colorado Health Sciences) have focused on early intervention for children with autism. Mean 10 gains of 7-28 points were reported in studies of behavior analytic programs, and 3-9 in studies on TEACCH and Colorado.
Smith, T. (1999). Outcome of early intervention for children with autism. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 6(1), 33-49.
In this provocative and headline-making book, Michael Specter confronts the widespread fear of science and its terrible toll on individuals and the planet.
Smith, T. C. (2010). Denialism: How Irrational Thinking Hinders Scientific Progress, Harms the Planet, and Threatens our Lives.
The 2010 edition of the Digest of Education Statistics is the 46th in a series of publications initiated in 1962. The Digest includes a selection of data from many sources, both government and private, and draws especially on the results of surveys and activities carried out by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES).
Snyder, T. D., & Dillow, S. A., (2010). Digest of Education Statistics 2010. U.S. Department of Education: Washington, DC. Retrieved from http://nces.ed.gov/pubs2011/2011015.pdf
This review summarizes the structure of the generalization literature and its implicit embryonic technology, categorizing studies designed to assess or program generalization according to nine general headings:
Stokes, T. F., & Baer, D. M. (1977). An implicit technology of generalization 1. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 10(2), 349-367.
This volume provides a comprehensive summary of developments in theories and techniques within the areas of sampling, measurement, and statistical methods for analyzing behavioral data. By unifying new theories, techniques, methodologies, terminology, and language in behavioral observation research, the authors provide a comprehensive source for students and researchers.
Suen, H. K., & Ary, D. (2014). Analyzing quantitative behavioral observation data. psychology press.
At the request of David Barlow, President of Division 12, and under the aegis of Section III, this task force was constituted to consider methods for educating clinical psychologists, third party payors, and the public about effective psychotherapies
Task Force on Promotion and Dissemination of Psychological Procedures, Division of Clinical Psychology, American Psychological Association. (1995). Training in and Dissemination of Empirically-Validated Psychological Treatments: Report and Recommendations. The Clinical Psychologist, 48, 3-23.
The Sentinel Event Policy explains how The Joint Commission partners with health care organizations that have experienced a serious patient safety event to protect the patient, improve systems, and prevent further harm.
The Joint Commission, (2011), Sentinel Event, Retrieved from https://www.jointcommission.org/sentinel_event.aspx
Increasingly, school services are being guided by a problem solving approach and are evaluated by the achievement of positive outcomes. This shift is explored here in 96 chapters and 11 appendices. The volume provides a comprehensive reference relating contemporary research and thought to quality professional services
Thomas, A., & Grimes, J. (Eds.). (1995). Best practices in school psychology III.Washington, DC: National Association of School Psychologists.
The present article proposes some quality indicators for evaluating correlational research in efforts to inform evidence-based practice.
Thompson, B., Diamond, K. E., McWilliam, R., Snyder, P., & Snyder, S. W. (2005). Evaluating the quality of evidence from correlational research for evidence-based practice. Exceptional Children, 71(2), 181-194.
This chapter chronicles some of the major steps school psychology has taken toward adopting science as the basis of practice. Each step has yielded benefits for students as well as practice challenges to be overcome.
Tilly, W. D. (2008). The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology–5(pp. 17–36). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Originally published in 1992, the editors of this volume fulfill three main goals: to take stock of progress in the development of data-analysis procedures for single-subject research
Todman, J. B., & Dugard, P. (2001). Single-case and small-n experimental designs: A practical guide to randomization tests. Psychology Press.
This book is about the creation and 14 year evolution of a public alternative inner-city high school—New Haven, CT's High School in the Community (HSC). This school lived an idea—empowerment. Students were encouraged to participate in shaping many aspects of their education, teachers were responsible for running the school, and parents invited to help govern.
Trickett, E. J. (1991). Living an idea: Empowerment and the evolution of an alternative high school. Brookline Books.
The empirical correlation of self-efficacy statements and treatment outcome reported by Bandura (1977) is acknowledged. The question at issue is whether this correlation is due to an integrative construct called self or social contingencies.
Tryon, W. W. (1982). Reinforcement history as possible basis for the relationship between self-percepts of efficacy and responses to treatment. Journal of behavior therapy and experimental psychiatry, 13(3), 201-202.
This paper examines the types of research to consider when evaluating programs, how to know what “evidence’ to use, and continuums of evidence (quantity of the evidence, quality of the evidence, and program development).
Twyman, J. S., & Sota, M. (2008). Identifying research-based practices for response to intervention: Scientifically based instruction. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 9(2), 86-101.
Employment status of the civilian population 25 years and over by educational attainment
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2013). Employment status of the civilian population 25 years and over by educational attainment. [Table A-4]. Retrieved from https://www.bls.gov/webapps/legacy/cpsatab4.htm
The Statistical Abstract of the United States is the authoritative and comprehensive summary of statistics on the social, political, and economic organization of the United States.
U.S. Census Bureau. (2011). Abstract of the United States: 2012 (131st Edition). [Table 232]. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2011/compendia/statab/131ed.html
The text and graphics contained in the 26th Annual Report to Congress were developed primarily from data from the Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP) Data Analysis System (DANS). DANS is a repository for all the data mandated by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to be collected from states annually.
US Department of Education. (1998). Twentieth annual report to Congress on the implementation of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act.
The Innovation Journey presents the results of a major longitudinal study that examined the process of innovation from concept to implementation of new technologies, products, processes, and administrative arrangements.
Van de Ven, A. H., Polley, D. E., Garud, R., & Venkataraman, S. (1999). The Innovation Journey, New York: Oxford Univ.
In order to determine the reliability and accuracy of model identification, 12 extensively trained subjects were each asked to identify 32 different computer-generated time series. The purpose of the analysis is to determine if the intervention resulted in a significant change in the level and/or slope of the series.
Velicer, W. F., & Harrop, J. (1983). The reliability and accuracy of time series model identification. Evaluation Review, 7(4), 551-560.
This article extends the general transformation matrix approach to the analysis of multiple-unit data by the development of a patterned transformation matrix.
Velicer, W. F., & McDonald, R. P. (1991). Cross-sectional time series designs: A general transformation approach. Multivariate behavioral research, 26(2), 247-254.
Education and law are two general approaches that have been used in efforts to prevent alcohol-related problems among young people. This book focuses on the legal approach, commonly expressed in legislation that specifies the legal-drinking age.
Wagenaar, A. C. (1983). Alcohol, young drivers, and traffic accidents. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
Results of a 6-year follow-up of previous research evaluating the effects of Michigan's December 1978 increase in the legal drinking age from IS to 21 are reported.
Wagenaar, A. C. (1986). Preventing highway crashes by raising the legal minimum age for drinking: the Michigan experience 6 years later. Journal of Safety Research, 17(3), 101-109.
This article discusses the effects of minimum drinking age on alcohol use, effects of minimum drinking age on traffic crashes, effect of minimum drinking age on other health and social problems. In the end, the author calls for research needs on youth alcohol availability.
Wagenaar, A. C. (1993). Minimum drinking age and alcohol availability to youth: Issues and research needs. Economics and the Prevention of Alcohol-Related Problems. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 175-200.
Effects on motor vehicle crash involvement of raising the legal drinking age in Texas from 18 to 19 were examined, using an interrupted time-series design. It is clear that the l-year increase in legal age in Texas had a significant effect on youth crash involvement.
Wagenaar, A. C., & Maybee, R. G. (1986). The legal minimum drinking age in Texas: Effects of an increase from 18 to 19. Journal of safety research, 17(4), 165-178.
Effects of Michigan's law requiring all young children to be restrained when traveling in automobiles were assessed. Data on all reported residents of the state who were involved in crashes from 1978 through 1983 were examined using times-series analysis methods.
Wagenaar, A. C., & Webster, D. W. (1986). Preventing injuries to children through compulsory automobile safety seat use. Pediatrics, 78(4), 662-672.
Communities Mobilizing for Change on Alcohol (CMCA) is a 15-community randomized trial designed to develop, implement, and evaluate a 2¹⁄â year community organizing intervention to change policies and practices of major community institutions.
Wagenaar, A. C., Gehan, J. P., JonesâWebb, R., Toomey, T. L., Forster, J. L., Wolfson, M., & Murray, D. M. (1999). Communities mobilizing for change on alcohol: Lessons and results from a 15âcommunity randomized trial. Journal of Community Psychology, 27(3), 315-326.
Communities Mobilizing for Change on Alcohol (CMCA) was a randomized 15-community trial of a community organizing intervention designed to reduce the accessibility of alcoholic beverages to youths under the legal drinking age
Wagenaar, A. C., Murray, D. M., Gehan, J. P., Wolfson, M. F. J. L., Forster, J. L., Toomey, T. L., ... & Jones-Webb, R. (2000). Communities mobilizing for change on alcohol: outcomes from a randomized community trial. Journal of studies on alcohol, 61(1), 85-94.
Describes the evaluation design of the CMCA (Communities Mobilizing for Change on Alcohol) project. The effects of the intervention on youth alcohol access, alcohol use, and related problems were determined using a combination of a randomized community trial and a time-series design.
Wagenaar, A. C., Murray, D. M., Wolfson, M., & Forster, J. L. (1994). Communities mobilizing for change on alcohol: Design of a randomized community trial. Journal of Community Psychology.
This book is the first to comprehensively plot humankind's fascinating efforts to visualize data, from a key seventeenth-century precursor--England's plague-driven initiative to register vital statistics--right up to the latest advances.
Wainer, H. (2005). Graphic discovery: A trout in the milk and other visual adventures. Princeton University Press.
This paper describes three of the best known of these paradoxes --Simpson’s Paradox, Kelley’s Paradox, and Lord’s Paradox -- and illustrate them in a single data set.
Wainer, H., & Brown, L. (2004). Two statistical paradoxes in the interpretation of group differences: Illustrated with medical school admission and licensing data. The American Statistician, 58, 117–123. http://www.statlit.org/pdf/2004wainer_threeparadoxes.pdf
This kit presents the Systematic Screening for Behavior Disorders (SSBD) as a tool to identify behavior disorders in elementary-aged students. The kit contains a user's guide and administration manual, a technical manual reporting psychometric properties of the SSBD, an observer training manual, and multiple copies of the screening instruments.
Walker, H. M., Severson, H., & Feil, E. G. (1990). Systematic screening for behavior disorders (SSBD). Longmont, CO: Sopris West.
The impact of the anti-smoking campaign on the consumption of cigarettes is measured by fitting cigarette demand functions to pre-campaign data, projecting "ahead" as if the campaign had not occurred, and then comparing these predictions with realized consumption.
Warner, K. E. (1977). The effects of the anti-smoking campaign on cigarette consumption. American journal of public health, 67(7), 645-650.
The Child Task Force report represents an important initial step in this direction. Here they offer both praise and critique, suggesting a number of ways the task force process and product may be improved.
Weisz, J. R., & Hawley, K. M. (1998). Finding, evaluating, refining, and applying empirically supported treatments for children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 27(2), 206-216.
This article addresses the gap between clinical practice and the research laboratory. We focus on the issue as it relates specifically to interventions for children and adolescents.
Weisz, J. R., Donenberg, G. R., Han, S. S., & Weiss, B. (1995). Bridging the gap between laboratory and clinic in child and adolescent psychotherapy. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 63(5), 688.
The study does suggest that "more is not always better" (L. Bickman, 1996), but more of what? Little is known about the specific interventions that were combined to form the Fort Bragg system of care, so the study does not really reveal what failed or what needs to be changed.
Weisz, J. R., Han, S. S., & Valeri, S. M. (1997). More of what? Issues raised by the Fort Bragg study.
The Society of Clinical Psychology's task forces on psychological intervention developed criteria for evaluating clinical trials, applied those criteria, and generated lists of empirically supported treatments. Building on this strong base, the task force successor, the Committee on Science and Practice, now pursues a threeâpart agenda
Weisz, J. R., Hawley, K. M., Pilkonis, P. A., Woody, S. R., & Follette, W. C. (2000). Stressing the (other) three Rs in the search for empirically supported treatments: Review procedures, research quality, relevance to practice and the public interest. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 7(3), 243-258.
This article provides a critical review of the assumptions and findings of studies used to establish psychotherapies as empirically supported.
Westen, D., Novotny, C. M., & Thompson-Brenner, H. (2004). The empirical status of empirically supported psychotherapies: assumptions, findings, and reporting in controlled clinical trials. Psychological bulletin, 130(4), 631.
This slide show presents what is EBE and what are EBE goals in education.
Whitehurst, G. J. (2002). Evidence-based education (EBE). Washington, DC. Retrieved Juanuary, 9(2), 6.
This paper considers what the research can tell us about how critical thinking is acquired, and the implications for how education might best develop young people’s critical thinking capabilities.
Willingham, D. (2019). How to teach critical thinking. New South Wales (NSW) Department of Education.
The cognitive principle that guides this article is: People are naturally curious, but they are not naturally good thinkers; unless the cognitive conditions are right, people will avoid thinking.
Willingham, D. T. (2009). Why don't students like school?: A cognitive scientist answers questions about how the mind works and what it means for the classroom. John Wiley & Sons.
In addition to their now required use in controlled outcome studies, treatment manuals offer important advantages for clinical practice. Manual-based treatments are often empirically-validated, more focused, and more disseminable.
Wilson, G. T. (1996). Manual-based treatments: The clinical application of research findings. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 34(4), 295-314.
This paper describes guidelines for reporting findings from studies using single subject methods, an approach from which early intervention has benefited substantially.
Wolery, M., & Dunlap, G. (2001). Reporting on Studies Using Single-Subject Experimental Methods. Journal of Early Intervention, 24(2), 85-89.
In this manuscript, we respond to the minimum standards for describing research subjects as proposed by the Council for Learning Disabilities (CLD) Research Committee. Three issues are raised about the standards: (a) whether justification exists for the recommended standards.
Wolery, M., & Ezell, H. K. (1993). Subject descriptions and single-subject research. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 26(10), 642-647.
This manuscript was presented as an invited address to the Division of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, American Psychological Association, Washington, D.C., September, 1976.
Wolf, M. M. (1978). SOCIAL VALIDITY: THE CASE FOR SUBJECTIVE MEASUREMENT or HOW APPLIED BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS IS FINDING ITS HEART 1. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 11(2), 203-214.
In 1995 the Division 12 Task Force on Promotion and Dissemination of Psychological Procedures published its report in this journal. A major focus of that report was increasing training in psychological interventions that have been supported in empirical research by making clinical psychologists and students more aware of these treatments and facilitating training opportunities.
Woody, S. S., Beutler, L., Williams, D. A., & McCurry, S. (1996). An update on empirically validated therapies. Clinical Psychologist, 49, 5-18.
This report defines alternate assessment, describe methods that can be used to collect data and describe domains in which data should be collected.
Ysseldyke, J., & Olsen, K. (1999). Putting alternate assessments into practice: What to measure and possible sources of data. Exceptional Children, 65(2), 175-185.
These guidelines describe the strengths and limitations of several approaches to the assessing the magnitude of an intervention’s effect.
