Abundant knowledge informs us that teachers play the pivotal role in student success. A comparison of key variables reveals that teachers lead all other school factors with an effect size between 0.30 and 0.42 (Wenglinsky, 2002; Hattie, 2009). More important, how teachers instruct and interact with students is the cornerstone around which effective schools are built. To maximize teacher performance, preparation programs must recruit the best possible talent, train candidates using teaching practices supported by the best available evidence, and employ evidence-based pedagogical methods. Research supports an explicit model of instruction that emphasizes teachers as the active agents responsible for planning, delivering, and monitoring instruction. In such a system, teachers provide systematic instruction tied to standards and goals. Using research-based pedagogy, they instruct students in concepts, skills, and knowledge linked to higher order thinking founded on student mastery of foundation skills in key subjects such as reading, mathematics, and writing. Effective teachers must monitor and adjust teaching strategies to meet the needs of gifted students and those who are struggling. Finally, quality teachers require ongoing mentoring and oversight from principals to ensure quality teaching is supported and maintained over time.
Which competencies make the biggest difference? An examination of the research on education practices that make a difference shows that four classes of competencies yield the greatest results.
- Instructional delivery
- Classroom management
- Formative assessment
- Personal competencies (soft skills)
Further, the research indicates that these competencies can be used to organize the numerous specific skills and knowledge available for building effective teacher development.
Instructional delivery: Research tells us what can be expected from a teacher employing instructional strategies and practices that are proven to lead to increased mastery of lessons. Better learning happens in a dynamic setting in which teachers offer explicit active instruction than in situations in which teachers do not actively guide instruction and instead turn control over content and pace of instruction to students (Hattie, 2009).
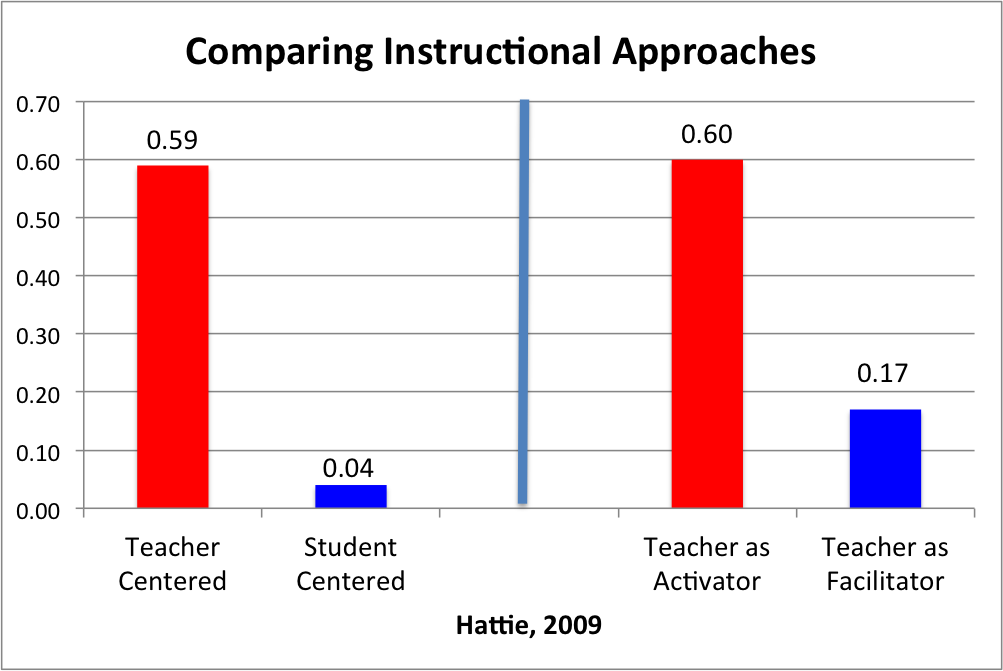
Is there a diverse set of practices that teachers can efficiently and effectively use to increase mastery of content for a variety of curricula? The structured and systematic approach of explicit instruction emphasizes mastery of the lesson to ensure that students understand what has been taught, become fluent in new material, and can generalize what they learn to novel situations they encounter in the future.
The following are hallmarks of an explicit approach for teachers (Archer & Hughes, 2011; Knight, 2012).
- Teacher selects the learning area to be taught.
- Teacher sets criteria for success.
- Teacher informs students of criteria ahead of the lesson.
- Teacher demonstrates to the students successful use of the knowledge/skills through modeling.
- Teacher evaluates student acquisition.
- Teacher provides remedial opportunities for acquiring the knowledge/skills, if necessary.
- Teacher provides closure at the end of the lesson.
A common complaint of an explicit instruction approach is that it does not offer sufficient opportunities for students to build on acquired knowledge/skills in creative and novel ways that help them to assimilate the material. The reality is that all effective instruction, regardless of philosophy, must aid students in generalizing newly taught knowledge/skills in a context that is greater than a single lesson. An explicit model accomplishes the goal of building toward “big ideas” by first emphasizing mastery of foundation skills such as reading and mathematics, and then systematically introducing opportunities to integrate these critical skills in discovery-based lessons to maximize students’ experience of success.
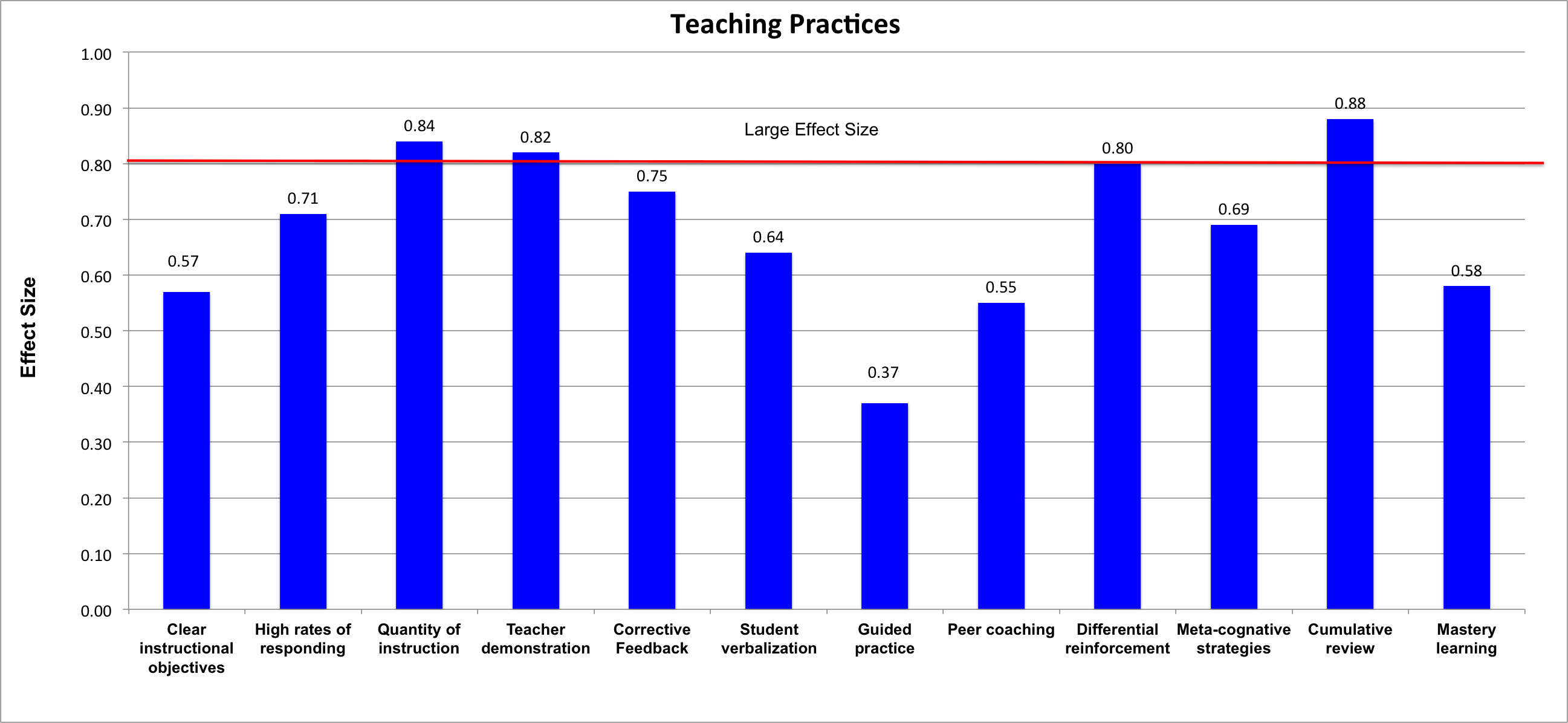
Effective explicit instruction practices include these features.
- Well-designed and planned instruction: Instruction that is well planned moves students from their current level of competency toward explicit criteria for success.
- Instructional design with clear instructional objectives: The teacher should present these objectives to students for each lesson.
- Scope and sequencing: The teacher should teach the range of related skills and the order in which they should be learned.
- Instruction that offers sufficient opportunities for successful acquisition:
- High rates of responding for each student to practice the skill: The teacher should provide sufficient opportunities for unpunished errors and ample reinforcement for success.
- Sufficient quantity of instruction: The teacher should allocate enough time to teach a topic.
- Teaching to mastery: Students need to learn the knowledge/skills to criteria that are verified by teachers or students’ peers.
- Teaching foundation knowledge/skills that become the basis for teaching big ideas: Current lessons should be built on past knowledge to increase fluency and maintain mastery of material. The teacher should relate lessons to complex issues and big ideas that provide deeper meaning and give students better understanding of the content.
Classroom management: Classroom management is one of the most persistent areas of concern voiced by school administrators, the public, and teachers (Evertson & Weinstein, 2013). Research consistently places classroom management among the top five issues that affect student achievement.
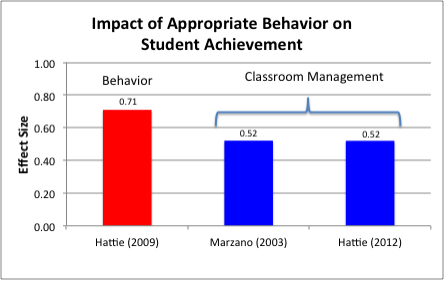
To put its in perspective, classroom management was associated with an increase of 20% in student achievement when classroom rules and procedures were applied systematically (Hattie, 2005).
A good body of research highlights four important areas that classroom teachers should be proficient in to create a climate that maximizes learning and induces a positive mood and tone.
- Rules and procedures: Effective rules and procedures identify expectations and appropriate behavior for students. To be effective, these practices must be observable and measurable.
- Schoolwide rules and procedures: Clearly stated rules identify, define, and operationalize acceptable behavior specific to a school. These rules, applicable to all students, are designed to build pro-social behavior and reduce problem behavior in a school. They distinguish appropriate from problem behavior as well as specify consequences for infractions.
- Classroom rules and procedures: Another set of clearly stated rules establishes acceptable behavior specific in a classroom. These rules need to be consistent with schoolwide rules, but may be unique to meet the needs of an individual classroom.
- Proactive classroom management: These are the practices that teachers and administrators can employ to teach and build acceptable behavior that is positive and helpful, promotes social acceptance, and leads to greater success in school. The key to proactive classroom management is active teacher supervision. The practice elements that constitute active supervision require staff to observe and interact with students regularly. The goal is to build a positive teacher-student relationship by providing timely and frequent positive feedback for appropriate behavior, and to swiftly and consistently respond to inappropriate behaviors.
- Effective classroom instruction: The key to maintaining a desirable classroom climate is to provide students with quality instructional delivery aligned to the skill level of each student. This enables students to experience success and keeps them attentive.
- Behavior reduction: These practices, designed to reduce problem and unacceptable behavior, are employed in the event the first three strategies fail. Behavior reduction strategies include giving students corrective feedback at the time of an infraction, minimizing reinforcement of a student’s unacceptable behavior, and guiding students in how to behave appropriately.
Formative assessment: Effective ongoing assessment, referred to in education literature as formative assessment and progress monitoring, is indispensable in promoting teacher and student success. It is frequently listed at the top of interventions for school improvement (Walberg, 1999).
Feedback, a core component of formative assessment, is recognized as an essential tool for improving performance in sports, business, and education. Hattie (2009) identified feedback as the single most powerful educational tool available for improving student performance, with a medium to large effect size ranging from 0.66 to 0.94.
Formative assessment consists of a range of formal and informal diagnostic testing procedures, conducted by teachers throughout the learning process, for modifying teaching and adapting activities to improve student attainment. Systemic interventions such as Response to Intervention (RtI) and Data-Based Decision Making depend heavily on the use of formative assessment (Hattie, 2009; Marzano, Pickering, & Pollock, 2001).
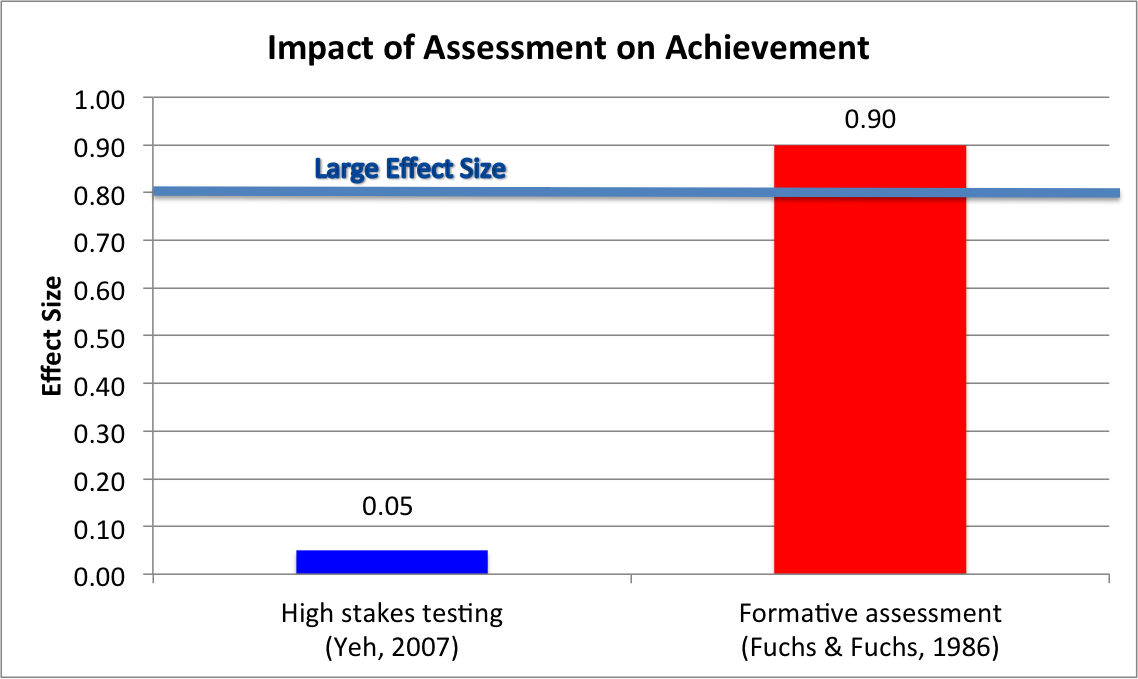
The following are the practice elements of formative assessment (Fuchs & Fuchs, 1986).
- Assessment: (Effect size 0.26) Assessing a student’s performance throughout a lesson offers a teacher insight into who is succeeding and who is falling behind. It is important that teachers collect and maintain data gained through both informal and formal assessments.
- Data display: (Effect size 0.70) Displaying the data in the form of a graphic has a surprisingly powerful effect on formative assessment’s usefulness as a tool.
- Data analysis following defined rules: (Effect size 0.90) Formative assessment is most valuable when teachers use evidence-based research and their own professional judgment to develop specific remedial interventions, before it is too late, for those falling behind.
Personable competencies (soft skills): An inspiring teacher can affect students profoundly by stimulating their interest in learning. It is equally true that most students have encountered teachers who were uninspiring and for whom they performed poorly. Unfortunately, effective and ineffective teachers have no readily discernable personality differences. Some of the very best teachers are affable, but many ineffective instructors can be personable and caring. Conversely, some of the best teachers appear as stern taskmasters, but whose influence is enormous in motivating students to accomplish things they never thought possible.
What soft skills do successful teachers have in common? Typically, the finest teachers display enthusiasm and excitement for the subjects they teach. More than just generating excitement, they provide a road map for students to reach the goals set before them. The best teachers are proficient in the technical competencies of teaching: instructional delivery, formative assessment, and classroom management. Equally significant, they are fluent in a multilayered set of social skills that students recognize and respond to, which leads to greater learning (Attakorn, Tayut, Pisitthawat, & Kanokorn, 2014). These skills must be defined as clear behaviors that teachers can master for use in classrooms.
Indispensable soft skills include:
- Establishing high but achievable expectations
- Encouraging a love for learning
- Listening to others
- Being flexible and capable of adjusting to novel situations
- Showing empathy
- Being culturally sensitive
- Embedding and encouraging higher order thinking along with teaching foundation skills
- Having a positive regard for students
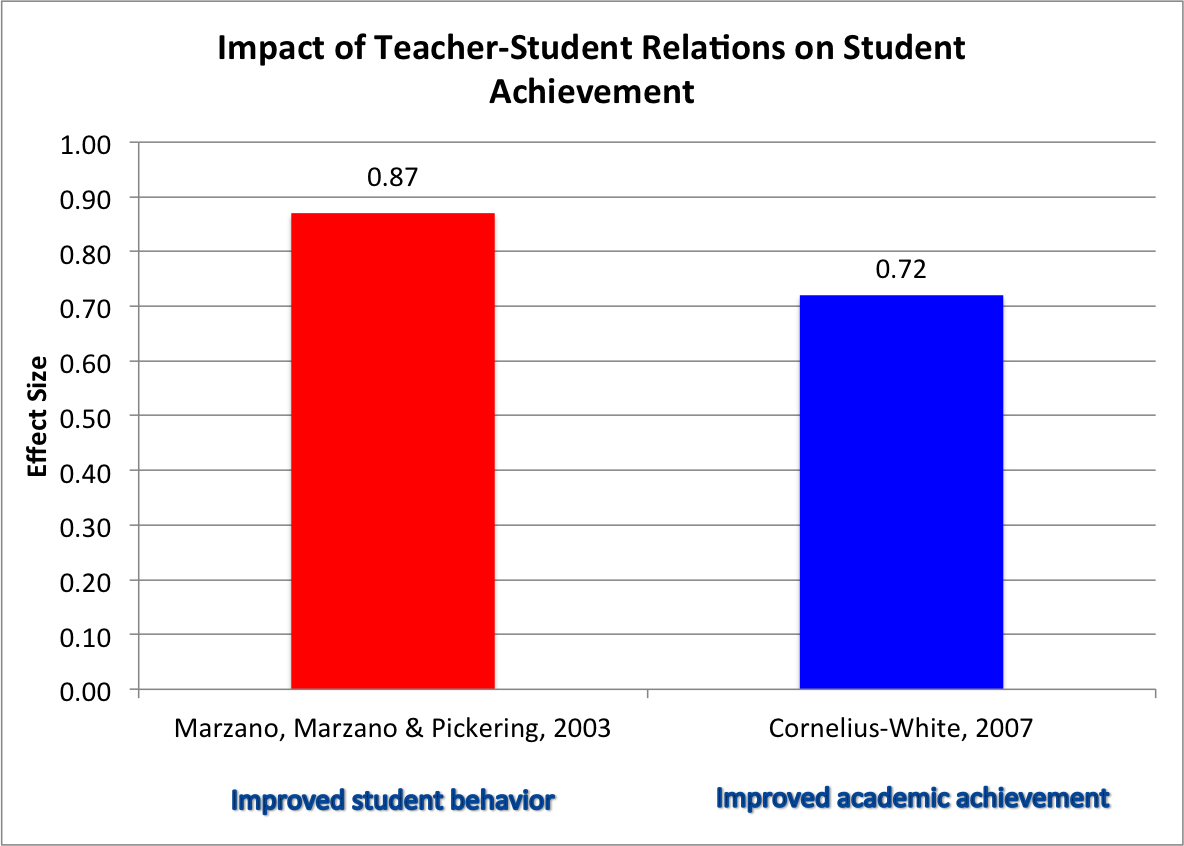
What does research tell us about personal competencies? Quantitative studies provide an overall range of effect sizes from 0.72 to 0.87 for effective teacher-student relations. Better teacher-student relations promote increased student academic performance and improve classroom climate by reducing disruptive student behavior (Cornelius-White, 2007; Marzano, Marzano & Pickering, 2003).
Conclusion
There is abundant research to support the notion that teachers play the critical role in improving student achievement in schools. What teachers do in the classroom is crucial in this process. The breadth of high-quality research accumulated over the past 40 years offers educators a clear picture of how to maximize teacher competency in four critical categories: instructional delivery, classroom management, formative assessment, and personal competencies. There is now ample evidence to recommend these competencies as the core around which to build teacher preparation, teacher hiring, teacher development, and teacher and school evaluations.
Citations
Archer, A. L., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010–1013.
Babu, S., & Mendro, R. (2003). Teacher accountability: HLM-based teacher effectiveness indices in the investigation of teacher effects on student achievement in a state assessment program. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association (AERA), Chicago, IL, April.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113–143.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of systematic formative evaluation: A meta-analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199–208.
Hattie, J., (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses related to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Knight, J. (2012). High-impact instruction: A framework for great teaching. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Value-Added Research and Assessment Center. Retrieved from http://heartland.org/policy-documents/cumulative-and-residual-effects-teachers-future-student-academic-achievement.
Walberg, H. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), New directions for teaching practice and research (pp. 75–104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416–436.
Publications
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
Performance Feedback Overview
This overview examines the current understanding of research on performance feedback as a way to improve teacher performance and student outcomes.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2019). Overview of Performance Feedback. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-evaluation-feedback.
Teacher Preparation: Overview
The purpose of this overview is to provide information about the methods of teacher preparation, the current state of research on teacher preparation, challenges, trends, questions, and recommendations for those working to prepare teachers for success in the classroom.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2020). Overview of Teacher Preparation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-pre-service.
Treatment Integrity: Fundamental to Education Reform
To produce better outcomes for students two things are necessary: (1) effective, scientifically supported interventions (2) those interventions implemented with high integrity. Typically, much greater attention has been given to identifying effective practices. This review focuses on features of high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. (2014). Treatment integrity: Fundamental to education reform. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 13(2), 258-271.
Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation.
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Working Paper: Understanding Rural Teacher Recruitment and the Role of Community Amenities
This paper is the first attempt to test the community amenity hypotheses in a multivariate framework using administrative data on teacher employment patterns.
Miller, L. C. (2012). Understanding rural teacher recruitment and the role of community amenities. Journal of Research in Rural Education, 27(13), 1-52.
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Thirty years of Getting Teachers to be More Effective
This paper presents a model for building a school organizational culture that trains and supports teachers in an effective, efficient, and sustainable manner.
Fitch, S. (2013). Thirty years of Getting Teachers to be More Effective Retrieved from ../../uploads/docs/2013WingSummitSF.pdf.
Data Mining
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Are Schools Adequately Attracting and Retaining Teaching Staff?
This inquiry analyzes data from National Center for Education Statistics to look at the impact of race experience and age on teacher recruiting and retention.
Keyworth, R. (2010). Are Schools Adequately Attracting and Retaining Teaching Staff? Retrieved from are-schools-adequately-attracting899.
How do teacher working conditions impact teacher turnover?
This item analyzes teacher reports of differing working condition issues and how they correlate to student achievement.
Keyworth, R. (2009). How do teacher working conditions impact teacher turnover? Retrieved from how-do-teacher-working.
What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance?
This item analyzes teacher reports of differing working condition issues and how they correlate to student achievement.
Keyworth, R. (2009). What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance? Retrieved from what-is-relationship-between900.
What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance?
This item analyzes teacher reports of working conditions how this correlates to student performance.
Keyworth, R. (2009). What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance? Retrieved from what-is-relationship-between901.
Does teacher induction impact teacher turnover for beginning teachers?
This analysis examines evidence on the influence of teacher induction programs on reducing teacher turnover.
Keyworth, R. (2010). Does teacher induction impact teacher turnover for beginning teachers? Retrieved from does-teacher-induction-impact884.
How Much Formal Training Do Teachers Get?
The analysis reviews school teacher earned degree data obtained from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) Digest of Education Statistics (2008).
Keyworth, R. (2010). How Much Formal Training Do Teachers Get? Retrieved from how-much-formal-training.
What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance?
This inquiry looks at the effect of time on the job and the quality of a teacher's skills.
Keyworth, R. (2010). What is the relationship between teacher working conditions and school performance? Retrieved from what-is-relationship-between882.
What is the status of experimental research on teacher induction?
This analysis reviews the quality of research on the effectiveness of teacher induction programs.
Keyworth, R. (2010). What is the status of experimental research on teacher induction? Retrieved from what-is-status-of.
How Do Teacher Turnover Rates Differ Among Schools With Different Percentages of Minority Students?
This piece analyzes data from National Center for Education Statistics to look at the impact of race on teacher attrition and mobility.
Keyworth, R. (2011). How Do Teacher Turnover Rates Differ Among Schools With Different Percentages of Minority Students? Retrieved from how-do-teacher-turnover898.
How Do Teacher Turnover Rates Differ Among Schools With Different Socio-Economic Conditions?
This inquiry analyzes data from National Center for Education Statistics to look at the impact of poverty on teacher attrition and mobility.
Keyworth, R. (2011). How Do Teacher Turnover Rates Differ Among Schools With Different Socio-Economic Conditions? Retrieved from how-do-teacher-turnover897.
How Has Percent of Teacher Turnover Changed Over Time?
This piece analyzes data from National Center for Education Statistics to look at trends in teacher turnover for public and private schools.
Keyworth, R. (2011). How Has Percent of Teacher Turnover Changed Over Time? Retrieved from how-has-percent-of.
How Has Teacher Turnover Changed Over Time?
This analysis lookes at data from National Center for Education Statistics to look at trends in teacher turnover.
Keyworth, R. (2011). How Has Teacher Turnover Changed Over Time? Retrieved from how-has-teacher-turnover.
What percentage of new teachers receive induction services?
This probe examines the increasing use of teacher induction as a tool for offering new teachers training and support.
Keyworth, R. (2011). What percentage of new teachers receive induction services? Retrieved from what-percentage-of-new.
Presentations
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Thirty years of Getting Teachers to be More Effective
This paper presents a model for building a school organizational culture that trains and supports teachers in an effective, efficient, and sustainable manner.
Fitch, S. (2013). Thirty years of Getting Teachers to be More Effective [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-suzanne-fitch.
ROKs: Remote Observation Kits
This paper presents a teacher coaching model using high quality audio and video technology to address the needs of teacher training in remote areas.
Hager, K. (2013). ROKs: Remote Observation Kits [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-karen-hager.
Effective Teaching Practices: Narrowing the Field
This paper distills the research on effective teaching practices to basic assumptions and core practices. It presents a impact-cost paradigm for rating and prioritizing such practices.
Heward, W. (2013). Effective Teaching Practices: Narrowing the Field [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-william-heward.
Teacher Professional Development
This paper reviewed the current research on best practices for teacher training, the current model for teacher training, and the gaps between research and practice.
Keyworth, R. (2013). Teacher Professional Development [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-redux-randy-keyworth.
Project AIM: Assess, Improve & Maintain Effective Teaching Practices
This paper shared a model for teacher assessment and professional development that address theneeds of large school districts in an effective and efficient manner.
Lewis, T. (2013). Project AIM: Assess, Improve & Maintain Effective Teaching Practices [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-teri-lewis.
From "Learning to Learn" to "Training to Teach": Changing the Culture of Teacher Preparation
This paper discusses the results of the National Council on Teacher Quality’s first nation-wide study of 2,420 university teacher preparation programs across 1,130 institutions.
McKee, A. (2014). From "Learning to Learn" to "Training to Teach": Changing the Culture of Teacher Preparation [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2014-wing-presentation-arthur-mckee.
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Learning About Learning: What Every New Teacher Needs to Know
This paper examines teacher education textbooks for discussion of research-based strategies that every teacher candidate should learn in order to promote student learning and retention.
Learning About Learning: What Every New Teacher Needs to Know Retrieved from http://www.nctq.org/dmsView/Learning_About_Learning_Report.
Teachers’ subject matter knowledge as a teacher qualification: A synthesis of the quantitative literature on students’ mathematics achievement
The main focus of this study is to find different kinds of variables that might contribute to variations in the strength and direction of the relationship by examining quantitative studies that relate mathematics teachers’ subject matter knowledge to student achievement in mathematics.
Ahn, S., & Choi, J. (2004). Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement. Online Submission.
Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement
The aim of this paper is to examine a variety of features of research that might account for mixed findings of the relationship between teachers' subject matter knowledge and student achievement based on meta-analytic technique.
Ahn, S., & Choi, J. (2004). Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement. Online Submission.
Distraction, privacy, and classroom design
Environmental features of elementary school classrooms are examined in relation to distraction and privacy. Teachers' adjustments of their activities to make their settings less distracting are also explored.
Ahrentzen, S., & Evans, G. W. (1984). Distraction, privacy, and classroom design. Environment and Behavior, 16(4), 437-454.
Is the three-term contingency trial a predictor of effective instruction?
Two experiments are reported which test the effect of increased three-term contingency trials on students' correct and incorrect math responses. The results warrant further research to test whether or not rates of presentation of three-term contingency trials are predictors of effective instruction.
Albers, A. E., & Greer, R. D. (1991). Is the three-term contingency trial a predictor of effective instruction?. Journal of Behavioral Education, 1(3), 337-354.
Critical issues in special education
This book is an analysis of important conceptual and practical issues that face special education professionals.
Algozzine, J. E., Thurlow, M., & Ysseldyke, J. E. (2000). Critical issues in special education.
The schools teachers leave: Teacher mobility in Chicago Public Schools.
In this report, we examine the degree to which teacher mobility is problematic in Chicago Public Schools (CPS) and look at the factors associated with high mobility rates, including teachers’ background characteristics, school structure, students’ characteristics, and workplace conditions.
Allensworth, E., Ponisciak, S., & Mazzeo, C. (2009). The schools teachers leave: teacher mobility in Chicago public schools. Consortium on Chicago School Research.
Not Prepared for Class: High-Poverty Schools Continue to Have Fewer In-Field Teachers.
As Secretary of Education from 1993 to 2001, Richard Riley had serious concerns about out-of-field teaching. The practice— which places in core academic classes instructors who have neither certification nor a major in the subject field taught— just didn’t make sense to him.
Almy, S., & Theokas, C. (2010). Not Prepared for Class: High-Poverty Schools Continue to Have Fewer In-Field Teachers. Education Trust.
The effectiveness of a technologically facilitated classroom-based early reading intervention.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of a classroom-teacher-delivered reading intervention for struggling readers called the Targeted Reading Intervention (TRI), designed particularly for kindergarten and first-grade teachers and their struggling students in rural, low-wealth communities.
Amendum, S. J., Vernon-Faegans, L. V., & Ginsberg, M. C. (2011). The effectiveness of a technologically facilitated classroom-based early reading intervention. The Elementary School Journal, 112, 107-131.
The Clinical Preparation of Teachers: A Policy Brief
This policy brief focuses on the clinical aspects of teacher preparation in each of these key features. These aspects include the typical processes of clinical work, the location, and the duration of the training.
American Association of Colleges for Teacher Education (AACTE). (2010). The clinical preparation of teachers: A policy brief. Washington, DC: Author.
Teachers Matter: Evidence from Value-Added Assessments.
Value-added assessment proves that very good teaching can boost student learning and that family background does not determine a student's destiny. Students taught by highly effective teachers several years in a row earn higher test scores than students assigned to particularly ineffective teachers.
American Education Research Association (AERA). (2004). Teachers matter: Evidence from value-added assessments. Research Points, 2(2). Retrieved from http://www.aera.net/ Portals/38/docs/Publications/Teachers%20Matter.pdf
ASA statement on using value-added models for educational assessment
Value-Added Models (VAMs) has been embraced by many states and school districts as part of educational accountability systems. Value-Added Assessment (VAA) Models attempt to estimate effects of individual teachers or schools on student achievement while accounting for differences in student background. This paper provides a summary of the American Statistical Associations analysis of the efficacy of value-added modeling in education.
American Statistical Association. (2014). ASA statement on using value-added models for educational assessment. Alexandria, VA.
Teacher evaluations: What is the issue and why does it matter? Policy snapshot
A report by TNTP finds 99 percent of teachers are rated good or great, confirming related findings that evaluation systems are not meaningfully differentiating teachers or providing useful feedback. TNTP recommends states use student growth as one measure of teacher effectiveness.
Aragon, S. (2018). Teacher Evaluations: What Is the Issue and Why Does It Matter? Policy Snapshot. Education Commission of the States.
Explicit Instruction: Effective and Efficient Teaching
This book gives special and general education teachers the tools to implement explicit instruction in any grade level or content area. The authors provide clear guidelines for identifying key concepts, skills, and routines to teach; designing and delivering effective lessons; and giving students opportunities to practice and master new material.
Archer, A., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Evaluating the impact of performance-related pay for teachers in England.
This paper evaluates the impact of a performance-related pay scheme for teachers in England.
Atkinson, A., Burgess, S., Croxson, B., Gregg, P., Propper, C., Slater, H., & Wilson, D. (2009). Evaluating the impact of performance-related pay for teachers in England. Labour Economics, 16(3), 251-261.
Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand.
This research objective was to study soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. The data were collected from 60 purposive samples of new teachers by interviewing and questionnaires. The results of this study were informed that new teachers have all of soft skills at high level totally. Communicative skills were highest among seven of soft skills and next Life-long learning and information management skills, Critical and problem solving skills, Team work skills, Ethics, moral and professional skills, Leadership skills and Innovation invention and development skills were lowest in all skills. Based on the research findings obtained, the sub-skills of seven soft skills will be considered and utilized in the package of teacher development program of next research.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010-1013.
Problems with the use of student test scores to evaluate teachers
There is also little or no evidence for the claim that teachers will be more motivated to improve student learning if teachers are evaluated or monetarily rewarded for student test score gains.
Baker, E. L., Barton, P. E., Darling-Hammond, L., Haertel, E., Ladd, H. F., Linn, R. L., ... & Shepard, L. A. (2010). Problems with the Use of Student Test Scores to Evaluate Teachers. EPI Briefing Paper# 278. Economic Policy Institute.
The Gates Foundation bet big on teacher evaluation. The report it commissioned explains how those efforts fell short.
Bad teachers were the problem; good teachers were the solution. It was a simplified binary, but the idea and the research it drew on had spurred policy changes across the country, including a spate of laws establishing new evaluation systems designed to reward top teachers and help weed out low performers. Behind that effort was the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which backed research and advocacy that ultimately shaped these changes.
Barnum, M. (2018, June 21). The Gates Foundation bet big on teacher evaluation. The report it commissioned explains how those efforts fell short. Chalkbeat.Retrieved from https://www.chalkbeat.org/posts/us/2018/06/21/the-gates-foundation-bet-big-on-teacher-evaluation-the-report-it-commissioned-explains-how-those-efforts-fell-short/
Finding your feedback strategies for designing and delivering performance feedback systems.
This article focuses on one method of follow-up: performance feedback
Barton, E. E., Kinder, K., Casey, A. M., & Artman, K. M. (2011). Finding your feedback fit: Strategies for designing and delivering performance feedback systems. Young Exceptional Children, 14(1), 29–46. doi: 10.1177/1096250610395459
Evaluating teacher preparation programs with teacher evaluation ratings: Implications for program accountability and improvement
The author uses teachers’ ratings on the North Carolina Educator Evaluation System to determine whether teacher preparation programs (TPPs) are associated with the evaluation ratings of their initially prepared teachers.
Bastian, K. C., Patterson, K. M., & Pan, Y. (2017). Evaluating teacher preparation programs with teacher evaluation ratings: Implications for program accountability and improvement. Journal of Teacher Education, 69(5), 429–447.
A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction model on children in fifth and sixth grades.
The later effects of the Direct Instruction Follow Through program were assessed at five diverse sites. Low-income fifth and sixth graders who had completed the full 3 years of this first- through third-grade program were tested on the Metropolitan Achievement Test (Intermediate level) and the Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT).
Becker, W. C., & Gersten, R. (1982). A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction Model on children in fifth and sixth grades. American Educational Research Journal, 19(1), 75-92.
Learning about teaching: Initial findings from the measures of effective teaching project
In fall 2009, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation launched the Measures of Effective Teaching (MET) project to test new approaches to measuring effective teaching. The goal of the MET project is to improve the quality of information about teaching effectiveness available to education professionals within states and districts.
Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. (2010). Learning about teaching: Initial findings from the measures of effective teaching project.Retrieved from https://docs.gatesfoundation.org/documents/preliminary-findings-research-paper.pdf
Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice
This is a review of the literature on classroom formative assessment. Several studies show firm evidence that innovations designed to strengthen the frequent feedback that students receive about their learning yield substantial learning gains.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice, 5(1), 7-74.
Conceptions of beginning teacher quality: Models for conducting research
In this paper, we consider traditions of research on teaching and how conceptions of good teaching evolved as traditions changed.
Blanton, L. P., Sindelar, P. T., Correa, V., Harman, M., McDonnell, J., & Kuhel, K. (2003). Conceptions of beginning teacher quality: Models for conducting research(COPSSE Doc. No. RS-6). Gainesville, FL: Center on Personnel Studies in Special Education (COPSSE), University of Florida.
Human characteristics and school learning
This paper theorizes that variations in learning and the level of learning of students are determined by the students' learning histories and the quality of instruction they receive.
Bloom, B. (1976). Human characteristics and school learning. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Houston ties teachers’ pay to test scores.
Over the objection of the teachers' union, the Board of Education here on Thursday unanimously approved the nation's largest merit pay program, which calls for rewarding teachers based on how well their students perform on standardizes tests.
Blumenthal, R. (2006). Houston ties teachers’ pay to test scores. New York Times, 13.
The narrowing gap in New York City teacher qualifications and its implications for student achievement in high-poverty schools.
By estimating the effect of teacher attributes using a value-added model, the analyses in this paper predict that observable qualifications of teachers resulted in average improved achievement for students in the poorest decile of schools of .03 standard deviations.
Boyd, D., Lankford, H., Loeb, S., Rockoff, J., & Wyckoff, J. (2008). The narrowing gap in New York City teacher qualifications and its implications for student achievement in high‐poverty schools. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management: The Journal of the Association for Public Policy Analysis and Management, 27(4), 793-818.
The role of teacher quality in retention and hiring: Using applications-to-transfer to uncover preferences of teachers and schools.
This study uses applications-to-transfer data to examine separately which teachers apply for transfer and which get hired and, in so doing, differentiates teachers from school preferences.
Boyd, D., Lankford, H., Loeb, S., Ronfeldt, M., & Wyckoff, J. (2010). The role of teacher quality in retention and hiring: Using applications-to-transfer to uncover preferences of teachers and schools. Working Paper No. 15966. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research. Retrieved from https://www.nber.org/papers/w15966.pdf
Organizing schools for improvement: Lessons from Chicago
The authors of this illuminating book identify a comprehensive set of practices and conditions that were key factors for improvement, including school leadership, the professional capacity of the faculty and staff, and a student-centered learning climate.
Bryk, A. S., Sebring, P. B., Allensworth, E., Easton, J. Q., & Luppescu, S. (2010). Organizing schools for improvement: Lessons from Chicago. University of Chicago Press.
Direct Instruction Reading
This book provide detailed information on how to systematically and explicitly teach essential reading skills. The procedures describe in this text have been shown to benefit all student, especially powerful with the most vulnerable learners, children who are at risk because of poverty, disability, or limited knowledge of English.
Carnine, D., Silbert, J., Kameenui, E. J., & Tarver, S. G. (1997). Direct instruction reading. Columbus, OH: Merrill.
The Performance Effect of Feedback Frequency and Detail: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Customer Satisfaction
This paper presents the results from a field experiment that examines the effects of nonfinancial performance feedback on the behavior of professionals working for an insurance repair company.
Casas‐Arce, P. A. B. L. O., Lourenço, S. M., & MARTÍNEZ‐JEREZ, F. A. (2017). The performance effect of feedback frequency and detail: Evidence from a field experiment in customer satisfaction. Journal of Accounting Research, 55(5), 1051-1088.
Buried Treasure: Developing a Management Guide From Mountains of School Data
This report provides a practical “management guide,” for an evidence-based key indicator data decision system for school districts and schools.
Celio, M. B., & Harvey, J. (2005). Buried Treasure: Developing A Management Guide From Mountains of School Data. Center on Reinventing Public Education.
Value-added measures: How and why the strategic data project uses them to study teacher effectiveness
This brief explains how and why Strategic Data Project (SDP) uses value-added measures for our diagnostic work. We also explain how value-added measures relate to other measures of teacher effectiveness and the limitations of value-added measures.
Center for Education Policy Research. (2011). Value-added measures: How and why the strategic data project uses them to study teacher effectiveness. Retrieved from https://hwpi.harvard.edu/files/sdp/files/sdp-va-memo_0.pdf
How much are districts spending to implement teacher evaluation systems: Case studies of Hillsborough County Public Schools, Memphis City Schools, and Pittsburgh Public Schools.
This report presents case studies of the efforts by three school districts, Hillsborough County Public Schools (HCPS), Memphis City Schools (MCS), and Pittsburgh Public Schools (PPS), to launch, implement, and operate new teacher evaluation systems as part of a larger reform effort called the Partnership Sites to Empower Effective Teaching.
Chambers, J., Brodziak de los Reyes, I., & O'Neil, C. (2013). How Much are Districts Spending to Implement Teacher Evaluation Systems?.
The Teacher's Craft: The 10 Essential Skills of Effective Teaching
This book provides evidence-based principles of effective teaching. College students preparing to teach, new teachers struggling to find their way, and experienced teachers eager to hone their skills will benefit from this set of commonsense principles that, when practiced together, will markedly improve student performance.
Chance, P. (2008). The teacher's craft: The 10 essential skills of effective teaching. Waveland PressInc.
The Long-Term Impacts Of Teachers: Teacher Value-Added And Student Outcomes In Adulthood
This paper examines the issue of efficacy of value-added measures in evaluating teachers. This question is important in understanding whether value-added analysis provides unbiased estimates of teachers’ impact on student achievement and whether these teachers improve long-term student outcomes.
Chetty, R., Friedman, J. N., & Rockoff, J. E. (2011). The long-term impacts of teachers: Teacher value-added and student outcomes in adulthood (No. w17699). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
Performance Feedback Overview
This overview examines the current understanding of research on performance feedback as a way to improve teacher performance and student outcomes.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2019). Overview of Performance Feedback. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-evaluation-feedback.
Teacher Preparation: Overview
The purpose of this overview is to provide information about the methods of teacher preparation, the current state of research on teacher preparation, challenges, trends, questions, and recommendations for those working to prepare teachers for success in the classroom.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2020). Overview of Teacher Preparation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-pre-service.
Qualifications and assignments of alternatively certified teachers: Testing core assumptions.
By analyzing data from the Schools and Staffing Survey, the authors empirically test four of the core assumptions embedded in current arguments for expanding alternative teacher certification (AC):
Cohen-Vogel, L., & Smith, T. M. (2007). Qualifications and assignments of alternatively certified teachers: Testing core assumptions. American Educational Research Journal, 44(3), 732-753.
Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education.
The purpose of this appear is to describe a school-wide staff development model that is based on a proactive instructional approach to solving problem behavior on a school-wide basis and utilizes effective staff development procedures.
Colvin, G., Kameenui, E. J., & Sugai, G. (1993). Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education. Education and treatment of children, 361-381.
Using active supervision and precorrection to improve transition behaviors in an elementary school
This study investigates the effect of a school-wide intervention plan, consisting of precorrection and active supervision strategies, on the social behavior of elementary students.
Colvin, G., Sugai, G., Good III, R. H., & Lee, Y. Y. (1997). Using active supervision and precorrection to improve transition behaviors in an elementary school. School Psychology Quarterly, 12(4), 344.
An Evaluation of Teachers Trained Through Different Routes to Certification, Final Report
The study compares the effectiveness of different routes to teaching. It finds there is no significant difference in the effectiveness of teachers who were traditionally trained when compared to teachers who obtained training through alternative credential programs.
Constantine, J., D. Player, T. Silva, K. Hallgren, M. Grider, and J. Deke, 2009. An Evaluation of Teachers Trained Through Different Routes to Certification, Final Report (NCEE 2009- 4043). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
Applied Behavior Analysis
This book is a comprehensive description of the principles and procedures for systematic change of socially significant behavior. It includes basic principles, applications, and behavioral research methods.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis.
Can teachers be evaluated by their students’ test scores? Should they be? The use of value-added measures for teacher effectiveness in policy and practice
In this report, the author aim to provide an accessible introduction to these new measures of teaching quality and put them into the broader context of concerns over school quality and achievement gaps.
Corcoran, S. P. (2010). Can Teachers Be Evaluated by Their Students' Test Scores? Should They Be? The Use of Value-Added Measures of Teacher Effectiveness in Policy and Practice. Education Policy for Action Series. Annenberg Institute for School Reform at Brown University (NJ1).
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
This is a meta-analysis that examines teacher-student relations impact on student performance. The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students.
Person-centered education is a counseling-originated, educational psychology model, overripe for meta-analysis, that posits that positive teacher-student relationships are associated with optimal, holistic learning. It includes classical, humanistic education and today’s constructivist learner-centered model.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
The proficiency illusion
The Proficiency Illusion reveals that the tests that states use to measure academic progress under the No Child Left Behind Act are creating a false impression of success, especially in reading and especially in the early grades.
Cronin, J., Dahlin, M., Adkins, D., & Kingsbury, G. G. (2007). The Proficiency Illusion. Thomas B. Fordham Institute.
Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching
The framework for teaching is a research-based set of components of instruction that are grounded in a constructivist view of learning and teaching. The framework defines four levels of performance--Unsatisfactory, Basic, Proficient, and Distinguished--for each element, providing a valuable tool that all teachers can use.
Danielson, C. (2007). Enhancing professional practice: A framework for teaching. ASCD.
Evaluations that help teachers learn.
This article addresses the topics of staff assessment, teacher supervision, and professional development.
Danielson, C. (2011). Evaluations that help teachers learn. Educational leadership, 68(4), 35-39.
Strengthening clinical preparation: The holy grail of teacher education.
This article outlines the challenges to creating productive clinical experiences for prospective teachers, and identifies strategies that have been found successful in confronting these challenges
Darling-Hammond, L. (2014). Strengthening clinical preparation: The holy grail of teacher education. Peabody Journal of Education, 89(4), 547-561.
Evaluating teacher evaluation: Popular modes of evaluating teachers are fraught with inaccuracies and inconsistencies
Popular modes of evaluating teachers are fraught with inaccuracies and inconsistencies, but the field has identified better approaches. Value-added models enable researchers to use statistical methods to measure changes in student scores over time while considering student characteristics and other factors often found to influence achievement.
Darling-Hammond, L., Amrein-Beardsley, A., Haertel, E., & Rothstein, J. (2012). Evaluating teacher evaluation: Popular modes of evaluating teachers are fraught with inaccuracies and inconsistencies, but the field has identified better approaches. Phi Delta Kappan, 93(6), 8–15.Retrieved from https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2012/03/01/kappan_hammond.html
Wanted: A national teacher supply policy for education: The right way to meet the “highly qualified teacher” challenge
The authors study the mal-distribution of teachers and examine its causes then describe examples of both states and local school districts that have fashioned successful strategies for strengthening their teaching forces.
Darling-Hammond, L., and Sykes, G. (2003). Wanted: A national teacher supply policy for education: The right way to meet the “highly qualified teacher” challenge. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 11(33), 1–55.
What research says about using value-added measures to evaluate teachers.
A growing number of researchers are studying whether value-added measures can do a good job of measuring the contribution of teachers to test score growth. Here I summarize a handful of analyses that shed light on two questions.
David, J. L. (2010). What research says about using value-added measures to evaluate teachers. Educational Leadership, 67(8), 81–82. Retrieved from http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational_leadership/may10/vol67/num08/Using_Value-Added_Measures_to_Evaluate_Teachers.aspx
A million new teachers are coming: Will they be ready to teach
Research shows that the most powerful, in-school influence on learning is the quality of instruction that teachers bring to their students. In the next decade, more than 1.5 million new teachers will be hired for our schools; unfortunately, teacher preparation programs may not be up to the task of delivering the teacher workforce we need, and critics have identified lax selection of teacher candidates, coursework disconnected from classroom practice, and weak clinical opportunities as indications that we are inadequately preparing teachers.
DeMonte, J. (2015). A Million New Teachers Are Coming: Will They Be Ready to Teach?. American Institutes for Research.
Treatment Integrity: Fundamental to Education Reform
To produce better outcomes for students two things are necessary: (1) effective, scientifically supported interventions (2) those interventions implemented with high integrity. Typically, much greater attention has been given to identifying effective practices. This review focuses on features of high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. (2014). Treatment integrity: Fundamental to education reform. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 13(2), 258-271.
Implementation Quality: Lessons Learned in the Context of the Head Start REDI Trial
This study uses data collected in the intervention classrooms of Head Start REDI (Research- based, Developmentally Informed), a randomized clinical trial testing the efficacy of a comprehensive preschool curriculum targeting children’s social-emotional competence, language, and emergent literacy skills delivered by teachers who received weekly coaching support.
Domitrovich, C. E., Gest, S. D., Jones, D., Gill, S., & DeRousie, R. M. S. (2010). Implementation quality: Lessons learned in the context of the Head Start REDI trial. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 25(3), 284-298.
How do principals really improve schools?
Principals are in a paradoxical position. On one hand, they're called on to use research-based strategies to improve student achievement. On the other, they're increasingly required to micromanage teachers by observing in classrooms and engaging in intensive evaluation. The authors point out that these two positions are at odds with each other.
Dufour, R., & Mattos, M. (2013). How Do Principals Really Improve Schools?. Educational Leadership, 70(7), 34-40.
Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement
This meta-analysis systematically synthesized results from 26 component studies, including dissertations and published articles, which reported at least one correlation between collective teacher efficacy and school achievement.
Eells, R. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement.
Effective Teaching Principles and the Design of Quality Tools for Educators
This monograph presents a synthesis of the literature on empirically supported effective teaching principles that have been derived from research on behavioral, cognitive, social-learning, and other theories.
Ellis, E. S., Worthington, L. A., & Larkin, M. J. (1994). research synthesis on effective teaching principles and the design of quality tools for educators.(Tech. Rep. No. 6). Eugene, OR: University of Oregon, National Center to Improve the Tools of Educators.
Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues
Classroom management is a topic of enduring concern for teachers, administrators, and the public. It consistently ranks as the first or second most serious educational problem in the eyes of the general public, and beginning teachers consistently rank it as their most pressing concern during their early teaching years. Management problems continue to be a major cause of teacher burnout and job dissatisfaction. Strangely, despite this enduring concern on the part of educators and the public, few researchers have chosen to focus on classroom management or to identify themselves with this critical field.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
Teacher quality and teacher mobility
Using matched student-teacher panel data from the state of Florida, the authors study the determinants of teacher job change and the impact of such mobility on the distribution of teacher quality.
Feng, L., & Sass, T. R. (2017). Teacher quality and teacher mobility. Education Finance and Policy, 12(3), 396–418.
Implementation Research: A Synthesis of the Literature
This is a comprehensive literature review of the topic of Implementation examining all stages beginning with adoption and ending with sustainability.
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blase, K. A., & Friedman, R. M. (2005). Implementation research: A synthesis of the literature.
Teacher Incentives and Student Achievement: Evidence from New York City Public Schools
This article describes a school-based randomized trial in over 200 New York City public schools designed to better understand the impact of teacher incentives.
Fryer, R. G. (2013). Teacher incentives and student achievement: Evidence from New York City public schools. Journal of Labor Economics, 31(2), 373-407.
Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis
In this meta-analysis of studies that utilize formative assessment the authors report an effective size of .7.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199-208.
Validity of High-School Grades in Predicting Student Success beyond the Freshman Year: High-School Record vs. Standardized Tests as Indicators of Four-Year College Outcomes
High-school grades are often viewed as an unreliable criterion for college admissions, owing to differences in grading standards across high schools, while standardized tests are seen as methodologically rigorous, providing a more uniform and valid yardstick for assessing student ability and achievement. The present study challenges that conventional view. The study finds that high-school grade point average (HSGPA) is consistently the best predictor not only of freshman grades in college, the outcome indicator most often employed in predictive-validity studies, but of four-year college outcomes as well.
Geiser, S., & Santelices, M. V. (2007). Validity of High-School Grades in Predicting Student Success beyond the Freshman Year: High-School Record vs. Standardized Tests as Indicators of Four-Year College Outcomes. Research & Occasional Paper Series: CSHE. 6.07. Center for studies in higher education.
The academic quality of prospective teachers: The impact of admissions and licensure testing.
This study examined the academic and demographic profile of the pool of prospective teachers and then explored how this profile is affected by teacher testing.
Gitomer, D. H., Latham, A. S., & Ziomek, R. (1999). The academic quality of prospective teachers: The impact of admissions and licensure testing. Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service. Retrieved from http://www.ets.org/Media/Research/pdf/RR-03-35.pdf
Approaches to Evaluating Teacher Effectiveness: A Research Synthesis
This research synthesis examines how teacher effectiveness is currently measured (i.e., formative vs. summative evaluation).
Goe, L., Bell, C., & Little, O. (2008). Approaches to Evaluating Teacher Effectiveness: A Research Synthesis. National Comprehensive Center for Teacher Quality.
A Practical Guide to Designing Comprehensive Teacher Evaluation Systems: A Tool to Assist in the Development of Teacher Evaluation Systems
This guide is a tool designed to assist states and districts in constructing high-quality teacher evaluation systems in an effort to improve teaching and learning.
Goe, L., Holdheide, L., & Miller, T. (2011). A Practical Guide to Designing Comprehensive Teacher Evaluation Systems: A Tool to Assist in the Development of Teacher Evaluation Systems. National Comprehensive Center for Teacher Quality.
A survey of principles instructors: Why lecture prevails.
This paper confirms the predominance of lecture and adds to the existing literature by asking why principles instructors have selected their particular teaching methods.
Goffe, W. L., & Kauper, D. (2014). A survey of principles instructors: Why lecture prevails. The Journal of Economic Education, 45(4), 360-375.
The mystery of good teaching
Who should be recruited to fill the two to three million K–12 teaching positions projected to come open during the next decade? What kinds of knowledge and training should these new recruits have? These are the questions confronting policymakers as a generation of teachers retires at the same time that the so-called baby boom echo is making its way through the education system.
Goldhaber, D. (2002). The mystery of good teaching. Education next, 2(1), 50-55.
In school, teacher quality matters most. Education Next
FIFTY YEARS after the release of "Equality of Educational Opportunity"--widely known as the Coleman Report--much of what James Coleman and his colleagues reported holds up well to scrutiny. It is, in fact, remarkable to read through the 700-plus pages and see how little has changed about what the empirical evidence says matters. The report's conclusions about the importance of teacher quality, in particular, have stood the test of time, which is noteworthy, given that today's studies of the impacts of teachers use more-sophisticated statistical methods and employ far better data.
Goldhaber, D. (2016). In schools, teacher quality matters most: today's research reinforces Coleman's findings. Education Next, 16(2), 56-63.
Can teacher quality be effectively assessed?
In this paper, we describe the results of the first large-scale study, based on a unique data set from North Carolina, assessing the relationship between the certification of teachers by the National Board for Professional Teaching Standards (NBPTS) and elementary level student achievement
Goldhaber, D., & Anthony, E. (2004). Can teacher quality be effectively assessed? Seattle, WA: Center on Reinventing Public Education, Daniel J. Evans School of Public Affairs, University of Washington. https://m.cedr.us/papers/value/2007-Can%20Teacher%20Quality.pdf
Is it just a bad class? Assessing the stability of measured teacher performance.
This paper report on work estimating the stability of value-added estimates of teacher effects, an important area of investigation given that new workforce policies implicitly assume that effectiveness is a stable attribute within teachers.
Goldhaber, D., & Hansen, M. (2012). Is It Just a Bad Class? Assessing the Long-Term Stability of Estimated Teacher Performance. Working Paper 73. National Center for Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Education Research.
Public Accountability and Nudges: The Effect of an Information Intervention on the Responsiveness of Teacher Education Programs to External Ratings
This paper provides the first empirical examination of National Council on Teacher Quality (NCTQ) ratings, beginning with a descriptive overview of the ratings and documentation of how they evolved from 2013-2016, both in aggregate and for programs with different characteristics.
Goldhaber, D., & Koedel, C. (2019). Public Accountability and Nudges: The Effect of an Information Intervention on the Responsiveness of Teacher Education Programs to External Ratings. American Educational Research Journal, 0002831218820863.
Teacher career paths, teacher quality, and persistence in the classroom: Are public schools keeping their best?
In this paper we examine the mobility of early-career teachers of varying quality, measured using value-added estimates of teacher performance.
Goldhaber, D., Gross, B., & Player, D. (2011). Teacher career paths, teacher quality, and persistence in the classroom: Are public schools keeping their best?. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, 30(1), 57-87.
Uneven Playing Field? Assessing the Teacher Quality Gap Between Advantaged and Disadvantaged Students
In this study, we present a comprehensive, descriptive analysis of the inequitable distribution of both input and output measures of teacher quality across various indicators of student disadvantage across all school districts in Washington State.
Goldhaber, D., Lavery, L., & Theobald, R. (2015). Uneven playing field? Assessing the teacher quality gap between advantaged and disadvantaged students. Educational researcher, 44(5), 293-307.
Identifying effective teachers using performance on the job
This paper provide some recommendations to increase the pool of potential teachers, make it tougher to award tenure to those who perform least well, and reward effective teachers who are willing to work in schools serving large numbers of low-income, disadvantaged children.
Gordon, R., Kane, T. J., & Staiger, D. O. (2006). Identifying Effective Teachers Using Performance on the Job. The Hamilton Project Policy Brief No. 2006-01. Brookings Institution.
Measurable change in student performance: Forgotten standard in teacher preparation?
This paper describe a few promising assessment technologies tat allow us to capture more direct, repeated, and contextually based measures of student learning, and propose an improvement-oriented approach to teaching and learning.
Greenwood, C. R., & Maheady, L. (1997). Measurable change in student performance: Forgotten standard in teacher preparation?. Teacher Education and Special Education, 20(3), 265-275.
Undue process: Why bad teachers in twenty-five diverse districts rarely get fired
Is dismissing poorly performing teachers truly feasible in America today? After all the political capital (and real capital) spent on reforming teacher evaluation, can districts actually terminate ineffective teachers who have tenure or have achieved veteran status?
Griffith, D., & McDougald, V. (2016). Undue process: Why bad teachers in twenty-five diverse districts rarely get fired. Washington DC: Thomas B. Fordham Institute. Retrieved from http://edex. s3-us-west-2. amazonaws. com/publication/pdfs, 2812, 29.
Principal effectiveness and principal turnover.
This study investigate the association between principal effectiveness and principal turnover using longitudinal data from Tennessee, a state that has invested in multiple measures of principal performance through its educator evaluation system.
Grissom, J. A., & Bartanen, B. (2019a). Principal effectiveness and principal turnover. Education Finance and Policy, 14(3), 355–382. Retrieved from https://www.mitpressjournals.org/doi/full/10.1162/edfp_a_00256
Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies
To assess the effect of “metacognitive” instruction on reading comprehension, 20 studies, with a total student population of 1,553, were compiled and quantitatively synthesized. In this compilation of studies, metacognitive instruction was found particularly effective for junior high students (seventh and eighth grades). Among the metacognitive skills, awareness of textual inconsistency and the use of self-questioning as both a monitoring and a regulating strategy were most effective. Reinforcement was the most effective teaching strategy.
Haller, E. P., Child, D. A., & Walberg, H. J. (1988). Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies. Educational researcher, 17(9), 5-8.
Teacher characteristics and gains in student achievement: Estimation using micro-data.
The major objective of this data analysis was to estimate the relationship between variables which can be controlled by public policy and educational output.
Hanushek, E. A. (1971). Teacher characteristics and gains in student achievement: Estimation using micro data. American Economic Review, 61(2), 280-288.
Teacher Deselection.
This discussion provides a quantitative statement of one approach to achieving the governors’ (and the nation’s) goals – teacher deselection.
Hanushek, E. A. (2009). Teacher deselection. Creating a new teaching profession, 168, 172-173.
Teacher Quality
This chapter of Handbook of The Economics of Education reviews research on teacher labor markets, the importance of teacher quality in the determination of student achievement, and the extent to which specific observable characteristics often related to hiring decisions and salary explain the variation in the quality of instruction.
Hanushek, E. A., & Rivkin, S. G. (2006). Teacher quality. In E. A. Hanushek & F. Welch (Eds.), Handbook of the economics of education, vol. 2 (pp. 1051–1078). Amsterdam, Netherlands: North Holland.
Generalizations about using value-added measures of teacher quality.
The precise method of attributing differences in classroom achievement to teachers is the
subject of considerable discussion and analysis.
Hanushek, E. A., & Rivkin, S. G. (2010). Generalizations about using value-added measures of teacher quality. American Economic Review, 100(2), 267-71.
The Value of Smarter Teachers: International Evidence on Teacher Cognitive Skills and Student Performance
This new research addresses a number of critical questions: Are a teacher’s cognitive skills a good predictor of teacher quality? This study examines the student achievement of 36 developed countries in the context of teacher cognitive skills. This study finds substantial differences in teacher cognitive skills across countries that are strongly related to student performance.
Hanushek, E. A., Piopiunik, M., & Wiederhold, S. (2014). The value of smarter teachers: International evidence on teacher cognitive skills and student performance (No. w20727). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Teacher training, teacher quality and student achievement
The authors study the effects of various types of education and training on the ability of teachers to promote student achievement.
Harris, D. N., & Sass, T. R. (2011). Teacher training, teacher quality and student achievement. Journal of Public Economics, 95(7–8), 798-812.
Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Visible learning
This influential book is the result of 15 years research that includes over 800 meta-analyses on the influences on achievement in school-aged students. This is a great resource for any stakeholder interested in conducting a serious search of evidence behind common models and practices used in schools.
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning. A synthesis of over, 800.
Visible Learning for Teachers: Maximizing Impact on Learning
This book takes over fifteen years of rigorous research into education practices and provides teachers in training and in-service teachers with concise summaries of the most effective interventions and offers practical guidance to successful implementation in classrooms.
Hattie, J. (2012). Visible learning for teachers: Maximizing impact on learning. Routledge.
Visible Learning Insights
Offering a concise introduction into the ‘Visible Learning Story’, the book provides busy teachers with a guide to why the Visible Learning research is so vital and the difference it can make to learning outcomes.
Hattie, J., & Zierer, K. (2019). Visible Learning Insights. Routledge.
Teacher evaluation as a policy target for improved student learning: A fifty-state review of statute and regulatory action since NCLB
This paper reports on the analysis of state statutes and department of education regulations in fifty states for changes in teacher evaluation in use since the passage of No Child Left Behind Act of 2001.
Hazi, H. M., & Rucinski, D. A. (2009). Teacher evaluation as a policy target for improved student learning: A fifty-state review of statute and regulatory action since NCLB. education policy analysis archives, 17, 5.
Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die
This book reveal the anatomy of ideas that stick and explain ways to make ideas stickier, such as applying the human scale principle, using the Velcro Theory of Memory, and creating curiosity gaps. Along the way, we discover that sticky messages of all kinds draw their power from the same six traits.
Heath, C., & Heath, D. (2007). Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die. Random House.
Impact of performance feedback delivered via electronic mail on preschool teachers’ use of descriptive praise.
This paper examined the effects of a professional development intervention that included data-based performance feedback delivered via electronic mail (e-mail) on preschool teachers’ use of descriptive praise and whether increased use of descriptive praise was associated with changes in classroom-wide measures of child engagement and challenging behavior.
Hemmeter, M. L., Snyder, P., Kinder, K., & Artman, K. (2011). Impact of performance feedback delivered via electronic mail on preschool teachers’ use of descriptive praise. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 26(1), 96-109.
Learning from teacher observations: Challenges and opportunities posed by new teacher evaluation systems
This article discusses the current focus on using teacher observation instruments as part of new teacher evaluation systems being considered and implemented by states and districts.
Hill, H., & Grossman, P. (2013). Learning from teacher observations: Challenges and opportunities posed by new teacher evaluation systems. Harvard Educational Review, 83(2), 371-384.
Teacher turnover and teacher shortages: An organizational analysis
This paper investigates organizational characteristics and conditions in schools that drive staffing problems and teacher turnover.
Ingersoll, R. (2001). Teacher turnover and teacher shortages: An organizational analysis. American Educational Research Journal, 38(3), 499-534.
A quarter century of changes in the elementary and secondary teaching force: From 1987 to 2012
This report utilizes the nationally representative Schools and Staffing Survey (SASS) to examine changes in the elementary and secondary teaching force in the United States over the quarter century from 1987–88 to 2011–12.
Ingersoll, R. M. (2017). A Quarter Century of Changes in the Elementary and Secondary Teaching Force: From 1987 to 2012-Statistical Analysis Report.
The impact of induction and mentoring programs for beginning teachers: A critical review of the research
This review critically examines 15 empirical studies, conducted since the mid1980s, on the effects of support, guidance, and orientation programs—collectively known as induction—for beginning teachers.
Ingersoll, R. M., & Strong, M. (2011). The impact of induction and mentoring programs for beginning teachers: A critical review of the research. Review of educational research, 81(2), 201-233.
Seven trends: The transformation of the teaching force—updated October 2018
This report summarizes the results of an exploratory research project that investigated what trends and changes have, or have not, occurred in the teaching force over the past three decades.
Ingersoll, R. M., Merrill, E., Stuckey, D., & Collins, G. (2018). Seven Trends: The Transformation of the Teaching Force–Updated October 2018.
Is the supply of mathematics and science teachers sufficient?
This study seeks to empirically ground the debate over mathematics/science teacher shortages, and evaluate the extent to which there is, or is not, a sufficient supply of teachers in these fields.
Ingersoll, R., & Perda, D. A. (2010). Is the supply of mathematics and science teachers sufficient? American Educational Research Journal, 43(3), 563–594.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Focusing the new design: The NAEP 1988 technical report
The 1988 NAEP surveyed American students' knowledge of reading, writing, civics, U.S. history, and geography.
Johnson, E. G., & Zwick, R. (1990). Focusing the new design: The NAEP 1988 technical report. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Studies, 17,95–109.
Who stays in teaching and why: A review of the literature on teacher retention
The Literature Review considers research that provides insight into problems of teacher shortage and turnover, offers a comprehensive explanation for why some able teachers leave the classroom prematurely, and suggests current strategies for increasing retention rates.
Johnson, S. M., Berg, J. H., & Donaldson, M. L. (2005). Who stays in teaching and why?: A review of the literature on teacher retention. Project on the Next Generation of Teachers, Harvard Graduate School of Education.
How context matters in high-need schools: The effects of teachers’ working conditions on their professional satisfaction and their students’ achievement.
the authors build on this body of work by further examining how working conditions predict both teachers‘ job satisfaction and their career plans.
Johnson, S. M., Kraft, M. A., & Papay, J. P. (2012). How context matters in high-need schools: The effects of teachers’ working conditions on their professional satisfaction and their students’ achievement. Teachers College Record, 114(10), 1-39.
Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions
Demonstrates the experimenting society model using data-based decision making and collaborative consultation to evaluate behavior-management intervention strategies in 25 seventh graders. Each intervention results in improved behavior, but active teaching of classroom rules was determined to be most effective.
Johnson, T. C., Stoner, G., & Green, S. K. (1996). Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions. School Psychology Review, 25(2), 199-214.
Training Teachers to Use Environmental Arrangement and Milieu Teaching with Nonvocal Preschool Children
This study investigated the effects of training preschool teachers to use environmental arrangement and milieu teaching in interactions with children using augmented communication systems. Three teachers were taught seven environmental strategies and four milieu teaching procedures through written materials, lecture, modeling, role-playing, and feedback.
Kaiser, A. P., Ostrosky, M. M., & Alpert, C. L. (1993). Training teachers to use environmental arrangement and milieu teaching with nonvocal preschool children. Journal of the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps, 18(3), 188-199.
Estimating teacher impacts on student achievement: An experimental evaluation
This study used a random-assignment experiment in Los Angeles Unified School District to evaluate various non-experimental methods for estimating teacher effects on student test scores. Having estimated teacher effects during a pre-experimental period, the authors used these estimates to predict student achievement following random assignment of teachers to classrooms.
Kane, T. J., & Staiger, D. O. (2008). Estimating teacher impacts on student achievement: An experimental evaluation (No. w14607). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Gathering Feedback for Teaching: Combining High-Quality Observations with Student Surveys and Achievement Gains.
This report presents an in-depth discussion of the analytical methods and findings from the Measures of Effective Teaching (MET) project’s analysis of classroom observations.1 A nontechnical companion report describes implications for policymakers and practitioners.
Kane, T. J., & Staiger, D. O. (2012). Gathering Feedback for Teaching: Combining High-Quality Observations with Student Surveys and Achievement Gains. Research Paper. MET Project. Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
What does certification tell us about teacher effectiveness? Evidence from New York City
The authors use six years of data on student test performance to evaluate the effectiveness of certified, uncertified, and alternatively certified teachers in the New York City public schools. This study also evaluates turnover among teachers with different certification status and the impact on student achievement of hiring teachers with predictably high turnover
Kane, T. J., Rockoff, J. E., & Staiger, D. O. (2008). What does certification tell us about teacher effectiveness? Evidence from New York City. Economics of Education review, 27(6), 615-631.
Identifying effective classroom practices using student achievement data
This paper combines information from classroom-based observations and measures of teachers' ability to improve student achievement as a step toward addressing these challenges. The results point to the promise of teacher evaluation systems that would use information from both classroom observations and student test scores to identify effective teachers.
Kane, T. J., Taylor, E. S., Tyler, J. H., & Wooten, A. L. (2011). Identifying effective classroom practices using student achievement data. Journal of human Resources, 46(3), 587-613.
Teacher retention: Evidence to inform policy
This policy brief summarizes the available evidence on the policy relevant factors that affect teacher turnover.
Katz, V. (2018). Teacher retention: Evidence to inform policy. Charlottesville, VA: University of Virginia.
Identifying Specific Learning Disability: Is Responsiveness to Intervention the Answer?
Responsiveness to intervention (RTI) is being proposed as an alternative model for making decisions about the presence or absence of specific learning disability. The author argue that there are many questions about RTI that remain unanswered, and radical changes in proposed regulations are not warranted at this time.
Kavale, K. A. (2005). Identifying specific learning disability: Is responsiveness to intervention the answer?. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 38(6), 553-562.
Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Does teaching experience increase teacher effectiveness? A review of the research
The goal of this paper is to provide researchers and policymakers with a comprehensive and timely review of this body of work.
Kini, T., & Podolsky, A. (2016). Does teaching experience increase teacher effectiveness? A review of the research. Palo Alto, CA: Learning Policy Institute. Retrieved from https://learningpolicyinstitute.org/sites/default/files/product-files/Teaching_Experience_Report_June_2016.pdf
The Effects of Feedback Interventions on Performance: A Historical Review, a Meta-Analysis, and a Preliminary Feedback Intervention Theory
The authors proposed a preliminary FI theory (FIT) and tested it with moderator analyses. The central assumption of FIT is that FIs change the locus of attention among 3 general and hierarchically organized levels of control: task learning, task motivation, and meta-tasks (including self-related) processes.
Kluger, A. N., & DeNisi, A. (1996). The effects of feedback interventions on performance: A historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychological bulletin, 119(2), 254.
High-Impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching.
This book offers strategies that make a difference in student learning including: content planning, instructional practices, and community building.
Knight, J. (2013). High-impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching. Corwin Press.
Teacher layoffs, teacher quality, and student achievement: Evidence from a discretionary layoff policy.
This study present some of first evidence on the implementation and subsequent effect of discretionary layoff policies, by studying the 18th largest public school district in the nation, Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools (CMS).
Kraft, M. A. (2013). Teacher Layoffs, Teacher Quality and Student Achievement: The Implementation and Consequences of a Discretionary Reduction-in-Force Policy. Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness.
Teacher layoffs, teacher quality, and student achievement: Evidence from a discretionary layoff policy.
This study present some of first evidence on the implementation and subsequent effect of discretionary layoff policies, by studying the 18th largest public school district in the nation, Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools (CMS).
Kraft, M. A. (2013). Teacher Layoffs, Teacher Quality and Student Achievement: The Implementation and Consequences of a Discretionary Reduction-in-Force Policy. Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness.
School organizational contexts, teacher turnover, and student achievement: Evidence from panel data
This study is among the first to address the empirical limitations of prior studies on organizational contexts by leveraging one of the largest survey administration efforts ever conducted in the United States outside of the decennial population census.
Kraft, M. A., Marinell, W. H., & Shen-Wei Yee, D. (2016). School organizational contexts, teacher turnover, and student achievement: Evidence from panel data. American Educational Research Journal, 53(5), 1411-1449.
Teachers’ perceptions of their working conditions: How predictive of planned and actual teacher movement?
This quantitative study examines the relationship between teachers’ perceptions of their working conditions and their intended and actual departures from schools.
Ladd, H. F. (2011). Teachers’ perceptions of their working conditions: How predictive of planned and actual teacher movement?. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 33(2), 235-261.
The impact of feedback frequency on learning and task performance: Challenging the “more is better” assumption.
This paper challenge the “more is better” assumption and propose that frequent feedback can overwhelm an individual’s cognitive resource capacity, thus reducing task effort and producing an inverted-U relationship with learning and performance over time.
Lam, C. F., DeRue, D. S., Karam, E. P., & Hollenbeck, J. R. (2011). The impact of feedback frequency on learning and task performance: Challenging the “more is better” assumption. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 116(2), 217-228.
Social skills instruction for students at risk for
antisocial behavior: The effects of small-group instruction.
This study examined the effectiveness of social skills instruction for seven elementary-age students at risk for antisocial behavior who were unresponsive to a school wide primary intervention program
Lane, K. L., Wehby, J., Menzies, H. M., Doukas, G. L., Munton, S. M., & Gregg, R. M. (2003). Social skills instruction for students at risk for antisocial behavior: The effects of small-group instruction. Behavioral Disorders, 28(3), 229-248.
Examining the validity of ratings from a classroom observation instrument for use in a district’s teacher evaluation system
The purpose of this study was to examine the validity of teacher evaluation scores that are derived from an observation tool, adapted from Danielson's Framework for Teaching, designed to assess 22 teaching components from four teaching domains.
Lash, A., Tran, L., & Huang, M. (2016). Examining the Validity of Ratings from a Classroom Observation Instrument for Use in a District's Teacher Evaluation System. REL 2016-135. Regional Educational Laboratory West.
Changes in teacher education: The Holy Grail of quality
The Teacher Education Committee at Northwestern Oklahoma State University approved the development of a competency-based teacher education program. A subcommittee identified and wrote professional education competencies which students should master prior to program completion.
Lehr, M. (1981). Changes in Teacher Education: The Holy Grail of Quality.
Reading on grade level in third grade: How is it related to high school performance and college enrollment.
This study uses longitudinal administrative data to examine the relationship between third- grade reading level and four educational outcomes: eighth-grade reading performance, ninth-grade course performance, high school graduation, and college attendance.
Lesnick, J., Goerge, R., Smithgall, C., & Gwynne, J. (2010). Reading on grade level in third grade: How is it related to high school performance and college enrollment. Chicago: Chapin Hall at the University of Chicago, 1, 12.
Cost-effectiveness and educational policy.
This article provides a summary of measuring the fiscal impact of practices in education
educational policy.
Levin, H. M., & McEwan, P. J. (2002). Cost-effectiveness and educational policy. Larchmont, NY: Eye on Education.
Teacher quality: A report on the preparation and qualifications of public school teachers.
This report is based on efforts by the National Center for Education Statistics to collect data on teacher preparation and qualifications using a nationally representative survey of full-time public school teachers whose main teaching assignment is in English/language arts, social studies/social sciences, foreign language, mathematics, or science (or who teach a self-contained classroom).
Lewis, L., Parsad, B., Carey, N., Bartfai, N., Farris, E., & Smerdon, B. (1999). Teacher quality: A report on the preparation and qualifications of public school teachers. NCES 1999-080. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/pubs99/1999080.pdf
The effects of social skills instruction on the social behaviors of students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders
The authors examined the effects of pullout small-group and teacher-directed classroom-based social skills instruction on the social behaviors of five third- and fourth-grade students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders.
Lo, Y. Y., Loe, S. A., & Cartledge, G. (2002). The effects of social skills instruction on the social behaviors of students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 27(4), 371-385.
How teaching conditions predict teacher turnover in California schools.
Using California teacher survey data linked to district data on salaries and staffing patterns, this study examines a range of school conditions as well as demographic factors and finds that high levels of school turnover are strongly affected by poor working conditions and low salaries, as well as by student characteristics.
Loeb, S., & Luczak, L. D. H. (2013). How Teaching Conditions Predict: Teacher Turnover in California Schools. In Rendering School Resources More Effective (pp. 48-99). Routledge.
Principal Preferences and the Uneven Distribution of Principals Across Schools
The authors use longitudinal data from one large school district to investigate the distribution of principals across schools. They find that schools serving many low-income, non-White, and low-achieving students have principals who have less experience and less education and who attended less selective colleges. This distribution of principals is partially driven by the initial match of first-time principals to schools, and it is exacerbated by systematic attrition and transfer away from these schools.
Loeb, S., Kalogrides, D., & Horng, E. L. (2010). Principal preferences and the uneven distribution of principals across schools. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 32(2), 205-229.
Who stays and who leaves? Findings from a three-part study of teacher turnover in NYC middle schools
This research summary focuses on aspects of the study’s results that are likely to be most useful for policymakers and school leaders as they strive to maintain and manage an effective teacher workforce.
Marinell, W. H., & Coca, V. M. (2013). " Who Stays and Who Leaves?" Findings from a Three-Part Study of Teacher Turnover in NYC Middle Schools. Online Submission.
A behavioral analysis of effective teaching.
Characterizes classroom instruction (CRI) from a behavior analytic perspective. It is argued that effective teaching strategies also serve managerial functions through the development of stimulus control and the management of behavioral choice.
Martens, B. K., & Kelly, S. Q. (1993). A behavioral analysis of effective teaching. School Psychology Quarterly, 8(1), 10.
A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
This research synthesis examines instructional research in a functional manner to provide guidance for classroom practitioners.
Marzano, R. J. (1998). A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
The two purposes of teacher evaluation
Over one year, the author asked more than 3,000 educators their opinions about these two basic purposes by presenting them with a scale that has five values.
Marzano, R. J. (2012). Teacher Evaluation: What’s fair? What’s effective? The two purposes of teacher evaluation. Educational Leadership, 70(3), 14–19. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Effective supervision: Supporting the art and science of teaching
The authors show school and district-level administrators how to set the priorities and support the practices that will help all teachers become expert teachers. Their five-part framework is based on what research tells us about how expertise develops.
Marzano, R. J., Frontier, T., & Livingston, D. (2011). Effective supervision: Supporting the art and science of teaching. Ascd.
Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher
How does classroom management affect student achievement? What techniques do
teachers find most effective? How important are schoolwide policies and practices in setting
the tone for individual classroom management? In this follow-up to What Works in Schools,
Robert J. Marzano analyzes research from more than 100 studies on classroom
management to discover the answers to these questions and more. He then applies these
findings to a series of" Action Steps"--specific strategies.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Classroom Instruction That Works: Research Based Strategies For Increasing Student Achievement
This is a study of classroom management on student engagement and achievement.
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Ascd
Multiple effects of home and daycare crowding.
This research examines the relationship between noise and preschool children's acquisition of prereading skills, environmental factors in preschool inclusive classrooms, and children's use of outdoorplay equipment.
Maxwell, L. E. (1996). Multiple effects of home and day care crowding. Environment and Behavior, 28(4), 494-511.
The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs.
This study provides a description of 34 practicing teachers' beliefs regarding the role of empathy as an attribute in their effectiveness with culturally diverse students. Empathy involves cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that teachers believed were manifested in their practice.
McAllister, G., & Irvine, J. J. (2002). The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs. Journal of teacher education, 53(5), 433-443.
Alternative student growth measures for teacher evaluation: Implementation experiences of early-adopting districts
This study examines implementation of alternative student growth measures in a sample of eight school districts that were early adopters of the measures. It builds on an earlier Region al Educational Laboratory Mid-Atlantic report that described the two types of alternative student growth measures—alternative assessment–based value-added models and student learning objectives—in the early-adopting districts.
McCullough, M., English, B., Angus, M. H., & Gill, B. (2015). Alternative student growth measures for teacher evaluation: Implementation experiences of early-adopting districts (No. 8a9dfcb1bc6143608448114ea9b69d06). Mathematica Policy Research.
What is the purpose of teacher evaluation today? A conversation between Bellwether and Fordham.
In December 2016, Bellwether Education Partners and The Thomas B. Fordham Institute independently released two reports centered on teacher evaluation and its consequences. Both reports offer a glimpse into ongoing challenges and opportunities with teacher evaluation reform, but they have very different analyses.
McDougald, V., Griffith, D., Pennington, K., & Mead, S. (2016). What is the purpose of teacher evaluation today? A conversation between Bellwether and Fordham. Retrieved from https://edexcellence.net/articles/what-is-the-purpose-of-teacher-evaluation-today-a-conversation-between-bellwether-and
Effective teaching: A review of instructional and environmental variables.
this chapter is based on the following premise: that variables operative in the classroom environment, such as the specific behaviors of the teacher and the manner in which the classroom is arranged (e.g., seating arrangement, noise level), influence student behavior and student learning
McKee, W. T., & Witt, J. C. (1990). Effective teaching: A review of instructional and environmental variables.
Improving education through standards-based reform.
This report offers recommendations for the implementation of standards-based reform and outlines possible consequences for policy changes. It summarizes both the vision and intentions of standards-based reform and the arguments of its critics.
McLaughlin, M. W., & Shepard, L. A. (1995). Improving Education through Standards-Based Reform. A Report by the National Academy of Education Panel on Standards-Based Education Reform. National Academy of Education, Stanford University, CERAS Building, Room 108, Stanford, CA 94305-3084..
The supply of and demand for special education teachers: A review of research regarding the chronic shortage of special education teachers
This article provides an analysis of factors influencing the supply of and demand for special education teachers
McLeskey, J., Tyler, N. C., & Saunders Flippin, S. (2004). The supply of and demand for special education teachers: A review of research regarding the chronic shortage of special education teachers. The Journal of Special Education, 38(1), 5-21.
The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes.
The constituent parts of a five component behavioural intervention package are described and the effect of the intervention on the on‐task behaviour of two “disruptive” secondary school classes reported.
McNamara, E., Evans, M., & Hill, W. (1986). The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 56(2), 209-215.
Providing Teachers with Performance Feedback on Praise to Reduce Student Problem Behavior
This study examined the effect of a visual performance feedback intervention (i.e., a simple, computer-generated line graph) on teachers' rate of praise for students' academic and behavioral performance and subsequent changes in students' rates of problem behavior.
Mesa, J., Lewis-Palmer, T., & Reinke, W. (2005). Providing Teachers with Performance Feedback on Praise to Reduce Student Problem Behavior. Beyond Behavior, 15(1), 3-7.
Ensuring Equitable Access to Strong Teacher: Important Elements of an Effective State Action Plan
This short guide, based on what we have learned from two decades of work on this issue, provides a few ideas on what could be included in a good plan. Our recommendations are grouped into three categories: Analyze, Build, and Create.
Metz, R. (2015). Ensuring Equitable Access to Strong Teachers: Important Elements of an Effective State Action Plan. Education Trust.
Validity research on teacher evaluation systems based on the framework for teaching.
This paper summarizes validity evidence pertaining to several different implementations of the Framework. It is based primarily on reviewing the published and unpublished studies that have looked at the relationship between teacher evaluation ratings made using systems based on the Framework and value-added measures of teacher effectiveness.
Milanowski, A. T. (2011). Validity Research on Teacher Evaluation Systems Based on the Framework for Teaching. Online Submission.
Recruiting and Retaining High-Quality Teachers in Rural Areas
In examining recruitment and retention of teachers in rural areas, David Monk begins by noting the numerous possible characteristics of rural communities—small size, sparse settlement, distance from population concentrations, and an economic reliance on agricultural industries that are increasingly using seasonal and immigrant workers to minimize labor costs.
Monk, D. H. (2007). Recruiting and retaining high-quality teachers in rural areas. Future of Children, 17(1), 155–174.
The Use of Weekly Performance Feedback to Increase Teacher Implementation of a Pre-referral Academic Intervention.
This study evaluated the effects of performance feedback on the implementation of a classroom intervention.
Mortenson, B. P., & Witt, J. C. (1998). The use of weekly performance feedback to increase teacher implementation of a prereferral academic intervention. School Psychology Review, 613-627.
Training Head Start Teachers to Use Incidental Teaching
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of group inservice training plus written and verbal feedback on four Head Start teachers’ use of incidental teaching.
Mudd, J. M., & Wolery, M. (1987). Training head start teachers to use incidental teaching. Journal of the Division for Early Childhood, 11(2), 124-134.
Do charter schools alleviate the negative effect of teacher
Using data on charter and public school districts in Texas, the authors test the hypothesis that the labor practices in charter schools, in particular, their ability to easily dismiss poorly performing teachers, diminishes the negative effect of teacher turnover on student achievement and graduation rates in comparison to public schools.
Naslund, K., & Ponomariov, B. (2019). Do charter schools alleviate the negative effect of teacher turnover? Management in Education, 33(1), 11–20.
The condition of education 2018: Characteristics of public school teachers
National Center for Education Statistics. U.S. Department of Education presents the data of public school teachers who held a postbaccalaureate degree, public school teachers who held the certificate, and the year of experience.
National Center for Education Statistics. U.S. Department of Education. (2018b). The condition of education 2018: Characteristics of public school teachers. NCES 2018-144. Retrieved from https://nces.ed.gov/fastfacts/display.asp?id=58
Empowered educators: How high-performing systems shape teaching quality around the world
This book examines seven jurisdictions that have worked to develop comprehensive teaching policy systems: Singapore and Finland, the states of New South Wales and Victoria in Australia, the provinces of Alberta and Ontario in Canada, and the province of Shanghai in China.
National Center on Education and the Economy. (2016). Empowered educators: How high-performing systems shape teaching quality around the world. Washington, DC: Author.
Status of the American Public School Teacher, 2000-2001.
This report presents the results of the 2000-01 Status of the American Public School Teacher survey. This survey has been conducted every 5 years since 1956
National Education Association. (2003). Status of the American public school teacher, 2000-2001. NEA Professional Library.
Report of the National Reading Panel. Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction: Reports of the subgroups
This report present the panel’s conclusions, an indication of the readiness for application in the classroom of the results of this research, and, if appropriate, a strategy for rapidly disseminating this information to facilitate effective reading instruction in the schools.
National Reading Panel. (2000). Report of the National Reading Panel. Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction: Reports of the subgroups(NIH Publication No. 00-4754). Washington, DC: U. S. Government Printing Office.
Teacher turnover in organizational context: Staffing stability in Los Angeles charter, magnet, and regular public schools
Prior research on teacher turnover focused mostly on whether or not and who leaves. This research builds on and extends prior studies by investigating not only whether and who but also when a teacher leaves. The phenomenon of this study emphasizes the dynamic nature of teacher exit.
Newton, X., Rivero, R., Fuller, B., & Dauter, L. (2018). Teacher turnover in organizational context: Staffing stability in Los Angeles charter, magnet, and regular public schools. Teachers College Record, 120(3), 1–36.
Who Knows if our Teachers are Prepared? Three Different Perspectives on Graduates' Instructional Readiness and the Features of Preservice Preparation that Predict them
This study follows 305 preservice teachers (PSTs) who student taught in Chicago Public Schools (CPS) in 2014-15 and were subsequently hired in CPS in 2015-16.
Ngang, T. K., Yunus, H. M., & Hashim, N. H. (2015). Soft skills integration in teaching professional training: Novice teachers’ perspectives. Procedia-social and behavioral sciences, 186, 835-840.
How large are teacher effects?
This research use data from a four-year experiment in which teachers and students were randomly assigned to classes to estimate teacher effects on student achievement.
Nye, B., Konstantopoulos, S., & Hedges, L. V. (2004). How large are teacher effects? Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 26(3),237–257.
How large are teacher effects? Educational Evaluation and Policy
The authors use data from a four-year experiment in which teachers and students were randomly assigned to classes to estimate teacher effects on student achievement. Teacher effects are estimated as between-teacher (but within-school) variance components of achievement status and residualized achievement gains.
Nye, N., Konstantopoulos, S., & Hedges, L. (2004). How large are teacher effects? Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 26(3), 237–257. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3102/01623737026003237
Teacher classroom management practices: Effects on disruptive or aggressive student behavior.
This Campbell systematic review examines the effect of multi‐component teacher classroom management programmes on disruptive or aggressive student behaviour and which management components are most effective.
Oliver, R. M., Wehby, J. H., & Reschly, D. J. (2011). Teacher classroom management practices: Effects on disruptive or aggressive student behavior. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 7(1), 1-55.
Lessons from PISA for the United States–Strong performers and successful reformers in education
US President Obama has launched one of the world’s most ambitious education reform agendas. Under the heading “Race to the Top”, this agenda encourages US states to adopt internationally benchmarked standards and assessments that prepare students for success in college and the workplace: recruit, develop, reward, and retain effective teachers and principals.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2011). Lessons from PISA for the United States–Strong performers and successful reformers in education. OECD Publishing. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264096660-en
Why are private-school teachers paid less than public-school teachers?
One explanation: The working conditions are better in private schools, so instructors are willing to take a salary cut.
Orlin, B. (2013, October 24). Why are private-school teachers paid less than public-school teachers? The Atlantic. Retrieved from https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2013/10/why-are-private-school-teachers-paid-less-than-public-school-teachers/280829/
Meeting the highly qualifed teachers challenge: The secretary’s annual report on teacher quality.
Under the 1998 reauthorization of Title II of the Higher Education Act, the secretary of education is required to issue annual reports to Congress on the state of teacher quality nationwide. "Meeting the Highly Qualified Teachers Challenge" is the inaugural report on this important issue.
Paige, R. (2002). Meeting the Highly Qualified Teachers Challenge: The Secretary's Annual Report on Teacher Quality. US Department of Education.
The challenge of teacher retention in urban schools: Evidence in variation from a cross-site analysis
Applying consistent data practices and analytical techniques to administrative data sets from 16 urban districts, the authors document substantial cross-district variation in teacher retention rates. They also explore the influence of temporary leaves of absence and cross-district, within-state movement on retention estimates.
Papay, J. P., Bacher-Hicks, A., Page, L. A., & Marinell, W. H. (2017). The challenge of teacher retention in urban schools: Evidence in variation from a cross-site analysis. Educational Researcher, 46(8), 434–448.
What to Make of Declining Enrollment in Teacher Preparation Programs
This policy report provides a look at the decline in the enrollment of American teacher preparation programs, along with potential consequences for schools and the student they serve.
For good measure? Teacher evaluation policy in the ESSA era.
As states and districts consider potential changes to their teacher evaluation systems and policies, this paper seeks to inform those efforts by reviewing the evolution of the teacher evaluation policy movement over the last several years, identifying positive outcomes of new systems and negative consequences, and describing risks that should be considered.
Pennington, K., & Mead, S. (2016). For good measure? Teacher evaluation policy in the ESSA era. Washington, DC: Bellwether Education Partners. Retrieved from https://bellwethereducation.org/publication/good-measure-teacher-evaluation-policy-essa-era
Teacher inequality: How poor and minority students are shortchanged on teacher quality
This report provides new information on the impact of teacher quality on student achievement and offers specific steps states should take to remedy the persistent practice of denying the best teachers to the children who need them the most.
Peske, H. G., & Haycock, K. (2006). Teacher inequality: How poor and minority students are shortchanged on teacher quality. Retrieved from The Education Trust website: http:// www.edtrust.org/dc/publication/teaching-inequality-how-poor-and-minority-students-areshortchanged-on-teacher-qualit
Teacher evaluation: A comprehensive guide to new directions and practices
This handbook advocates a new approach to teacher evaluation as a cooperative effort undertaken by a group of professionals.
Peterson, K. D. (2000). Teacher evaluation: A comprehensive guide to new directions and practices. Corwin Press.
Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us
In this provocative and persuasive new book, the author asserts that the secret to high performance and satisfaction-at work, at school, and at home—is the deeply human need to direct our own lives, to learn and create new things, and to do better by ourselves and our world.
Pink, D. H. (2011). Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us. Penguin.
The supply and demand for rural teachers.
The purpose of this paper is to summarize what we know about the current state of rural teacher labor markets by contrasting them with the same data from urban, suburban, and large and small town settings.
Player, D. (2015). The supply and demand for rural teachers. Rural Opportunities Consortium of Idaho. Retrieved from http://www.rociidaho.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/ROCI_2015_RuralTeachers_FINAL.pdf
Teacher compensation systems in the United States K–12 public school system.
This paper provides a review of the current teacher compensation system and examines the structure of teacher compensation in the U.S. K-12 public education system.
Podgursky, M., & Springer, M. (2011). Teacher compensation systems in the United States K-12 public school system. National Tax Journal, 64(1), 165.
Solving the Teacher Shortage: How to Attract and Retain Excellent Educators
This report reviews an extensive body of research on teacher recruitment and retention, and identifies five major factors that influence a teacher’s decision to enter, remain in, or leave the teaching profession, generally, and high-need schools, specifically.
Podolsky, A., Kini, T., Bishop, J., & Darling-Hammond, L. (2016). Solving the teacher shortage: How to attract and retain excellent educators. Palo Alto, CA: Learning Policy Institute.
Instructional alignment as a measure of teacher quality.
This article is the first to explore the extent to which teachers’ instructional alignment is associated with their contributions to student learning and their effectiveness on new composite evaluation measures using data from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation’s Measures of Effective Teaching study.
Polikoff, M. S, & Porter, A. C. (2014). Instructional alignment as a measure of teacher quality. Education Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 64(3), 212–225. Retrieved from http://www.aera.net/Newsroom/Recent-AERA-Research/Instructional-Alignment-as-a-Measure-of-Teaching-Quality
Linking professional development, teacher outcomes, and student achievement: The case of a learner-centered mathematics program for elementary school teachers.
This study examined the influence of three year-long cohorts of elementary school teachers' participating in a learner-centered mathematics professional development program.
Polly, D., McGee, J., Wang, C., Martin, C., Lambert, R., & Pugalee, D. K. (2015). Linking professional development, teacher outcomes, and student achievement: The case of a learner-centered mathematics program for elementary school teachers. International Journal of Educational Research, 72, 26–37. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883035515000282
Career paths of beginning school teachers: Results for the first through fifth waves of the 2007–08 Beginning Teacher Longitudinal Study
This report examines the career paths of beginning public school teachers and how these career paths vary by characteristics during the teachers' first year of teaching and most recent year of teaching.
Raue, K., & Gray, L. (2015). Career Paths of Beginning Public School Teachers: Results from the First through Fifth Waves of the 2007-08 Beginning Teacher Longitudinal Study. Stats in Brief. NCES 2015-196. National Center for Education Statistics.
A teacher like me: A review of the effect of student-teacher racial/ethnic matching on teacher perceptions of students and student academic and behavioral outcomes
Underlying this research is the belief that the cultural fit between students and teachers has the potential to improve a child’s academic and nonacademic performance in school.
Redding, C. (2019). A Teacher Like Me: A Review of the Effect of Student–Teacher Racial/Ethnic Matching on Teacher Perceptions of Students and Student Academic and Behavioral Outcomes. Review of Educational Research, 0034654319853545.
New evidence on the frequency of teacher turnover: Accounting for within-year turnover.
Teacher turnover occurs during and at the end of the school year, although documentation of within-year turnover currently rests on anecdotal evidence.
Redding, C., & Henry, G. T. (2018). New evidence on the frequency of teacher turnover: Accounting for within-year turnover. Educational Researcher, 47(9), 577-593.
Leaving school early: An examination of novice teachers’ within- and end-of-year turnover
This research use data from North Carolina to measure teacher turnover monthly throughout the entire year and conduct an analysis of their persistence to examine the differences in early career teacher turnover.
Redding, C., & Henry, G. T. (2019). Leaving school early: An examination of novice teachers’ within-and end-of-year turnover. American Educational Research Journal, 56(1), 204-236.
Easy in, easy out: Are alternatively certified teachers turning over at increased rates?
The authors report on descriptive evidence of growing differences in the characteristics of alternatively and traditionally certified teachers and the schools in which they teach.
Redding, C., & Smith, T. M. (2016). Easy in, easy out: Are alternatively certified teachers turning over at increased rates?. American Educational Research Journal, 53(4), 1086-1125.
Motivational interviewing for effective management: The classroom check-up.
This book focuses on helping K-12 teachers increase their use of classroom management strategies that work. The Classroom Check-Up is a step-by-step model for assessing teachers' organizational, instructional, and behavior management practices; helping them develop a menu of intervention options; and overcoming obstacles to change.
Reinke, W. M., Lewis-Palmer, T., & Martin, E. (2007). The effect of visual performance feedback on teacher behavior-specific praise. Behavior Modifications, 31(3), 247–263.
Teachers, schools, and academic achievement.
This paper disentangles the impact of schools and teachers in influencing achievement with special attention given to the potential problems of omitted or mismeasured variables and of student and school selection.
Rivkin, S. G., Hanushek, E. A., & Kain, J. F. (2005). Teachers, schools, and academic achievement. Econometrica, 73(2), 417-458.
Stay or go? Turnover in CMO, EMO and regular charter schools.
We examine whether working conditions in different types of charter schools lead to different levels of teacher turnover.
Roch, C. H., & Sai, N. (2018). Stay or go? Turnover in CMO, EMO and regular charter schools. The Social Science Journal, 55(3), 232-244.
How are they now? Longer term effects of eCoaching through online bug-in-ear technology.
In this study, using mixed methods, we investigated the longer term effects of eCoaching through advanced online bug-in-ear (BIE) technology.
Rock, M. L., Schumacker, R. E., Gregg, M., Howard, P. W., Gable, R. A., & Zigmond, N. (2014). How are they now? Longer term effects of e coaching through online bug-in-ear technology. Teacher Education and Special Education, 37(2), 161-181.
The impact of individual teachers on student achievement: Evidence from panel data
In order to provide accurate estimates of how much teachers affect the achievement of their students, this study used panel data covering over a decade of elementary student test scores and teacher assignment in two contiguous New Jersey school districts.
Rockoff, J. E. (2004). The impact of individual teachers on student achievement: Evidence from panel data. American economic review, 94(2), 247-252.
Review of research on the impact of beginning teacher induction on teacher quality and retention.
The objective in this review was to summarize and critique empirical research on the impact of beginning teacher induction on teacher retention and teacher quality (particularly studies in which teacher effectiveness was evaluated by using student achievement measures).
Rogers, M., Lopez, A., Lash, A., Schaffner, M., Shields, P., & Wagner, M. (2004). Review of research on the impact of beginning teacher induction on teacher quality and retention.
Does cooperating teachers’ instructional effectiveness improve preservice teachers’ future performance?
Increasingly, states and teacher education programs are establishing minimum requirements for cooperating teachers’ (CTs’) years of experience or tenure. Undergirding these policies is an assumption that to effectively mentor preservice teachers (PSTs), CTs must themselves be instructional effective. The authors test this assumption using statewide administrative data on nearly 2,900 PSTs mentored by over 3,200 CTs.
Ronfeldt, M., Brockman, S. L., & Campbell, S. L. (2018). Does cooperating teachers’ instructional effectiveness improve preservice teachers’ future performance. Educational Researcher, 47(7), 405–418.
How teacher turnover harms student achievement
This study used a version of value added modeling to evaluate the impact of teacher turnover has on student achievement.
Ronfeldt, M., Lankford, H., Loeb, S., & Wyckoff, J. (2011). How Teacher Turnover Harms Student Achievement. National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series, No. 17176. doi:10.3386/w17176
Maximizing the effectiveness of structured classroom management programs: Implementing rule-review procedures with disruptive and distractible students.
The present study assessed the relative strength of daily rule review and rehearsal on student behavior when such procedures were added to a token economy. The token program was designed to increase appropriate classroom behaviors of disruptive boys attending a multi categorical resource room.
Rosenberg, M. S. (1986). Maximizing the effectiveness of structured classroom management programs: Implementing rule-review procedures with disruptive and distractible students. Behavioral Disorders, 11(4), 239-248.
Teacher quality in educational production: Tracking, decay, and student achievement.
The author develop falsification tests for three widely used VAM specifications, based on the idea that future teachers cannot influence students' past achievement.
Rothstein, J. (2010). Teacher quality in educational production: Tracking, decay, and student achievement. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 125(1), 175-214.
Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
The Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System determines the effectiveness of school systems, schools, and teachers based on student academic growth over time. Research conducted utilizing data from the TVAAS database has shown that race, socioeconomic level, class size, and classroom heterogeneity are poor predictors of student academic growth. Rather, the effectiveness of the teacher is the major determinant of student academic progress.
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
The Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System determines the effectiveness of school systems, schools, and teachers based on student academic growth over time. Research conducted utilizing data from the TVAAS database has shown that race, socioeconomic level, class size, and classroom heterogeneity are poor predictors of student academic growth. Rather, the effectiveness of the teacher is the major determinant of student academic progress.
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
Teacher and Classroom Context Effects on Student Achievement: Implications for Teacher Evaluation.
This study examined the relative magnitude of teacher effects on student achievement while simultaneously considering the in¯uences of intraclassroom heterogeneity, student achievement level, and class size on academic growth.
Sanders, W. L., Wright, S. P., & Horn, S. P. (1997). Teacher and classroom context effects on student achievement: Implications for teacher evaluation. Journal of Personnel Evaluation and Education, 11(1), 57–67.
Teacher evaluation: A conceptual framework and examples of country practices.
This paper proposes a conceptual framework to analyze teacher evaluation. It elaborates on the main components of a comprehensive teacher evaluation model and explains the main aspects to be taken into account for designing a teacher evaluation model.
Santiago, P., & Benavides, F. (2009). Teacher evaluation: A conceptual framework and examples of country practices.Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Teacher evaluation: An issue overview.
Teacher evaluations matter a lot—both to teachers and to those holding them accountable. But how can schools measure the performance of all teachers fairly? And what should they do with the results?
Sawchuk, S. (2015). Teacher evaluation: An issue overview. Education Week, 35(3), 1-6.
Teacher Evaluation
Teacher evaluation can be a very sensitive topic for teachers and program administrators alike. Evaluations need to be fair and relevant to both teachers and programs.
Sayavedra, M. (2014). Teacher evaluation. ORTESOL Journal, 31, 1–9.
The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness
This book looks at research and theoretical models used to define educational effectiveness with the intent on providing educators with evidence-based options for implementing school improvement initiatives that make a difference in student performance.
Scheerens, J. and Bosker, R. (1997). The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness. Oxford:Pergmon
Training support staff to embed teaching within natural routines of young children with disabilities in an inclusive preschool.
This paper evaluated a program for training 4 support staff to embed instruction within the existing activities of 5 children with disabilities in an inclusive preschool.
Schepis, M. M., Reid, D. H., Ownbey, J., & Parsons, M. B. (2001). Training support staff to embed teaching within natural routines of young children with disabilities in an inclusive preschool. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 34(3), 313-327.
Description and effects of prosocial instruction in an elementary physical education setting.
The purpose of this article was to describe the developmental effects of one elementary physical education teacher's proactive teaching of prosocial behavior. An ABA (B) design coupled with a control group comparison across six matched urban physical education classes was used to assess the teaching strategy.
Sharpe, T., Crider, K., Vyhlidal, T., & Brown, M. (1996). Description and effects of prosocial instruction in an elementary physical education setting. Education & Treatment of Children, 19(4), 435.
Teacher evaluation: Guide to professional practice.
This book is organized around four dominant interrelated core issues: professional standards, a guide to applying the Joint Committee's Standards, ten alternative models for the evaluation of teacher performance, and an analysis of these selected models.
Shinkfield, A. J., & Stufflebeam, D. L. (2012). Teacher evaluation: Guide to effective practice (Vol. 41). Springer Science & Business Media.
Teachers coaching teachers
This article describe teachers coaching teaching including the purpose, process, who should coach, and the effects of the coaching.
Showers, B. (1985). Teachers coaching teachers. Educational leadership, 42(7), 43-48.
Teacher Turnover in High-Poverty Schools: What We Know and Can Do
This paper reviews evidence from six recent studies, which collectively suggest that teachers who leave high-poverty schools are not fleeing their students, but rather the poor working conditions that make it difficult for them to teach and their students to learn. They include school leadership, collegial relationships, and elements of school culture.
Simon, N. S., & Johnson, S. M. (2013). Teacher turnover in high-poverty schools: What we know and can do. Teachers College Record, 117, 1-36
Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a systematic literature search to identify evidence-based classroom management practices.
Simonsen, B., Fairbanks, S., Briesch, A., Myers, D., & Sugai, G. (2008). Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice. Education and Treatment of Children, 31(3), 351-380.
A grounded theory of behavior management strategy selection, implementation, and perceived effectiveness reported by first-year elementary teachers.
In this grounded theory study, 19 teachers were interviewed and then, in constant comparative fashion, the interview data were analyzed. The theoretical model that emerged from the data describes novice teachers' tendencies to select and implement differing strategies related to the severity of student behavior.
Smart, J. B., & Igo, L. B. (2010). A grounded theory of behavior management strategy selection, implementation, and perceived effectiveness reported by first-year elementary teachers. The Elementary School Journal, 110(4), 567-584.
Barriers to the Preparation of Highly Qualified Teachers in Reading. TQ Research & Policy Brief.
This paper pointed out three prominent points of impact in addressing the poor performance of America’s fourth-graders on national examinations of reading proficiency.
Smartt, S. M., & Reschly, D. J. (2007). Barriers to the Preparation of Highly Qualified Teachers in Reading. TQ Research & Policy Brief. National Comprehensive Center for Teacher Quality.
The effect of performance feedback on teachers’ treatment integrity: A meta-analysis of the single-case literature.
The current study extracted and aggregated data from single-case studies that used Performance feedback (PF) in school settings to increase teachers' use of classroom-based interventions.
Solomon, B. G., Klein, S. A., & Politylo, B. C. (2012). The effect of performance feedback on teachers' treatment integrity: A meta-analysis of the single-case literature. School Psychology Review, 41(2).
The Hidden Cost of Teacher Turnover
This study asks how schools respond to spells of high teacher turnover, and assesses organizational and human capital losses in terms of the changing composition of the teacher pool.
Sorensen, L. C., & Ladd, H. F. (2018). The hidden costs of teacher turnover. Working Paper No. 203-0918-1. Washington, DC: National Center for Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Education Research (CALDER). Retrieved from https://caldercenter.org/publications/hidden-costs-teacher-turnover
Teacher pay for performance: Experimental evidence from the project on incentives in teaching
This paper presents the results of a rigorous experiment examining the impact of pay for performance on student achievement and instructional practice.
Springer, M. G., Ballou, D., Hamilton, L., Le, V. N., Lockwood, J. R., McCaffrey, D. F., ... & Stecher, B. M. (2011). Teacher Pay for Performance: Experimental Evidence from the Project on Incentives in Teaching (POINT). Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness.
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Improving teaching effectiveness: Final report: The intensive partnerships for effective teaching through 2015–2016
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation launched the Intensive Partnerships for Effective Teaching initiative. The initiative's goal is dramatic gains in student achievement, graduation rates, and college-going, especially for LIM students.
Stecher, B. M., Garet, M. S., Hamilton, L. S., Steiner, E. D., Robyn, A., Poirier, J., ... & de los Reyes, I. B. (2016). Improving Teaching Effectiveness: Implementation: The Intensive Partnerships for Effective Teaching Through 2013–2014. Rand Corporation.
Does teacher evaluation improve school performance? Experimental evidence from Chicago’s Excellence in Teaching project
Chicago Public Schools initiated the Excellence in Teaching Project, a teacher evaluation program designed to increase student learning by improving classroom instruction through structured principal–teacher dialogue.
Steinberg, M. P., & Sartain, L. (2015). Does teacher evaluation improve school performance? Experimental evidence from Chicago’s Excellence in Teaching project. Education Finance and Policy, 10(4), 535–572.
Implementing Tier 2 social behavioral interventions: Current issues, challenges, and promising approaches.
The purpose of this special issue is to address current issues, challenges, and promising approaches for providing Tier 2 behavioral interventions in school settings. Articles solicited for this issue address gaps in the literature and implementation needs and challenges specifically for Tier 2.
Stormont, M., & Reinke, W. M. (2013). Implementing Tier 2 social behavioral interventions: Current issues, challenges, and promising approaches. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 29(2), 121-125.
Teacher Quality Index
This book examines issues pertaining to making effective hiring decisions. The authors present a research-based interview protocol built on quality indicators.
Stronge, J. and Hindman, J., (2006). Teacher Quality Index. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Explaining the gap in charter and traditional public school teacher turnover rates
This study uses national survey data to examine why charter school teachers are more likely to turnover than their traditional public school counterparts.
Stuit, D. A., & Smith, T. M. (2012). Explaining the gap in charter and traditional public school teacher turnover rates. Economics of Education Review, 31(2), 268-279.
A coming crisis in teaching? Teacher supply, demand, and shortages in the US
Recent media reports of teacher shortages across the country are confirmed by the analysis of several national datasets reported in this brief. Shortages are particularly severe in special education, mathematics, science, and bilingual/English learner education, and in locations with lower wages and poorer working conditions. Shortages are projected to grow based on declines in teacher education enrollments, coupled with student enrollment growth, efforts to reduce pupil-teacher ratios, and ongoing high attrition rates.
Sutcher, L., Darling-Hammond, L., & Carver-Thomas, D. (2016). A coming crisis in teaching? Teacher supply, demand, and shortages in the US. Washington, DC: Learning Policy Institute. Available at: https://learningpolicyinstitute. org/sites/default/files/product-files/A_Coming_Crisis_in_Teaching_REPORT. pdf.
Understanding Teacher Shortages: An Analysis of Teacher Supply and Demand in the United States
This paper reviews the sources of and potential solutions to teacher shortages in the United States. It describes the sources of current and projected increases in teacher demand relative to enrollments, shift in pupil-teacher rations, and attrition.
Sutcher, L., Darling-Hammond, L., & Carver-Thomas, D. (2019). Understanding Teacher Shortages: An Analysis of Teacher Supply and Demand in the United States. education policy analysis archives, 27(35).
Effect on varying rates of behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of students with EBD.
This study has 2 purposes: examine the effect of an observation-feedback intervention on the rate of a teacher's behavior-specific praise of students with emotional and behavioral disorders (EBD) and the effect of increased rates of a teacher's behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of a class of students with EBD.
Sutherland, K. S., Wehby, J. H., & Copeland, S. R. (2000). Effect of varying rates of behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of students with EBD. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 8(1), 2-8.
Building special education teacher capacity in rural schools: Impact of a Grow Your Own program
The purpose of this study was to determine the extent to which a grow your own (GYO) program equitably increased special education teacher capacity in one Southern state's rural and non-rural school districts.
Sutton, J. P., Bausmith, S. C., O'connor, D. M., Pae, H. A., & Payne, J. R. (2014). Building special education teacher capacity in rural schools: Impact of a grow your own program. Rural Special Education Quarterly, 33(4), 14-23.
The effect of real-time visual performance feedback on teacher feedback: A preliminary investigation.
This study explored the effects of visual performance feedback (VPF) delivered in real-time using screen sharing technology on a discrete teacher practice (i.e., positive feedback) for four general education teachers in a middle school using a multiple baseline across teachers design.
Sweigart, C. A., Landrum, T. J., & Pennington, R. C. (2015). The effect of real-time visual performance feedback on teacher feedback: A preliminary investigation. Education and Treatment of Children, 38(4), 429-450.
A comprehensive model for estimating the impact of teacher turnover.
The purpose of this study was to develop a model that may be used to estimate the financial costs of teacher turnover in urban school districts.
Synar, E., & Maiden, J. (2012). A comprehensive model for estimating the financial impact of teacher turnover. Journal of Education Finance, 130-144.
Soft skills integration in teaching professional training: Novice teachers’ perspectives.
This paper is part of a bigger research project and focuses on issues related to soft skills and teaching professional training. The purpose of this paper is to explore the extent of soft skills that has been integrated in teaching professional training from the novice teachers’ perspectives.
Tang, K. N., Yunus, H. M., & Hashim, N. H. (2015). Soft skills integration in teaching professional training: Novice teachers’ perspectives. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 186, 835–840.
The effect of evaluation on teacher performance.
This paper offers evidence that evaluation can shift the teacher effectiveness distribution through a different mechanism: by improving teacher skill, effort, or both in ways that persist long-run.
Taylor, E. S., & Tyler, J. H. (2012). The effect of evaluation on teacher performance. American Economic Review, 102(7), 3628-51.
Can teacher evaluation improve teaching? Evidence of systematic growth in the effectiveness of mid-career teachers.
In the research reported here, the authors study one approach to teacher evaluation: practice-based assessment that relies on multiple, highly structured classroom observations conducted by experienced peer teachers and administrators.
Taylor, E. S., & Tyler, J. H. (2012a). Can teacher evaluation improve teaching? Evidence of systematic growth in the effectiveness of mid-career teachers. Education Next, 12(4), 79–84. Retrieved from http://educationnext.org/can-teacher-evaluation-improve-teaching/
Generating hypotheses about the function of student problem behavior by observing teacher behavior
We examined whether, as predicted by research on child effects, we could generate hypotheses about the function of student problem behavior by observing the amount of attention teachers provided to students.
Taylor, J. C., & Romanczyk, R. G. (1994). Generating hypotheses about the function of student problem behavior by observing teacher behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27(2), 251-265.
Teacher Evaluation 2.0.
This report proposes six design standards that any rigorous and fair teacher evaluation system should meet. It offers a blueprint for better evaluations that can help every teacher succeed in the classroom—and give every student the best chance at success.
The New Teacher Project. (2010). Teacher Evaluation 2.0.New York, NY: Author.
Rush to judgment: Teacher evaluation in public education
The authors examine the causes and consequences of the status of teacher evaluation and its implications for the current national debate about performance pay for teachers. The report also examines a number of national, state, and local evaluation systems that offer potential alternatives to current practice.
Toch, T., & Rothman, R. (2008). Rush to Judgment: Teacher Evaluation in Public Education. Education Sector Reports. Education Sector.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Keeping RTI on track: How to identify, repair and prevent mistakes that derail implementation
Keeping RTI on Track is a resource to assist educators overcome the biggest problems associated with false starts or implementation failure. Each chapter in this book calls attention to a common error, describing how to avoid the pitfalls that lead to false starts, how to determine when you're in one, and how to get back on the right track.
Vanderheyden, A. M., & Tilly, W. D. (2010). Keeping RTI on track: How to identify, repair and prevent mistakes that derail implementation. LRP Publications.
Live webcam coaching to help early elementary classroom teachers provide effective literacy instruction for struggling readers: The Targeted Reading Intervention
This study evaluated whether the Targeted Reading Intervention (TRI), a classroom teacher professional development program delivered through webcam technology literacy coaching, could provide rural classroom teachers with the instructional skills to help struggling readers progress rapidly in early reading.
Vernon-Feagans, L., Kainz, K., Hedrick, A., Ginsberg, M., & Amendum, S. (2013). Live webcam coaching to help early elementary classroom teachers provide effective literacy instruction for struggling readers: The Targeted Reading Intervention. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(4), 1175.
Promoting special educator teacher retention: A critical review of the literature
This article is a critical review of the literature on special education teacher attrition and retention. The research focused on journal articles from 2004 to present.
Vittek, J. E. (2015). Promoting special educator teacher retention: A critical review of the literature. Sage Open, 5(2), 2158244015589994.
Productive teaching
This literature review examines the impact of various instructional methods
Walberg H. J. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.) New directions for teaching, practice, and research (pp. 75-104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Effects of teacher induction on beginning teachers’ teaching: A critical review of the literature
Drawing on literature since 1997, this review explores the effects of teacher induction on beginning teachers' conceptions and practice of teaching, and it identifies three approaches to understanding such effects, as found in the literature.
Wang, J., Odell, S. J., & Schwille, S. A. (2008). Effects of teacher induction on beginning teachers' teaching: A critical review of the literature. Journal of teacher education, 59(2), 132-152.
The Widget Effect: Our National Failure to Acknowledge and Act on Differences in Teacher Effectiveness.
This report examines the pervasive and longstanding failure to recognize and respond to variations in the effectiveness of teachers.
Weisberg, D., Sexton, S., Mulhern, J., Keeling, D., Schunck, J., Palcisco, A., & Morgan, K. (2009). The widget effect: Our national failure to acknowledge and act on differences in teacher effectiveness. New Teacher Project.
How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance
Quantitative studies of school effects have generally supported the notion that the problems of U.S. education lie outside of the school. Yet such studies neglect the primary venue through which students learn, the classroom. The current study explores the link between classroom practices and student academic performance by applying multilevel modeling to the 1996 National Assessment of Educational Progress in mathematics. The study finds that the effects of classroom practices, when added to those of other teacher characteristics, are comparable in size to those of student background, suggesting that teachers can contribute as much to student learning as the students themselves.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education
Studies of the effectiveness of Direct Instruction programs with special education students
were examined in a meta-analysis comparison. To be included, the outcomes had to be
compared with outcomes for some other treatment to which students were assigned prior to
any interventions. Not one of 25 studies showed results favoring the comparison groups.
Fifty-three percent of the outcomes significantly favored DI with an average magnitude of
effect of. 84 standard deviation units. The effects were not restricted to a particular handicapping condition, age group or skill area.
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
The effects of peer feedback practices with elementary education teacher candidates
The report of the American Educational Research Association (AERA) Panel on Research and Teacher Education (2005) recommended that teacher educators need to systematically and empirically study their own practice. The premise of the report was that teacher educators need to carry out quality research in order to better inform those inside and outside the field of education.
Wilkins, E. A., Shin, E. K., & Ainsworth, J. (2009). The effects of peer feedback practices with elementary education teacher candidates. Teacher Education Quarterly, 36(2), 79-93.
The nature and effectiveness of feedback given by cooperating teachers to student teachers
Effective feedback from cooperating teachers is a critical component of a successful student teaching experience. Unfortunately, few cooperating teachers are trained to provide specific feedback to their student teachers, and the lack of such communication is one of the most commonly reported problems among field experience students.
Wilkins‐Canter, E. A. (1997). The nature and effectiveness of feedback given by cooperating teachers to student teachers. The Teacher Educator, 32(4), 235-249.
Teacher Evaluation: A Study of Effective Practices
A preliminary survey of 32 school districts identified as having highly developed teacher evaluation systems was followed by the selection of 4 case study districts.
Teacher use of interventions in general education settings: Measurement and analysis of? the independent variable
This study evaluated the effects of performance feedback on increasing the quality of implementation of interventions by teachers in a public school setting.
Witt, J. C., Noell, G. H., LaFleur, L. H., & Mortenson, B. P. (1997). Teacher use of interventions in general education settings: Measurement and analysis of ?the independent variable. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30(4), 693.
Quality teacher induction “fourth wave”
The purpose of this essay is to describe quality teacher induction that has evolved from “fourth-wave” (1997–2006) teacher induction program development and research. A definition of quality induction is proposed, and a set of induction goals and components are outlined.
Wood, A. L., & Stanulis, R. N. (2009). Quality teacher induction:“Fourth-wave”(1997–2006) induction programs. The new educator, 5(1), 1-23.
Time management: An experimental investigation.
Four groups of preservice teachers participating in student teaching seminars were randomly assigned to one of three conditions to test the effectiveness of brief training in time-management techniques.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: An experimental investigation. Journal of school Psychology, 24(3), 267-275.
Failing Teachers?
This book describes the research undertaken during the Teaching Competence Project, a two-year research project funded by the Gatsby Charitable Foundation. There were five interlinked studies in the research.
Wragg, E. C., Chamberlin, R. P., & Haynes, G. S. (2005). Failing teachers?. Routledge.
Filling the void: A grounded theory approach to addressing teacher recruitment and retention in urban schools
This research addresses the problem of teacher shortages in urban, high-needs schools.
Wronowski, M. L. (2018). Filling the void: A grounded theory approach to addressing teacher recruitment and retention in urban schools. Education and Urban Society, 50(6), 548-574.
Paired peer placement with peer coaching to enhance prospective teachers’ professional growth in early field experience.
The purpose of this descriptive study was to examine and document developmental concerns of participants in a paired peer placement peer coaching program. Research participants were 26 elementary education majors who were randomly paired for their first teaching experience. Data were collected from students' observations, feedback from each other, and participants' reflections on their teaching experiences.
Wynn, M., & Kromrey, J. (2000). Paired peer placement with peer coaching to enhance prospective teachers' professional growth in early field experience. Action in Teacher Education, 22(sup2), 73-83.
The Cost-Effectiveness of Five Policies for Improving Student Achievement
This study compares the effect size and return on investment for rapid assessment, between, increased spending, voucher programs, charter schools, and increased accountability.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416-436.
Reviewing the Evidence on How Teacher Professional Development Affects Student Achievement. Issues & Answers.
The purpose of this study is to examine research to answer the question, What is the impact of teacher professional development on student achievement.
Yoon, K. S., Duncan, T., Lee, S. W. Y., Scarloss, B., & Shapley, K. L. (2007). Reviewing the Evidence on How Teacher Professional Development Affects Student Achievement. Issues & Answers. REL 2007-No. 033. Regional Educational Laboratory Southwest (NJ1).
Independent Teacher Education Programs: Apocryphal Claims, Illusory Evidence
This policy brief surveys historical and contemporary trends in teacher preparation, and explores what is known about the quality of five of the most prominent independent teacher education programs in the U.S., including their impact on teacher quality and student learning. The author's analysis demonstrates that claims regarding the success of such programs are not substantiated by peer-reviewed research and program evaluations.
Zeichner, K. (2016). Independent Teacher Education Programs: Apocryphal Claims, Illusory Evi-dence. Boulder, CO: National Education Policy Center. Retrieved from http://nepc.colorado.edu/publication/teacher-education
Alliance for Excellent Education
This organization is a national policy and advocacy organization dedicated to ensuring that all students graduate from high school ready for success in college, work, and citizenship.
America Achieves | Home
America Achieves draws upon experts with proven track records to identify and support exemplar initiatives and programs in education.
American Association for Colleges for Teacher Education (AACTE)
AACTE represents more than 800 postsecondary institutions with educator preparation programs, providing support, policy leadership, and advocacy.
American Institutes for Research (AIR)
AIR is one of the world's largest behavioral and social science research and evaluation organizations. Its research focus includes most aspects of K-12 education.
Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD)
This organization develops and delivers innovative programs, products, and services to educators in support student learners with a focus on professional development support.
Bellwether Education Partners
Bellwether Education Partners is a nonprofit dedicated to helping education organizations in the public, private, and nonprofit sectors.
Brown Center on Educational Policy
This is national nonprofit public policy organization that conducts research and makes recommendations on a awide range of issues affecting American K-12 education.
Calder: Longitudinal Data in Education Research
CALDER is a National Research and Development Center that utilizes longitudinal state and district data on student and teachers to examine the effects of real policies and practices on the learning gains of students over time.
Center for American Progress
The Center for American Progress is an independent nonpartisan policy institute provides research, analyses and advocacy on a wide range of education issues.
Center for Education Policy Analysis (CEPA)
CEPA is a research center focusing education policy issues including Poverty and Inequality; Federal and State Education Policy; Technological Innovations in Education; and Teaching and Leadership Effectiveness.
Center for Educational Leadership
The Center for Educational Leadership provides research and training in teaching effectiveness and school leadership.
Center for Public Education (CPE)
The Center for Public Education provides up-to-date research, data, and analysis on current education issues and explores ways to improve student achievement and engage public support for public schools.
Center for Research and Reform in Education (CRRE)
CRRE is a research center who’s major goal is to improve the quality of education through high-quality research and evaluation studies and the dissemination of evidence-based research.
Center on Great Teachers and Leaders
The Center on Great Teachers and Leaders (GTL Center) is dedicated to supporting state education leaders in their efforts to grow, respect, and retain great teachers and leaders for all students.
Center on Teaching and Learning (CTL)
CTL is research center that conducts and disseminates research that focuses on practical solutions to serious problems in school systems.
Common Core of Data (CCD)
CCD is a program of the U.S. Department of Education's National Center for Education Statistics that annually collects fiscal and non-fiscal data about all public schools, public school districts and state education agencies in the United States
Condition of Education
The Condition of Education is an annual report on key indicators of the U.S. education system. It is published by the Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, U.S. Department of Education.
Consortium for Policy Research in Education (CPRE)
CPRE looks at issues of teacher compensation, school finance, and principal evaluation for PK20.
Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO)
CCSSO is a nonpartisan, nationwide, nonprofit organization of public officials who head departments of elementary and secondary education in the states, provides leadership, advocacy, and technical assistance on major educational issues.





