In this paper, the authors show that the questions we asked are fundamental and that our meta-analytic techniques are appropriate, robust, and statistically correct. In sum, the results and conclusions of our meta-analysis are not altered by our critics’ protests and accusations.
Education Drivers
Treatment Integrity in the Problem-Solving Process Overview
Treatment integrity is a core component of data-based decision making (Detrich, 2013). The usual approach is to consider student data when making decisions about an intervention; however, if there are no data about how well the intervention was implemented, then meaningful judgments cannot be made about effectiveness. Figure 1 contains hypothetical data to illustrate the necessity of treatment integrity data when making decisions about interventions. In this example, a student was identified as
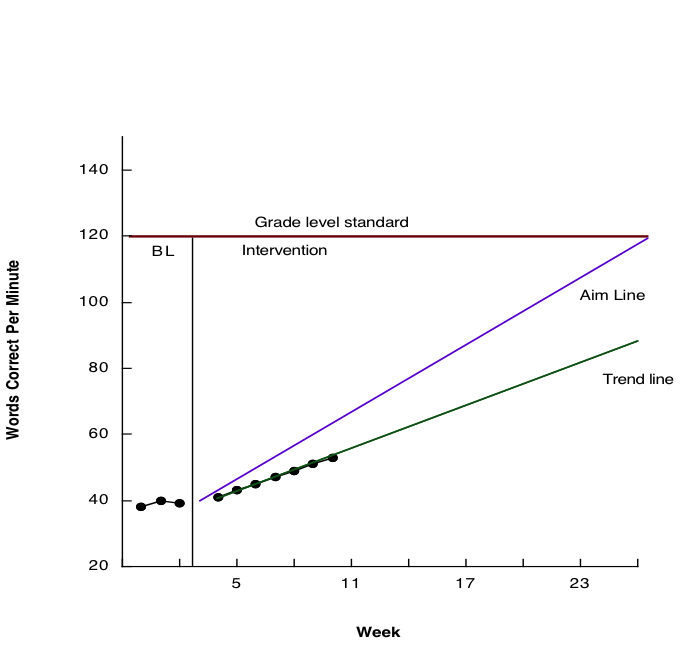
Figure 1 The analytical challenge of understanding the gap between expectations and actual performance
struggling with reading. Before the intervention, the student was reading grade-level materials at about 40 words correct per minute. The grade-level norm is about 120 words correct per minute. To close the achievement gap, an increase of two words correct per minute per week was established as a goal. After several weeks of intervention, the student’s actual improvement was only one word correct per minute per week. Although that slight increase constitutes progress, it will leave the student far behind his or her peers at the end of the year.
The analytical task for the educator is to determine whether the intervention is sufficiently effective to achieve adequate growth. This cannot be determined unless there are data about how well the intervention was implemented. If treatment integrity data indicate that the intervention was implemented with high quality, then an alternative intervention should be considered. On the other hand, if the data indicate that the intervention was poorly implemented, then efforts should be taken to improve the quality of implementation before making any decisions about the effectiveness of the intervention.
To make decisions about an intervention without treatment integrity data increases the risk that effective interventions will be discontinued because of apparent lack of progress. Although significant resources are required to assess treatment integrity, they are also required to implement an intervention poorly and then terminate it because of the incorrect assumption of failure.
A Pragmatic Problem-Solving Approach to Assessing Treatment Integrity
Measuring treatment integrity requires time and resources, both of which are in short supply in most schools. If assessing treatment integrity is an integral part of data-based decision making, then effective and efficient methods for doing so must be developed. One approach to increasing efficiency is illustrated in Figure 2.
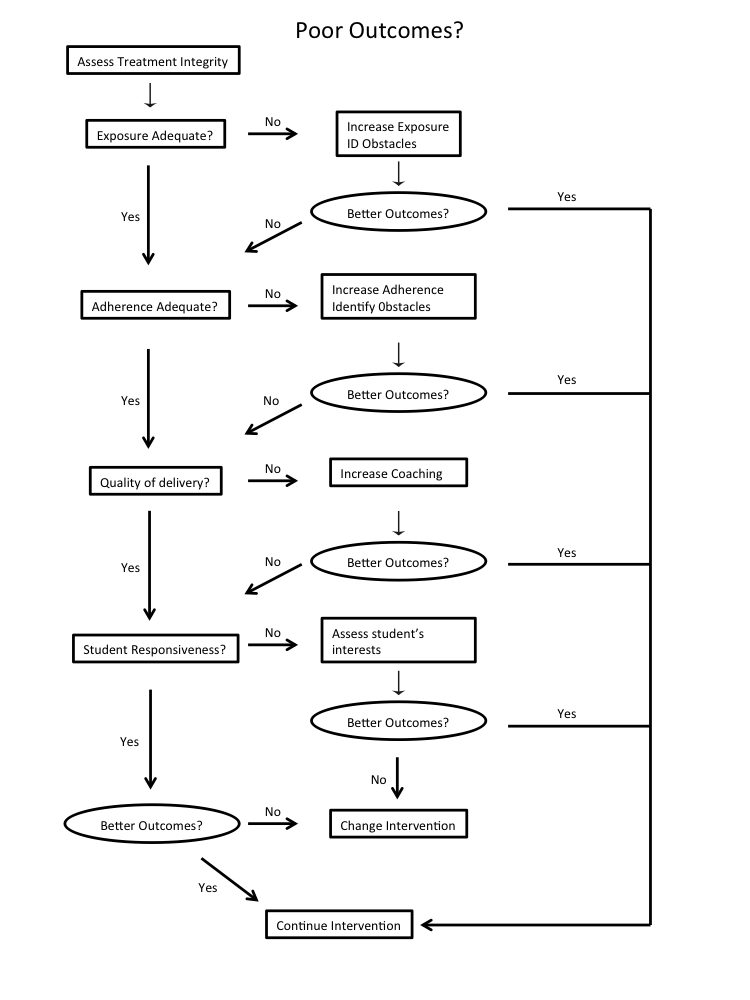
Figure 2. A pragmatic approach to assessing and intervening to improve treatment integrity
Used with permission. Originally published in Detrich, R. (2013). Innovation, implementation science, and data-based decision making: Components of successful reform. In M. Murphy, S. Redding, & J. Twyman (Eds.), Handbook on Innovations in Learning (pp. 33–49). Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing.
This approach is based on the notion that because it is difficult to measure all of the dimensions of treatment integrity at the same time, a better alternative is to measure them sequentially. A pragmatic choice is made to assess treatment integrity when a student is not benefitting from instruction. Perhaps the easiest dimension of treatment integrity to assess is exposure (dosage). If exposure is not occurring as prescribed, then efforts should be made to improve exposure before assessing any other dimensions. To do this, it is necessary to determine if there are organizational variables or other factors that make it difficult to deliver instruction at the frequency and duration defined in the intervention protocol. The problem may be insufficient time in the school schedule for the intervention to occur as planned. Lack of time can impact both frequency and duration of exposure. Once exposure has been improved and the student is receiving instruction as prescribed, student data can be monitored to determine if performance has improved. If it has improved to adequate levels, then no further assessment is required.
On the other hand, if student performance remains below expectations even though exposure is occurring as specified, it will be necessary to assess the next aspect of treatment integrity. Adherence should be assessed next. Research suggests that high adherence has a greater impact on student outcomes than any other dimension of integrity (Sanetti & Fallon, 2011); however, the different dimensions interact with each other and the combined effects can strengthen or weaken student outcomes.
If adherence is adequate, then assess quality of delivery. However, if assessed adherence is less than optimal, then the next step is to improve adherence. Poor adherence may result when those responsible for implementation do not have the skills to carry out the intervention (can’t do) or are not motivated to implement it because they do not perceive the intervention to be a solution to the identified problem (won’t do). A third possibility is that the intervention is not a good contextual fit with the classroom culture and routines. Once the problem has been identified and action taken to improve adherence, student data should again be reviewed to determine if performance has improved to acceptable levels. If it has improved sufficiently, there is no need to assess other dimensions of treatment integrity.
If student performance is still not at acceptable levels, then the next step is to assess quality of delivery. Both exposure and adherence can be objectively measured by direct observation. Assessing quality of delivery is more difficult because it is a more subjective measure. Consider the challenge of measuring praise. Certain aspects can be objectively measured; for example, specific praise can be discriminated from general praise. The qualitative features of praise are much more difficult to measure objectively. Measuring enthusiasm and sincerity is challenging but it requires assessment as it can impact student performance. Delivering praise in a monotone or robotically may result in poor student outcomes. Saying the same words with sincerity and enthusiasm is likely to result in very different outcomes.
If quality of delivery is inadequate, then action should be taken to improve it before making decisions about the effectiveness of the intervention on student performance. As with the previous steps, once the assessed quality of delivery is at an adequate level, data should be reviewed to determine if the student is making adequate progress. If the student is making adequate progress, then nothing further needs to be done.
If the student is not making adequate progress, then the final dimension of treatment integrity, student responsiveness, should be assessed. If student responsiveness, like all the other dimensions of treatment integrity, is sufficiently high, then a new intervention should be considered. If student engagement is low, then efforts should be taken to increase it before making any decisions about the intervention.
In summary, if a particular dimension of treatment integrity is increased to higher levels and student performance data indicate that adequate progress is being made then no further assessment of the other dimensions of treatment integrity is required. On the other hand, if student performance does not improve when a particular dimension of treatment integrity is increased then it is necessary to keep assessing and improving the other dimensions of treatment integrity until the student is making adequate progress. If all dimensions of treatment integrity are being implemented at high levels then the pragmatic choice is to change the intervention. This iterative process continues until the student is making adequate progress. Across all phases of this process, data about student performance and treatment integrity should be the primary consideration in making decisions about continuing or changing an intervention. Basing decisions on only one source of data increases the risk of error.
Citations
Detrich, R. (2013). Innovation, implementation science, and data-based decision making: Components of successful reform. In M. Murphy, S. Redding, & J. Twyman (Eds.), Handbook on Innovations in Learning (pp. 33–49). Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing.
Sanetti, L. M., & Fallon, L. M. (2011). Treatment integrity assessment: How estimates of adherence, quality, and exposure influence interpretation of implementation. Journal of Educational and Psychological Consultation, 21(3), 209–232.
Publications
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Treatment Integrity in the Problem-Solving Process Overview
Treatment integrity is a core component of data-based decision making (Detrich, 2013). The usual approach is to consider student data when making decisions about an intervention; however, if there are no data about how well the intervention was implemented, then meaningful judgments cannot be made about effectiveness.
Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress
This paper discusses the search for a “magic metric” in education: an index/number that would be generally accepted as the most efficient descriptor of school’s performance in a district.
Celio, M. B. (2013). Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Quality. In Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance (Vol. 3, pp. 97-118). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Evidence-based practice in the broader context: How can we really use evidence to inform decisions
This article examines the evidence-based practice decision-making heuristic in the broader context of clinical decision making.
Chorpita, B. F., & Starace, N. K. (2010). Evidence-based practice in the broader context: How can we really use evidence to inform decisions. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 11(1), 47-61.
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
Treatment Integrity: Fundamental to Education Reform
To produce better outcomes for students two things are necessary: (1) effective, scientifically supported interventions (2) those interventions implemented with high integrity. Typically, much greater attention has been given to identifying effective practices. This review focuses on features of high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. (2014). Treatment integrity: Fundamental to education reform. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 13(2), 258-271.
Innovation, Implementation Science, and Data-Based Decision Making: Components of Successful Reform
Schools are often expected to implement innovative instructional programs. Most often these initiatives fail because what we know from implementation science is not considered as part of implementing the initiative. This chapter reviews the contributions implementation science can make for improving outcomes for students.
Detrich, R. Innovation, Implementation Science, and Data-Based Decision Making: Components of Successful Reform. Handbook on Innovations in Learning, 31.
Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs.
Reform efforts tend to come and go very quickly in education. This paper makes the argument that the sustainability of programs is closely related to how well those programs are implemented.
Detrich, R., Keyworth, R. & States, J. (2010). Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 11(1), 4-29.
Effective Instruction Overview
A summary of the available studies accumulated over the past 40 years on a key education driver, teacher competencies offers practical strategies, practices, and rules to guide teachers in ways to improve instruction that improves student performance and the quality of the work experience.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Effective Instruction Overview. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-overview
Teacher Soft Skills Overview
This overview examines the available research on the topic of soft skills (personal competencies) and how these proficiencies support the technical competencies required for success in school
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2018). Overview of Teacher Soft Skills.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-compentencies-soft-skills.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Data Mining
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
How does performance feedback affect the way teachers carry out interventions?
This analysis examined the impact of performance feedback on the quality of implementation of interventions.
Detrich, R. (2015). How does performance feedback affect the way teachers carry out interventions? Retrieved from how-does-performance-feedback.
How long do reform initiatives last in public schools?
This analysis examined sustainability of education reforms in education.
Detrich, R. (2015). How long do reform initiatives last in public schools? Retrieved from how-long-do-reform.
How often are treatment integrity measures reported in published research?
This analysis examined the frequency that treatment integrity is reported in studies of research-based interventions.
Detrich, R. (2015). How often are treatment integrity measures reported in published research? Retrieved from how-often-are-treatment.
How well are Interventions Implemented in Educational Settings?
This analysis examined two studies to understand the reliability of self-reporting of practitioners implementing interventions.
Detrich, R. (2015). How well are Interventions Implemented in Educational Settings? Retrieved from how-well-are-interventions.
Presentations
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress
This paper discusses the search for a “magic metric” in education: an index/number that would be generally accepted as the most efficient descriptor of school’s performance in a district.
Celio, MB. (2011). Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2011-wing-presentation-mary-beth-celio.
Treatment Integrity and Program Fidelity: Necessary but Not Sufficient to Sustain Programs
If programs are to sustain they must be implemented with integrity. If there is drift over time, it raises questions about whether the program is sustaining or has been substantially changed.
Detrich, R. (2008). Treatment Integrity and Program Fidelity: Necessary but Not Sufficient to Sustain Programs [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2008-aba-presentation-ronnie-detrich.
Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Component of PBS
School-wide initatives have to be well implemented if there is to be any benefit. This talk describes methods for assuring high levels of treatment integrity.
Detrich, R. (2008). Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Component of PBS [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2008-apbs-txint-presentation-ronnie-detrich.
Treatment Integrity: Necessary by Not Sufficient for Improving Outcomes
Treatment integrity is necessary to improve outcomes but it is not sufficient. It is also necessary to implement scientifically supported interventions.
Detrich, R. (2015). Treatment Integrity: Necessary by Not Sufficient for Improving Outcomes [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2015-ebpindisabilities-txint-presentation-ronnie-detrich.
Student Research
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes.
This study evaluated the effects of a problem solving intervention package that included problem-solving information, performance feedback, and coaching in a student intervention planning protocol.
Vaccarello, C. A. (2011). Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes. Retrieved from student-research-2011.
Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes.
This study evaluated the effects of a problem solving intervention package that included problem-solving information, performance feedback, and coaching in a student intervention planning protocol.
Vaccarello, C. A. (2011). Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes. Retrieved from student-research-2011.
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Treatment Integrity in the Problem-Solving Process Overview
Treatment integrity is a core component of data-based decision making (Detrich, 2013). The usual approach is to consider student data when making decisions about an intervention; however, if there are no data about how well the intervention was implemented, then meaningful judgments cannot be made about effectiveness.
Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement
This study was guided by a reduced version of the Self-System Process Model developed by Connell. This paper report the optimal and risk thresholds for the Student Performance and Commitment Index (SPCI) and engagement, and then data on how much engagement matters for later success in school are presented.
Klem, A. M., & Connell, J. P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. Journal of school health, 74(7), 262-273.
Transforming the culture of schools: Yup’ik Eskimo examples
This book share issues of equity and school transformation, and shows how one indigenous minority teachers' group engaged in a process of transforming schooling in their community. Documented in one small locale far-removed from mainstream America, the personal narratives by Yupík Eskimo teachers.
Lipka, J., & Ilutsik, E. (2014). Transforming the Culture of Schools: Yup¡ k Eskimo Examples. Routledge.
The impact of communication factors on job satisfaction among Icelandic employees in the public sector
The main purpose of the present study was to explore the impact of communicative factors on job satisfaction and employee’s desired need for new ways of communicating.
Þorkelsson, J. The Impact of Communication Factors on Job Satisfaction Among Icelandic Employees in the Public Sector (Doctoral dissertation).
Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Sixth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance.
This book is compiled from the proceedings of the sixth summit entitled “Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance.” The 2011 summit topic was selected to help answer the following question: What basic practice has the potential for the greatest impact on changing the behavior of students, teachers, and school administrative personnel?
States, J., Keyworth, R. & Detrich, R. (2013). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Sixth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 3, pp. ix-xii). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Cultural Diversity and School Equity. A Model to Evaluate and Develop Educational Practices in Multicultural Education Contexts
The main purpose of this research is to explore whether the proper strategies to deal with cultural diversity in school is being implemented, and to assess how cultural diversity is addressed in our school.
Aguado, T., Ballesteros, B., & Malik, B. (2003). Cultural diversity and school equity. A model to evaluate and develop educational practices in multicultural education contexts. Equity &Excellence in Education, 36(1), 50-63.
Social Powers and Effective Classroom Management: Enhancing Teacher–Student Relationships
This article presents strategies developed by practicing teachers to illustrate the usefulness of one model for enhancing teacher-student relationships and four types of social power that teacher can use to influence students to excel both academically and behaviorally.
Alderman, G. L., & Green, S. K. (2011). Social powers and effective classroom management: enhancing teacher–student relationships. Intervention in School and Clinic, 47(1), 39-44.
Observations of effective teacher-student interactions in secondary school classrooms: Predicting student achievement with the classroom assessment scoring system–secondary
Multilevel modeling techniques were used with a sample of 643 students enrolled in 37 secondary school classrooms to predict future student achievement (controlling for baseline achievement) from observed teacher interactions with students in the classroom, coded using the Classroom Assessment Scoring System—Secondary.
Allen, J., Gregory, A., Mikami, A., Lun, J., Hamre, B., & Pianta, R. (2013). Observations of effective teacher–student interactions in secondary school classrooms: Predicting student achievement with the classroom assessment scoring system—secondary. School Psychology Review, 42(1), 76.
Best Practices in Collaborative Problem Solving for Intervention Design.
This chapter describes a process, collaborative problem solving, that can guide decision making and intervention planning for improving academic and behavior outcomes for students. The primary focus is on the two basic components of the term collaborative problem solving.
Allen, S. J., & Graden, J. L. (2002). Best Practices in Collaborative Problem Solving for Intervention Design.
ACHIEVEMENT AND ENROLLMENT STATUS OF SUSPENDED STUDENTS: Outcomes in a Large, Multicultural School District
This article presents the results of longitudinal retrospective analyses on suspensions, achievement, and long-term enrollment status of students in a large, urban school district. Findings indicated that suspended students had substantially lower presuspension achievement than did students in the comparison group, gained considerably less academically throughout 3 years with suspensions, and had high drop-out rates.
Arcia, E. (2006). Achievement and enrollment status of suspended students: Outcomes in a large, multicultural school district. Education and Urban Society, 38(3), 359-369.
The flip side of the coin: Understanding the school’s contribution to dropout and completion.
Using a structural perspective from organizational theory, the authors review aspects of schooling associated with dropout. They then briefly review selected reform initiatives that restructure the school environment to improve student achievement and retention.
Baker, J. A., Derrer, R. D., Davis, S. M., Dinklage-Travis, H. E., Linder, D. S., & Nicholson, M. D. (2001). The flip side of the coin: Understanding the school's contribution to dropout and completion. School psychology quarterly, 16(4), 406.
Effects of active student response during error correction on the acquisition and maintenance of geography facts by elementary students with learning disabilities.
This study compares the effects of Active Student Response error correction and No Response (NR) error correction during.
Barbetta, P. M., & Heward, W. L. (1993). Effects of active student response during error correction on the acquisition and maintenance of geography facts by elementary students with learning disabilities. Journal of Behavioral Education, 3(3), 217-233.
Teacher–Student Relationship Climate and School Outcomes: Implications for Educational Policy Initiatives
This study examined whether associations between teacher policies and student achievement were mediated by the teacher–student relationship climate. Results of this study were threefold. These findings are discussed in light of their educational policy implications.
Barile, J. P., Donohue, D. K., Anthony, E. R., Baker, A. M., Weaver, S. R., & Henrich, C. C. (2012). Teacher–student relationship climate and school outcomes: Implications for educational policy initiatives. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41(3), 256-267.
Psychometric qualities of professional practice.
This chapter is intended to help solve questions concerning how to judge the appropriateness of assessment or measurement decisions and of the information used to make decisions.
Barnett, D. W., Lentz Jr, F. E., & Macmann, G. (2000). Psychometric qualities of professional practice.
Enhancing Adherence to a Problem Solving Model for Middle-School Pre-Referral Teams: A Performance Feedback and Checklist Approach
This study looks at the use of performance feedback and checklists to improve middle-school teams problem solving.
Bartels, S. M., & Mortenson, B. P. (2006). Enhancing adherence to a problem-solving model for middle-school pre-referral teams: A performance feedback and checklist approach. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 22(1), 109-123.
Enhancing Adherence to a Problem Solving Model for Middle-School Pre-Referral Teams: A Performance Feedback and Checklist Approach
This study looks at the use of performance feedback and checklists to improve middle-school teams problem solving.
Bartels, S. M., & Mortenson, B. P. (2006). Enhancing adherence to a problem-solving model for middle-school pre-referral teams: A performance feedback and checklist approach. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 22(1), 109-123.
School Selection and the Social Class Divide: How Tracking Contributes to the Reproduction of Inequalities
Selection practices in education, such as tracking, may represent a structural obstacle that contributes to the social class achievement gap. The authors hypothesized that school’s function of selection leads evaluators to reproduce social inequalities in tracking decisions, even when performance is equal.
Batruch, A., Autin, F., Bataillard, F., & Butera, F. (2018). School Selection and the Social Class Divide: How Tracking Contributes to the Reproduction of Inequalities. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 0146167218791804.
Implicit discrimination
What drives people to discriminate? Economists focus on two main reasons: "taste-based" and "statistical" discrimination. Motivated by a growing body of psychological evidence, the authors put forward a third interpretation: implicit discrimination. The authors argue that discrimination may be unintentional and outside of the discriminator's awareness.
Bertrand, M., Chugh, D., & Mullainathan, S. (2005). Implicit discrimination. American Economic Review, 95(2), 94-98.
Assertive supervision: Building involved teamwork.
This well-written book on assertiveness clearly describes the non assertive, assertive, and aggressive styles of supervision. Each chapter provides numerous examples, practice exercises, and self-tests. The author identifies feelings and beliefs that support aggressiveness, non aggressiveness, or non assertiveness which help the reader "look beyond the words themselves."
Black, M. K. (1991). Assertive Supervision-Building Involved Teamwork. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 22(5), 224-224.
Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale
This study was conducted to create a reliable and valid low- to medium-inference, multidimensional measure of instructor clarity from seminal work across several academic fields. The five factors were explored in regards to their ability to predict the outcomes. Implications for instructional communication researchers are discussed.
Bolkan, S. (2017). Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale. Communication Education, 66(1), 19-36.
Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy.
The author shares nine teachable competencies that can serve as a principal's guide for empathy education. This paper will help answer which practices enhance empathy and how will principals know if teachers are implementing them effectively.
Borba, M. (2018). Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy. Educational Leadership, 76(2), 22-28.
Weighing the benefits of anchored math instruction for students with disabilities in general education classes
The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of enhanced anchor-instruction and traditional problem instruction in improving problem-solving performance.
Bottge, B. A., Heinrichs, M., Mehta, Z. D., & Hung, Y. H. (2002). Weighing the benefits of anchored math instruction for students with disabilities in general education classes. The Journal of Special Education, 35(4), 186-200.
Teacher behavior and student achievement
This paper, prepared as a chapter for the "Handbook of Research on Teaching" (third edition), reviews correlational and experimental research linking teacher behavior to student achievement. It focuses on research done in K-12 classrooms during 1973-83, highlighting several large-scale, programmatic efforts.
Brophy, J., & Good, T. L. (1984). Teacher Behavior and Student Achievement. Occasional Paper No. 73.
Parochial Empathy Predicts Reduced Altruism and the Endorsement of Passive Harm
This paper predicted that out-group empathy would inhibit inter-group harm and promote inter-group helping, whereas in-group empathy would have the opposite effect. In all samples, in-group and out-group empathy had independent, significant, and opposite effects on inter-group outcomes, controlling for trait empathic concern.
Bruneau, E. G., Cikara, M., & Saxe, R. (2017). Parochial empathy predicts reduced altruism and the endorsement of passive harm. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(8), 934-942.
Using performance feedback to enhance implementation fidelity of the problem-solving team process
This study examines the importance of implementation integrity for problem-solving teams (PST) and response-to-intervention models.
Burns, M. K., Peters, R., & Noell, G. H. (2008). Using performance feedback to enhance implementation fidelity of the problem-solving team process. Journal of School Psychology, 46(5), 537-550.
Burnout: Testing for the validity, replication, and invariance of causal structure across elementary, intermediate, and secondary teachers
The study investigated the impact of organizational and personality factors on three facets of burnout—Emotional Exhaustion, Depersonalization, and reduced Personal Accomplishment within one conceptual framework.
Byrne, B. M. (1994). Burnout: Testing for the validity, replication, and invariance of causal structure across elementary, intermediate, and secondary teachers. American Educational Research Journal, 31(3), 645–673.
Reinforcement, reward, and intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis.
This article reviews research on the effects of reinforcement/reward on intrinsic motivation. The main meta-analysis included 96 experimental stud- ies that used between-groups designs to compare rewarded subjects to nonrewarded controls on four measures of intrinsic motivation.
Cameron, J., & Pierce, W. D. (1994). Reinforcement, reward, and intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational research, 64(3), 363-423.
The debate about rewards and intrinsic motivation: Protests and accusations do not alter the results.
Cameron, J., & Pierce, W. D. (1996). The debate about rewards and intrinsic motivation: Protests and accusations do not alter the results. Review of Educational Research, 66(1), 39–51.
Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
This paper describes a survey of teachers trained in Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA). The study examined whether teachers: agreed that TESA interactions were useful with today's children; continued to practice the TESA coding and observation process after being trained; and would recommend TESA to colleagues.
Cantor, J., Kester, D., & Miller, A. (2000). Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
Expanding the notion of teachers’ rights: Access to tools that work
In most schools, resources are shrinking as the student body becomes more diverse and challenging. Yet if teachers advocate too loudly for additional resources or more support for education from the home, they are criticized for making excuses rather than solving problems.
Carnine, D. (1992). Expanding the notion of teachers' rights: Access to tools that work. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 25(1), 13.
Student cultural diversity: Understanding and meeting the challenge
In this article, the author argues convincingly for a view of American's cultural diversity as a self-evident reality - one that must be effectively addressed by inservice and preservice teacher education programmes.
Carrington, V. (1999). Student Cultural Diversity: Understanding and Meeting the Challenge. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 43(4), 386.
Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Quality
This paper discusses the search for a “magic metric” in education: an index/number that would be generally accepted as the most efficient descriptor of school’s performance in a district.
Celio, M. B. (2013). Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Quality. In Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance (Vol. 3, pp. 97-118). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
A multilevel study of leadership, empowerment, and performance in teams
A multilevel model of leadership, empowerment, and performance was tested using a sample of 62 teams, 445 individual members, 62 team leaders, and 31 external managers from 31 stores of a Fortune 500 company. Leader-member exchange and leadership climate-related differently to individual and team empowerment and interacted to influence individual empowerment.
Chen, G., Kirkman, B. L., Kanfer, R., Allen, D., & Rosen, B. (2007). A multilevel study of leadership, empowerment, and performance in teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(2), 331–346.
The Development of The Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) to Measure Clear Teaching in The Classroom
This study presents the Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) as an alternative to existing measures of teacher clarity. Analyses revealed a 10 item scale with an acceptable factor structure, acceptable reliability and validity.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The development of the teacher clarity short inventory (TCSI) to measure clear teaching in the classroom. Communication Research Reports, 15(3), 262-266.
The relationship of teacher clarity and teacher immediacy with students’ experiences of state receiver apprehension
This study examined the impact of state receiver apprehension in the instructional context. Because of its negative relationship with information processing effectiveness, receiver apprehension is an experience which can act as a barrier to elective learning.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The relationship of teacher clarity and teacher immediacy with students’ experiences of state receiver apprehension. Communication Quarterly, 46(4), 446–456.
Evidence-based practice in the broader context: How can we really use evidence to inform decisions
This article examines the evidence-based practice decision-making heuristic in the broader context of clinical decision making.
Chorpita, B. F., & Starace, N. K. (2010). Evidence-based practice in the broader context: How can we really use evidence to inform decisions. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 11(1), 47-61.
Access and persistence: Findings from 10 years of longitudinal research on students
To answer questions about who goes to college, who persists toward a degree or credential, and what happens to students after they enroll, the National Center for Education Statistics launched three national longitudinal studies to track students movements into and through the postsecondary education system. These three surveys, the National Education Longitudinal Study, the Beginning Postsecondary Student Longitudinal Study, and the Baccalaureate and Beyond Study, provide findings about college access, student characteristics, and academic persistence.
Choy, S. P. (2002). Access and persistence: Findings from 10 years of longitudinal research on students.Washington, DC: American Council on Education, Center for Policy Analysis.
Scientific practitioner: Assessing student performance: An important change is needed
A rationale and model for changing assessment efforts in schools from simple description to the integration of information from multiple sources for the purpose of designing interventions are described.
Christenson, S. L., & Ysseldyke, J. E. (1989). Scientific practitioner: Assessing student performance: An important change is needed. Journal of School Psychology, 27(4), 409-425.
Opportunities suspended: The devastating consequences of zero tolerance and school discipline policies. Report from a national summit on zero tolerance.
This is the first comprehensive national report to scrutinize the impact of strict Zero Tolerance approach in the America public school. This report illustrate that Zero Tolerance is unfair, is contrary to developmental needs of children, denies children educational opportunities, and often results in the criminalization of children.
Civil Rights Project. (2000). Opportunities suspended: The devastating consequences of zero tolerance and school discipline policies.
A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview for those interested in the current state‐of‐the‐art in time management research. The review demonstrates that time management behaviours relate positively to perceived control of time, job satisfaction, and health, and negatively to stress.
Claessens, B. J., Van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36(2), 255–276.
Early career teacher attrition: Intentions of teachers beginning
This study considered early career teacher attrition as an identity making process that involves a complex negotiation between individual and contextual factors.
Clandinin, D. J., Long, J., Schaefer, L., Downey, C. A., Steeves, P., Pinnegar, E., ... & Wnuk, S. (2015). Early career teacher attrition: Intentions of teachers beginning. Teaching Education, 26(1), 1-16.
Fostering the work motivation of individuals and teams
Solid evidence supports claims that motivational programs can increase the quality and quantity of performance from 20 to 40 percent. Motivation can solve three types of performance problems: 1) people are refusing to change; and/or 2) allowing themselves to be distracted and not persist at a key task; and/or 3) treating a novel task as familiar, making mistakes but not investing mental effort and taking responsibility because of overconfidence. After describing a number of general strategies for fostering individual motivation, the article focuses on the unique motivational issues faced by teams and how to overcome them.
Clark, R. E. (2003). Fostering the work motivation of individuals and teams. Performance Improvement, 42(3), 21–29.
Improving Mathematical Problem Solving in Grades 4 Through 8.
This practice guide provides five recommendations for improving students’ mathematical problem solving in grades 4 through 8. The manual is geared toward teachers, math coaches, other educators, and curriculum developers who want to improve the mathematical problem solving of students.
Clearinghouse, W. W. Improving Mathematical Problem Solving in Grades 4 Through 8. U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Science (IES) NCEE 2012-4055.
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
School climate and social-emotional learning: Predicting teacher stress, job satisfaction, and teaching efficacy.
The aims of this study were to investigate whether and how teachers’ perceptions of social-emotional learning and climate in their schools influenced three outcome variables—teachers’ sense of stress, teaching efficacy, and job satisfaction—and to examine the interrelationships among the three outcome variables
Collie, R. J., Shapka, J. D., & Perry, N. E. (2012). School climate and social–emotional learning: Predicting teacher stress, job satisfaction, and teaching efficacy. Journal of educational psychology, 104(4), 1189.
“I don’t have enough time”—Teachers’ interpretations of time as a key to learning and school change
This study investigated inner-city middle school teachers' perceptions of the importance of time in learning and sharing information. The survey identified ways that teachers shared what they had learned and discussed factors that helped or hindered them in sharing. Teacher interviews examined: knowledge, skills, and insights gained by participating in the EELC.
Collinson, V., & Fedoruk Cook, T. (2001). “I don’t have enough time”—Teachers’ interpretations of time as a key to learning and school change. Journal of Educational Administration, 39(3), 266–281.
Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education.
The purpose of this appear is to describe a school-wide staff development model that is based on a proactive instructional approach to solving problem behavior on a school-wide basis and utilizes effective staff development procedures.
Colvin, G., Kameenui, E. J., & Sugai, G. (1993). Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education. Education and treatment of children, 361-381.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
This is a meta-analysis that examines teacher-student relations impact on student performance. The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students.
Person-centered education is a counseling-originated, educational psychology model, overripe for meta-analysis, that posits that positive teacher-student relationships are associated with optimal, holistic learning. It includes classical, humanistic education and today’s constructivist learner-centered model.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
Why teams don’t work
The belief that working in teams makes us more creative and productive is so widespread that when faced with a challenging new task, leaders are quick to assume that teams are the best way to get the job done. Getting agreement is the leader’s job, and they must be willing to take great personal and professional risks to set the team’s direction. And if the leader isn’t disciplined about managing who is on the team and how it is set up, the odds are slim that a team will do a good job.
Coutu, D., & Beschloss, M. (2009). Why teams don’t work. Harvard business review, 87(5), 98-105.
On the teachability of communication strategies.
This article describes what communication strategies are and provides an overview of the teachability issue, discussing the arguments for and against strategy instruction, and suggests three possible reasons for the existing controversy.
Dörnyei, Z. (1995). On the teachability of communication strategies. TESOL quarterly, 29(1), 55-85.
Motivational Strategies in the language classroom
This book is the first of its kind in the second/foreign language (L2) ®eldthat is entirely devoted to discussing
motivational strategies, that is, methods and techniques to generate and maintain the learners' motivation.
Dörnyei, Z. (2001). Motivational strategies in the language classroom.Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Bringing Out The Best In People
This book by organizational psychologist Aubrey C. Daniels is a guide for anyone who is required to supervise people and is particularly relevant to school principals. It is based on applying positive consequences to improve performance and offers strategies to reduce undesirable behavior so your school and employees can be successful.
Daniels, A. C., Tapscott, D., & Caston, A. (2000). Bringing out the best in people. Columbus, OH: McGraw-Hill.
Effective teacher professional development
Teacher professional learning is of increasing interest as one way to support the increasingly complex skills students need to learn in preparation for further education and work in the 21st century. Sophisticated forms of teaching are needed to develop student competencies such as deep mastery of challenging content, critical thinking, complex problem-solving, effective communication and collaboration, and self-direction. In turn, effective professional development (PD) is needed to help teachers learn and refine the pedagogies required to teach these skills.
Darling-Hammond, L., Hyler, M. E., & Gardner, M. (2017). Effective teacher professional development. Learning Policy Institute.
Superintendents’ perspectives on the involuntary departure of public school principals: The most frequent reasons why principals lose their jobs
Few studies have examined factors relating to ineffective school leadership. Such knowledge can help principals refine leadership behaviors and enhance job security. This study used experiences and perceptions from 99 California public school superintendents to examine the reasons why some principals lose their jobs.
Davis, S. H. (1998). Superintendents’ perspectives on the involuntary departure of public school principals: The most frequent reasons why principals lose their jobs. Educational Administration Quarterly, 34(1), 58–90.
Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation
Conducted 2 laboratory and 1 field experiment with 24, 24, and 8 undergraduates to investigate the effects of external rewards on intrinsic motivation to perform an activity. In each experiment, Ss performed an activity during 3 different periods, and observations relevant to their motivation were made. External rewards were given to the experimental Ss during the 2nd period only, while the control Ss received no rewards.
Deci, E. L. (1971). Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 18,105–115.
The effects of team training on team outcomes: A meta‐analysis
A meta‐analysis was conducted to determine relationships between team training and team effectiveness. Results from the 21 studies provided evidence that training is positively related to team effectiveness and effectiveness in five outcome categories: affective, cognitive, subjective task‐based skill, objective task‐based skill, and teamwork skill.
Delise, L. A., Allen Gorman, C., Brooks, A. M., Rentsch, J. R., & Steele‐Johnson, D. (2010). The effects of team training on team outcomes: A meta‐analysis. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 22(4), 53–80.
School psychologist as problem solver
Deno, S. L. (1995). School psychologist as problem solver. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology III(pp. 471–484). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Developing Curriculum-Based Measurement Systems for Data-Based Special Education Problem Solving
This paper provides procedures for developing curriculum-based measurement systems in special education problem solving.
Deno, S. L., & Fuchs, L. S. (1987). Developing Curriculum-Based Measurement Systems for Data-Based Special Education Problem Solving. Focus on Exceptional Children, 19(8), 1-16.
Treatment Integrity: Fundamental to Education Reform
To produce better outcomes for students two things are necessary: (1) effective, scientifically supported interventions (2) those interventions implemented with high integrity. Typically, much greater attention has been given to identifying effective practices. This review focuses on features of high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. (2014). Treatment integrity: Fundamental to education reform. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 13(2), 258-271.
Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs.
Reform efforts tend to come and go very quickly in education. This paper makes the argument that the sustainability of programs is closely related to how well those programs are implemented.
Detrich, R., Keyworth, R. & States, J. (2010). Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 11(1), 4-29.
Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process
The usual approach to determining if an intervention is effective for a student is to review student outcome data; however, this is only part of the task. Student data can only be understood if we know something about how well the intervention was implemented. Student data without treatment integrity data are largely meaningless because without knowing how well an intervention has been implemented, no judgments can be made about the effectiveness of the intervention. Poor outcomes can be a function of an ineffective intervention or poor implementation of the intervention. Without treatment integrity data, there is a risk that an intervention will be judged as ineffective when, in fact, the quality of implementation was so inadequate that it would be unreasonable to expect positive outcomes.
Detrich, R., States, J. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process. Oakland, Ca. The Wing Institute.
Do smarter teams do better? A meta-analysis of team-level the cognitive ability and team performance
This study reports the results of several meta-analyses examining the relationship between four operational definitions of cognitive ability within teams (highest member score, lowest member score, mean score, standard deviation of scores) and team performance.
Devine, D. J., & Phillips, J. L. (2000). Do smarter teams do better? A meta-analysis of team-level the cognitive ability and team performance. Paper presented at the 15th Annual Conference of the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology, New Orleans, LA.
Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention
The authors developed a multi-faceted prejudice habit-breaking intervention to produce long-term reductions in implicit race bias. The intervention is based on the premise that implicit bias is like a habit that can be broken through a combination of awareness of implicit bias, concern about the effects of that bias, and the application of strategies to reduce bias.
Devine, P. G., Forscher, P. S., Austin, A. J., & Cox, W. T. (2012). Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 48(6), 1267–1278.
It’s about Time!! A Report on the Impact of Workload on Teachers and Students
Studying teacher workload issues has become somewhat of a trend in recent years with studies having already been completed in most other Canadian provinces. The consistency in teacher workload across the country is remarkable (see Appendix 2), and many of the findings in this study are supported by research in other jurisdictions. However, this discussion of the findings will deal primarily with the issues in Newfoundland and Labrador.
Dibbon, D. C. (2004). It’s about Time!! A Report on the Impact of Workload on Teachers and Students. St. John’s, NL: Memorial University of Newfoundland.
The bases of teacher experiences: A meta-analysis
Reports a meta-analysis of research on the bases of teacher expectancies. The following conclusions were drawn: Student attractiveness, conduct, cumulative folder information, race, and social class were related to teacher expectancies.
Dusek, J. B., & Joseph, G. (1983). The bases of teacher expectancies: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational psychology, 75(3), 327.
Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement
This meta-analysis systematically synthesized results from 26 component studies, including dissertations and published articles, which reported at least one correlation between collective teacher efficacy and school achievement.
Eells, R. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement.
Detrimental effects of reward: Reality or myth?
An analysis of a quarter century of research on intrinsic task interest and creativity revealed, however, that (a) detrimental effects of reward occur under highly restricted, easily avoidable conditions; (b) mechanisms of instrumental and classical conditioning are basic for understanding incremental and decremental effects of reward on task motivation; and (c) positive effects of reward on generalized creativity are easily attainable using procedures derived from behavior theory.
Eisenberger, R., & Cameron, J. (1996). Detrimental effects of reward: Reality or myth?. American psychologist, 51(11), 1153.
Planning, Implementing and Evaluating Evidence-Based Interventions
This section includes tools and resources that can help school leaders, teachers, and other stakeholders be more strategic in their decision-making about planning, implementing, and evaluating evidence-based interventions to improve the conditions for learning and facilitate positive student outcomes.
Elliott, S. N., Witt, J. C., & Kratochwill, T. R. (1991). Selecting, implementing, and evaluating classroom interventions. Interventions for achievement and behavior problems, 99-135.
Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?
Thirty-one studies were located in each of which students and faculty specified the instructional characteristics they considered particularly important to good teaching and effective instruction.
Feldman, K. A. (1988). Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?. Research in Higher Education, 28(4), 291-329.
The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis
This paper aim to determine the correlation between teacher clarity and the mean class student learning (achievement gain) in normal public-education classes in English-speaking, industrialized countries.
Fendick, F. (1992). The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis.
In search of program implementation: 792 replications of the Teaching-Family Model
This chapter discusses a solution-oriented and incremental approach to solving major social
problems.
Fixsen, D. L., Blase, K. A., Timbers, G. D., & Wolf, M. M. (2001). In search of program implementation: 792 replications of the Teaching-Family Model. Offender rehabilitation in practice: Implementing and evaluating effective programs, 149-166.
Is "Learning Disabilities" Just a Fancy Term for Low Achievement? A Meta-Analysis of Reading Differences between Low Achievers with and without the Label.
This paper reports the results of a study that investigated the reading differences between students who were low achieving, both with and without the label of learning disabilities (LD).
Fuchs, D., Fuchs, L. S., Mathes, P. G., Lipsey, M. W., & Roberts, P. H. (2001). Is" Learning Disabilities" Just a Fancy Term for Low Achievement?: A Meta-Analysis of Reading Differences Between Low Achievers with and Without the Label. Executive Summary. ERIC Clearinghouse.
Responsiveness‐to‐intervention: Definitions, evidence, and implications for the learning disabilities construct.
The authors describe both types of responsiveness-to-intervention (RTI), "problem solving" and "standard-protocol" then review empirical evidence bearing on their effectiveness and feasibility, and conclude that more needs to be understood before RTI may be viewed as a valid means of identifying students with Learning Disabilities
Fuchs, D., Mock, D., Morgan, P. L., & Young, C. L. (2003). Responsiveness‐to‐intervention: Definitions, evidence, and implications for the learning disabilities construct. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 18(3), 157-171.
Mathematics performance assessment in the classroom: Effects on teacher planning and student problem solving
The purpose of this study was to examine effects of classroom-basedperformance-assessment (PA)-driven instruction.
Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Karns, K., Hamlett, C. L., & Katzaroff, M. (1999). Mathematics performance assessment in the classroom: Effects on teacher planning and student problem solving. American educational research journal, 36(3), 609-646.
Enhancing third-grade student' mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies.
The authors assessed the contribution of self-regulated learning strategies (SRL), when combined with problem-solving transfer instruction (L. S. Fuchs et al., 2003), on 3rd-graders' mathematical problem solving. SRL incorporated goal setting and self-evaluation.
Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Prentice, K., Burch, M., Hamlett, C. L., Owen, R., & Schroeter, K. (2003). Enhancing third-grade student'mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies. Journal of educational psychology, 95(2), 306.
Enhancing third-grade students’ mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies
The authors assessed the contribution of self-regulated learning strategies (SRL), when combined with problem-solving transfer instruction (L. S. Fuchs et al., 2003), on 3rd-graders' mathematical problem solving. SRL incorporated goal setting and self-evaluation.
Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Prentice, K., Burch, M., Hamlett, C. L., Owen, R., & Schroeter, K. (2003). Enhancing third-grade students’ mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95(2), 306–315.
The benefits of computer-generated feedback for mathematics problem solving
The goal of the current research was to better understand when and why feedback has positive effects on learning and to identify features of feedback that may improve its efficacy. Results suggest that minimal computer-generated feedback can be a powerful form of guidance during problem solving.
Fyfe, E. R., & Rittle-Johnson, B. (2016). The benefits of computer-generated feedback for mathematics problem solving. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 147, 140-151.
Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited
Research begun in the 1960s provided the impetus for teacher educators to urge classroom teachers to establish classroom rules, deliver high rates of verbal/nonverbal praise, and, whenever possible, to ignore minor student provocations. The research also discuss several newer strategies that warrant attention.
Gable, R. A., Hester, P. H., Rock, M. L., & Hughes, K. G. (2009). Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited. Intervention in School and Clinic, 44(4), 195-205.
Preparing for culturally responsive teaching.
In this article, a case is made for improving the school success of ethnically diverse students through culturally responsive teaching and for preparing teachers in preservice education programs with the knowledge, attitudes, and skills needed to do this.
Gay, G. (2002). Preparing for culturally responsive teaching. Journal of teacher education, 53(2), 106-116.
Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice.
Combining insights from multicultural education theory with real-life classroom stories, this book demonstrates that all students will perform better on multiple measures of achievement when teaching is filtered through students’ own cultural experiences. This perennial bestseller continues to be the go-to resource for teacher professional learning and preservice courses.
Gay, G. (2018). Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice. Teachers College Press.
A practical application of time management
This chapter progresses four specific components of “a practical application of time management”.
George, D. (2012). A practical application of time management.Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221928054_A_Practical_Application_of_Time_Management
Incentives in organizations
The author summarizes four new strands in agency theory that help him think about incentives in real organizations. The author concludes by suggesting two avenues for further progress in agency theory: better integration with organizational economics, and cross-pollination with other fields that study organizations.
Gibbons, R. (1998). Incentives in organizations. Journal of economic perspectives, 12(4), 115-132.
Teamwork, soft skills, and research training.
This paper provide a list of soft skills that are important for collaboration and teamwork, based on the authors own experience and from an opinion survey of team leaders. This paper also outline workable short courses for graduate schools to strengthen teamwork and collaboration skills among research students.
Gibert, A., Tozer, W. C., & Westoby, M. (2017). Teamwork, soft skills, and research training. Trends in ecology & evolution, 32(2), 81-84.
Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement.
This article evaluates the extent to which quantity of instruction influences time spent on self‐
study and achievement. The results suggest that time spent on self‐study is primarily a function of the degree of time allocated to instruction.
Gijselaers, W. H., & Schmidt, H. G. (1995). Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement. Educational Research and Evaluation, 1(2), 183-201.
Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement.
This article evaluates the extent to which quantity of instruction influences time spent on self‐
study and achievement. The results suggest that time spent on self‐study is primarily a function of the degree of time allocated to instruction.
Gijselaers, W. H., & Schmidt, H. G. (1995). Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement. Educational Research and Evaluation, 1(2), 183-201.
Human Competence: Engineering Worthy Performance
This book is written by Tom Gilbert who is one of the most influential theorists in building a science of performance management. Although not explicitly written for educators, it offers concrete examples principals can apply to improve the performance of teachers and other school personnel so student’s can ultimately be successful.
Gilbert, T. F. (1978). Human competence�engineering worthy performance. NSPI Journal, 17(9), 19-27.
Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers.
The article presents an overview of these tenets drawn from opinion positions, practical experiences, and empirical research studies. There is clear evidence that additional empirical research would be beneficial.
Gillard, S. (2009). Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers. Issues in informing science & information technology, 6.
When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior.
This book discuss how extrinsic incentives may come into conflict with other motivations and examine the research literature in which monetary incentives have been used in a nonemployment context to foster the desired behavior. The conclusion sums up some lessons on when extrinsic incentives are more or less likely to alter such behaviors in the desired directions.
Gneezy, U., Meier, S., & Rey-Biel, P. (2011). When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 25(4), 191-210.
The skills Americans say kids need to succeed in life.
Pew Research Center recently asked a national sample of adults to select among a list of 10 skills: “Regardless of whether or not you think these skills are good to have, which ones do you think are most important for children to get ahead in the world today?”
Goo, S. A. R. A. (2015). The skills Americans say kids need to succeed in life. Pew Research Center.
Why marriages succeed or fail.
This breakthrough book guides you through a series of self-tests designed to help you determine what kind of marriage you have, where your strengths and weaknesses are, and what specific actions you can take to help your marriage.
Gottman, J., Gottman, J. M., & Silver, N. (1995). Why marriages succeed or fail: And how you can make yours last. Simon and Schuster.
Implicit bias: Scientific foundations.
This Article introduces implicit bias-an aspect of the new science of unconscious mental processes that has substantial bearing on discrimination law.
Greenwald, A. G., & Krieger, L. H. (2006). Implicit bias: Scientific foundations. California Law Review, 94(4), 945-967.
Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom
This study examined teachers' relational approach to discipline as a predictor of high school students' behavior and their trust in teacher authority.
Gregory, A., & Ripski, M. B. (2008). Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom. School Psychology Review, 37(3), 337.
Sustainability: An Enduring Commitment to Success
The infrastructure supporting organizational transformation to a problem-solving system occurred on two levels, global and local. The reform effort is described in four phases.
Grimes, J., Kurns, S., Tilly, W. D., & II, I. (2006). Sustainability: An enduring commitment to success. School Psychology Review, 35(2), 224.
A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: Interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships.
The purpose of the current study was to test theoretically derived hypotheses regarding the relationships between team efficacy, potency, and performance and to examine the moderating effects of level of analysis and interdependence on observed relationships.
Gully, S. M., Incalcaterra, K. A., Joshi, A., & Beaubien, J. M. (2002). A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships. Journal of applied psychology, 87(5), 819.
Treatment Integrity Assessment: How Estimates of Adherence, Quality, and Exposure Influence Interpretation of Implementation.
This study evaluated the differences in estimates of treatment integrity be measuring different dimensions of it.
Hagermoser Sanetti, L. M., & Fallon, L. M. (2011). Treatment Integrity Assessment: How Estimates of Adherence, Quality, and Exposure Influence Interpretation of Implementation. Journal of Educational & Psychological Consultation, 21(3), 209-232.
Mediation of interpersonal expectancy effects: 31 meta-analyses.
Reviews 135 studies on mediation and classifies results into 31 behavior categories (e.g., praise, climate, asks questions). Separate meta-analyses for each mediating variable were conducted. Results were also analyzed separately for studies that examined the relation between expectations and emitted behaviors and between mediating behaviors and outcome measures.
Harris, M. J., & Rosenthal, R. (1985). Mediation of interpersonal expectancy effects: 31 meta-analyses. Psychological bulletin, 97(3), 363.
Assessment for Intervention: A Problem-solving Approach
This book provides a complete guide to implementing a wide range of problem-solving assessment methods: functional behavioral assessment, interviews, classroom observations, curriculum-based measurement, rating scales, and cognitive instruments.
Harrison, P. L. (2012). Assessment for intervention: A problem-solving approach. Guilford Press.
Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Visible Learning for Teachers: Maximizing Impact on Learning
This book takes over fifteen years of rigorous research into education practices and provides teachers in training and in-service teachers with concise summaries of the most effective interventions and offers practical guidance to successful implementation in classrooms.
Hattie, J. (2012). Visible learning for teachers: Maximizing impact on learning. Routledge.
Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die
This book reveal the anatomy of ideas that stick and explain ways to make ideas stickier, such as applying the human scale principle, using the Velcro Theory of Memory, and creating curiosity gaps. Along the way, we discover that sticky messages of all kinds draw their power from the same six traits.
Heath, C., & Heath, D. (2007). Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die. Random House.
Hard evidence on soft skills.
This paper summarizes recent evidence on what achievement tests measure; how achievement tests relate to other measures of "cognitive ability" like IQ and grades; the important skills that achievement tests miss or mismeasure, and how much these skills matter in life.
Heckman, J. J., & Kautz, T. (2012). Hard evidence on soft skills. Labour economics, 19(4), 451-464.
Evaluating the relationships between poverty and school.
This study examined the relationships between poverty and a school's academic performance (both student achievement and growth).
Hegedus, A. (2018). Evaluating the Relationships between Poverty and School Performance. NWEA Research. NWEA.
What do we know about time management? A review of the literature and a psychometric critique of instruments assessing time management.
The purpose of this chapter is to examine the existing time management literature.
Hellsten, L. M. (2012). What do we know about time management. A review of the literature and a psychometric critique of instruments assessing time management. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech, 21-22.
A meta-analysis on the correlation between the implicit association test and explicit self-report measures.
A meta-analysis on the relationship between the Implicit Association Test (IAT) and corresponding explicit self-report measures was conducted.
Hofmann, W., Gawronski, B., Gschwendner, T., Le, H., & Schmitt, M. (2005). A meta-analysis on the correlation between the Implicit Association Test and explicit self-report measures. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31(10), 1369-1385.
Education reparation: an examination of Black teacher retention
The purpose of this study was to examine the workplace factors that positively and negatively impact Black K12 teacher retention. This study utilized a mixed-method approach to examine the qualitative and quantitative data.
Hollinside, M. M. (2017). Education reparation: an examination of Black teacher retention (Doctoral dissertation).
Principal’s time use and school effectiveness.
This paper examines the relationship between the time principals spent on different types of activities and school outcomes including student achievement, teacher and parent assessments of the school, and teacher satisfaction.
Horng, E. L., Klasik, D., & Loeb, S. (2010). Principal's time use and school effectiveness. American journal of education, 116(4), 491-523.
Defining the meaning of teacher success in Hong Kong.
This study have sought to investigate teacher success in Hong Kong. The study aims to achieve the following objectives: to acquire an initial understanding of how Hong Kong teachers conceptualize teacher success, to identify the factors hindering teacher success; to study the relationship between professional development and teacher success.
Hung, C. M., Oi, A. K., Chee, P. K., & Man, C. L. (2007). Defining the meaning of teacher success in Hong Kong. In Handbook of teacher education (pp. 415-432). Springer, Dordrecht.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
The existence of implicit bias is beyond reasonable doubt: A refutation of ideological and methodological objections and executive summary of ten studies that no manager should ignore
In this article, we respond at length to recent critiques of research on implicit bias, especially studies using the Implicit Association Test (IAT). These studies reveal that students, nurses, doctors, police officers, employment recruiters, and many others exhibit implicit biases with respect to race, ethnicity, nationality, gender, social status, and other distinctions.
Jost, J. T., Rudman, L. A., Blair, I. V., Carney, D. R., Dasgupta, N., Glaser, J., & Hardin, C. D. (2009). The existence of implicit bias is beyond reasonable doubt: A refutation of ideological and methodological objections and executive summary of ten studies that no manager should ignore. Research in organizational behavior, 29, 39-69.
Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices
The authors examined the effectiveness of self-monitoring for increasing the rates of teacher praise statements and the acceptability of using this technique for teachers. This study's results support the use of self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices, namely praise, and further demonstrates high social validity for the participant and the students.
Kalis, T. M., Vannest, K. J., & Parker, R. (2007). Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 51(3), 20-27.
Implicit bias in the courtroom.
What, if anything, should we do about implicit bias in the courtroom? The authors comprises legal academics, scientists, researchers, and even a sitting federal judge who seek to answer this question in accordance with behavioral realism.
Kang, J., Bennett, M., Carbado, D., & Casey, P. (2011). Implicit bias in the courtroom. UCLa L. rev., 59, 1124.
Teacher attrition and mobility: Results from the 2008–09 teacher follow-up survey
The objective of TFS is to provide information about teacher mobility and attrition among elementary and secondary school teachers who teach in grades K–12 in the 50 states and the District of Columbia.
Keigher, A. (2010). Teacher Attrition and Mobility: Results from the 2008-09 Teacher Follow-Up Survey. First Look. NCES 2010-353. National Center for Education Statistics.
How Does Reading Proficiency Correlate With a Student's Socio-Economic Status?
This analysis examines the influence of poverty on student reading performance across grade levels.
Keyworth, R. (2015). How does reading proficiency correlate with a student's socio-economic status? Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/how-does-reading-proficiency
Instructional coaching
This article discusses instructional coaching as well as the eight factors that can increase the likelihood that coaching will be a real fix for a school.
Knight, J. (2006). Instructional Coaching. School Administrator, 63(4), 36.
Work groups and teams in organizations.
This review chapter examines the literature on work team effectiveness. This paper consider their nature, define them, and identify four critical conceptual issues—context, workflow, levels, and time—that serve as review themes and discuss the multitude of forms that teams may assume.
Kozlowski, S. W., & Bell, B. S. (2003). Work groups and teams in organizations. Handbook of psychology, 333-375.
Teacher-student relationship, student mental health, and dropout from upper secondary school
The purpose of this literature search study was to assess the status of knowledge regarding the association between teacher–student relationship (TSR), dropout from upper secondary school, and student mental health.
Krane, V., Karlsson, B., Ness, O., & Kim, H. S. (2016). Teacher–student relationship, student mental health, and dropout from upper secondary school: A literature review. Lærer-elev-relasjoner, elevers psykiske helse og frafall i videregående skole. En eksplorerende studie om samarbeid og den store betydningen av de små ting.
Teacher stress and burnout: An international review
This paper reviews studies on teacher stress and burnout conducted over the past decade. The range of studies considered indicates that this topic is now of major international concern.
Kyriacou, C. (1987). Teacher stress and burnout: An international review. Educational research, 29(2), 146-152.
Toward a theory of culturally relevant pedagogy.
This article attempts to challenge notions about the intersection of culture and teaching that rely solely on microanalytic or macro analytic perspective
Ladson-Billings, G. (1995). Toward a theory of culturally relevant pedagogy. American educational research journal, 32(3), 465-491.
The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer
This article discusses differences that are hypothesized to exist between hard‐ (technical) and soft‐ (intrapersonal and interpersonal) skills training that we believe impact the degree of training transfer achieved.
Laker, D. R., & Powell, J. L. (2011). The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 22(1), 111-122.
Academic and social integration variables and secondary student persistence in distance education.
A survey of 351 secondary distance education students (181 responses) found significant relationships between 2 academic variables (educational goals and study time) and academic persistence;
Laube, M. R. (1992). Academic and Social Integration Variables and Secondary Student Persistence in Distance Education. Research in Distance Education, 4(1), 2-9.
Performance pay and productivity
Much of the theory in personnel economics relates to effects of monetary incentives on output, but the theory was untested because appropriate data were unavailable. A new data set for the Safelite Glass Corporation tests the predictions that average productivity will rise, the firm will attract a more able workforce, and variance in output across individuals at the firm will rise when it shifts to piece rates.
Lazear, E. P. (2000). Performance pay and productivity. American Economic Review, 90(5), 1346-1361.
Forgotten racial equality: Implicit bias, decision-making, and misremembering
In this article, the author claim that judges and jurors unknowingly misremember case facts in racially biased ways. Drawing upon studies from implicit social cognition, human memory research, and legal decisionmaking, I argue that implicit racial biases affect the way judges and jurors encode, store, and recall relevant case facts.
Levinson, J. D. (2007). Forgotten racial equality: Implicit bias, decisionmaking, and misremembering. Duke LJ, 57, 345.
Teaching anti-bias curriculum in teacher education programs: What and how.
In this article, the authors discuss what an anti-bias curriculum is, provide the theoretical framework and rationale for involving teacher candidates in certain activities that promote the anti-bias curriculum, and offer additional anti-bias strategies for teacher candidates and teacher educators to implement in their classrooms.
Lin, M., Lake, V. E., & Rice, D. (2008). Teaching anti-bias curriculum in teacher education programs: What and how. Teacher Education Quarterly, 35(2), 187-200.
Expectations for students.
The evidence in this paper suggest that schools can improve student learning by encouraging teachers and students to set their sights high.
Lumsden, L. (1997). Expectations for students (pp. 1-4). ERIC Clearinghouse on Educational Management, University of Oregon.
Effects of performance feedback and coaching on the problem-solving process: Improving the integrity of implementation and enhancing student outcomes
the present study was designed to learn more about how to strengthen the integrity of the problem-solving process
Lundahl, A. A. (2010). Effects of Performance Feedback and Coaching on the Problem-Solving Process: Improving the Integrity of Implementation and Enhancing Student Outcomes. ProQuest LLC. 789 East Eisenhower Parkway, PO Box 1346, Ann Arbor, MI 48106.
Problem solving and intervention design: Guidelines for the evaluation of technical adequacy.
In this article, guidelines for evaluating the technical adequacy of that process are described. The guidelines highlight the interdependencies among assessment functions, subsumed by the goal of helping, and the role of structural factors (e.g., collaboration) in shaping the meaningfulness, appropriateness, and usefulness of the assessment-intervention process.
Macmann, G. M., Barnett, D. W., Allen, S. J., Bramlett, R. K., Hall, J. D., & Ehrhardt, K. E. (1996). Problem solving and intervention design: Guidelines for the evaluation of technical adequacy. School Psychology Quarterly, 11(2), 137.
Using habit reversal to decrease filled pauses in public speaking.
This study evaluated the effectiveness of simplified habit reversal in reducing filled pauses that occur during public speaking. Filled pauses consist of “uh,” “um,” or “er”; clicking sounds; and misuse of the word “like.” During post-intervention assessments, all 6 participants exhibited an immediate decrease in filled pauses.
Mancuso, C., & Miltenberger, R. G. (2016). Using habit reversal to decrease filled pauses in public speaking. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 49(1), 188-192.
Creating A Problem-Solving Culture: Exploring Problem Resolution In The Workplace
This paper examines and solutions associated with effective problem solving.
Marone, M. and Blauth, C. (2004). Creating A Problem-Solving Culture: Exploring Problem Resolution In The Workplace. Achieveglogal, Inc.
Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher
How does classroom management affect student achievement? What techniques do
teachers find most effective? How important are schoolwide policies and practices in setting
the tone for individual classroom management? In this follow-up to What Works in Schools,
Robert J. Marzano analyzes research from more than 100 studies on classroom
management to discover the answers to these questions and more. He then applies these
findings to a series of" Action Steps"--specific strategies.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Team effectiveness 1997–2007: A review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future
The authors review team research that has been conducted over the past 10 years. They discuss the nature of work teams in context and note the substantive differences underlying different types of teams.
Mathieu, J., Maynard, M. T., Rapp, T., & Gilson, L. (2008). Team effectiveness 1997-2007: A review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future. Journal of management, 34(3), 410-476.
“Soft Skills”: A phrase in search of meaning
This literature review explores the definition of soft skills; contrasts skills with related concepts, such as personality traits, attitudes, beliefs, and values; and compares a set of soft skill typologies
Matteson, M. L., Anderson, L., & Boyden, C. (2016). " Soft Skills": A Phrase in Search of Meaning. portal: Libraries and the Academy, 16(1), 71-88.
The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs.
This study provides a description of 34 practicing teachers' beliefs regarding the role of empathy as an attribute in their effectiveness with culturally diverse students. Empathy involves cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that teachers believed were manifested in their practice.
McAllister, G., & Irvine, J. J. (2002). The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs. Journal of teacher education, 53(5), 433-443.
Teaching high-expectation strategies to teachers through an intervention process.
This study describes the outcomes of an intervention focused on the strategies and practices of high expectation teachers. Findings revealed that teachers involved in the intervention refined and changed their practices by creating flexible grouping, enhancing the class climate, and supporting students’ goal setting.
McDonald, L., Flint, A., Rubie-Davies, C. M., Peterson, E. R., Watson, P., & Garrett, L. (2016). Teaching high-expectation strategies to teachers through an intervention process. Professional Development in education, 42(2), 290-307.
Forewarning and forearming stereotype-threatened students.
This study investigated communicative strategies for helping female students cope with ‘‘stereotype threat’’. The results demonstrate that priming a positive achieved identity (e.g., private college student) can subdue stereotype threat associated with an ascribed identity (e.g., female).
McGlone, M. S., & Aronson, J. (2007). Forewarning and forearming stereotype-threatened students. Communication Education, 56(2), 119-133.
Exploring the Use of Social Media Network Methods in Designing Healthcare Quality Improvement Teams.
In this paper, the authors use tools from social network analysis (SNA) to derive principles for the design of effective clinical quality improvement teams and explore the implementation of these principles using social network data collected from the inpatient general medicine services at a large academic medical center in Chicago, USA
Meltzer, D., Chung, J., Khalili, P., Marlow, E., Arora, V., Schumock, G., & Burt, R. (2010). Exploring the use of social network methods in designing healthcare quality improvement teams. Social science & medicine, 71(6), 1119-1130.
Demanding Medical Excellence: Doctors and Accountability in The Information Age.
This book reveals how the information revolution is changing the way doctors make decisions. Michael Millenson, a three-time Pulitzer Prize nominee as a health-care reporter for the Chicago Tribune, illustrates serious flaws in contemporary medical practice and shows ways to improve care and save tens of thousands of lives.
Millenson, M. L. (2018). Demanding medical excellence: Doctors and accountability in the information age. University of Chicago Press.
Falling off track: How teacher-student relationships predict early high school failure rates
This paper examines the relationship between the climate of teacher-student relations within a school and individual student's likelihood of freshman year success. Results find that teacher-student climate does have a significant effect.
Miller, S. R. (2000). Falling Off Track: How Teacher-Student Relationships Predict Early High School Failure Rates.
Classroom social climate and student absences and grades
this paper investigated the relationship between student and teacher perceptions of the social environments of 19 high school classes and student absenteeism rates and the average final grades given by the teacher.
Moos, R. H., & Moos, B. S. (1978). Classroom social climate and student absences and grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 70(2), 263.
Updating the Project Management Bodies of Knowledge
This paper reviews the status of BOKs and reports research on what topics should be included in the BOK (1) conducted at the Center of Research in the Management of Projects (CRMP) using data from 117 companies and (2) through ongoing work on a Global framework sponsored by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and others.
Morris, P. W. (2001). Updating the project management bodies of knowledge. Project Management Journal, 32(3), 21-30.
Radical equations: Math literacy and civil rights
Begun in 1982, the Algebra Project is transforming math education in twenty-five cities. The Project works with entire communities-parents, teachers, and especially students-to create a culture of literacy around algebra, a crucial stepping-stone to college math and opportunity.
Moses, R., & Cobb, C. E. (2002). Radical equations: Civil rights from Mississippi to the Algebra Project. Beacon Press.
K–12 education: Discipline disparities for black students, boys, and students with disabilities.
This report examines: (1) patterns in disciplinary actions among public K-12 schools; (2) challenges selected school districts have with student behavior and how they approach school discipline; and (3) actions the Departments of Education and Justice have taken to identify and address disparities or discrimination in school discipline.
Nowicki, J. M. (2018). K-12 Education: Discipline Disparities for Black Students, Boys, and Students with Disabilities. Report to Congressional Requesters. GAO-18-258. US Government Accountability Office.
Examination of the relation between academic procrastination and time management skills of undergraduate students in terms of some variables
Academic procrastination is seen to be quite common among undergraduates and time management is thought to be one of the possible reasons of it. Two surveys, academic procrastination and time management, were given to 332 undergraduate students in this correlational research.
Ocak, G., & Boyraz, S. (2016). Examination of the relation between academic procrastination and time management skills of undergraduate students in terms of some variables. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4(5), 76-84.
Relating communication competence to teaching effectiveness: Implication for teacher education
This paper posits that teacher education should emphasize both content knowledge and communication skills. It follows up the contention by conceptualizing communication, exploring teacher communication competence, and finally suggesting the introduction of Teacher Communication Skills (TCS) course in the curricula of teacher education across levels.
Okoli, A. C. (2017). Relating Communication Competence to Teaching Effectiveness: Implication for Teacher Education. Journal of Education and Practice, 8(3), 150-154.
Losing our future: How minority youth are being left behind by the graduation rate crisis
This report seeks to highlight some disparities to draw the public’s and policymakers’ attention to the urgent need to address this educational and civil rights crisis. Using a more accurate method for calculating graduation rates, they provide estimates of high school graduation rates, distinguished at the state and district level, and disaggregated by race.
Orfield, G., Losen, D., Wald, J., & Swanson, C. B. (2004). Losing our future: How minority youth are being left behind by the graduation rate crisis. Civil Rights Project at Harvard University (The).
Predicting ethnic and racial discrimination: A meta-analysis of IAT criterion studies
This article reports a meta-analysis of studies examining the predictive validity of the Implicit Association Test (IAT) and explicit measures of bias for a wide range of criterion measures of discrimination.
Oswald, F. L., Mitchell, G., Blanton, H., Jaccard, J., & Tetlock, P. E. (2013). Predicting ethnic and racial discrimination: A meta-analysis of IAT criterion studies. Journal of personality and social psychology, 105(2), 171.
Work Teams in Schools
"More is better"--this precept lies behind the burgeoning use of work teams to handle problem-solving and decision-making in schools and school districts. Teams are said to build stronger relationships among those involved in education and, ultimately, to benefit students because more people with broader perspectives help to shape a stronger educational program.
Oswald, L. J. (1996). Work Teams in Schools. ERIC Digest, Number 103.
Time Management Behavior as a Moderator for the Job Demand-Control Interaction.
The interaction effects of time management, work demands, and autonomy on burnout were investigated in a survey study of 123 elementary teachers.
Peeters, M. A., & Rutte, C. G. (2005). Time management behavior as a moderator for the job demand-control interaction. Journal of occupational health psychology, 10(1), 64.
Classroom Assessment Scoring System (CLASS) Manual
Positive teacher-student interactions are a primary ingredient of quality early educational experiences that launch future school success. With CLASS, educators finally have an observational tool to assess classroom quality in pre-kindergarten through grade 3 based on teacher-student interactions rather than the physical environment or a specific curriculum
Pianta, R. C., La Paro, K. M., & Hamre, B. K. (2008). Classroom Assessment Scoring System™: Manual K-3. Baltimore, MD, US: Paul H Brookes Publishing.
Meta-analysis of field experiments shows no change in racial discrimination in hiring over time
This study investigates change over time in the level of hiring discrimination in US labor markets.
Quillian, L., Pager, D., Hexel, O., & Midtbøen, A. H. (2017). Meta-analysis of field experiments shows no change in racial discrimination in hiring over time. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(41), 10870–10875.
The effectiveness of teams in organizations: a meta-analysis
The proposed meta-analysis of 61 independent samples aims to identify whether, and if so under what conditions, team working in organizations is related to organizational effectiveness.
Richter, A. W., Dawson, J. F., & West, M. A. (2011). The effectiveness of teams in organizations: A meta-analysis.International Journal of Human Resource Management, 22(13), 2749–2769.
The Impact of Leadership On Student Outcomes: an Analysis Of The Differential Effects Of Leadership Types
The purpose of this study is to examine the relative impact of different types of leadership on students’ academic and nonacademic outcomes.
Robinson, V. M., Lloyd, C. A., & Rowe, K. J. (2008). The impact of leadership on student outcomes: An analysis of the differential effects of leadership types. Educational administration quarterly.
Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in
This study identified the top 10 soft skills as perceived the most important by business executives: integrity, communication, courtesy, responsibility, social skills, positive attitude, professionalism, flexibility, teamwork, and work ethic.
Robles, M. M. (2012). Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 75(4), 453–465.
Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace
This study identified the top 10 soft skills as perceived the most important by business executives: integrity, communication, courtesy, responsibility, social skills, positive attitude, professionalism, flexibility, teamwork, and work ethic.
Robles, M. M. (2012). Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 75(4), 453–465.
Interpersonal expectancy effects: The first 345 studies
This paper general purpose is to summarize the results of 345 experiments investigating interpersonal expectancy effects. These studies fall into eight broad categories of research: reaction time, inkblot tests, animal learning, laboratory interviews, psychophysical judgments, learning and ability, person perception, and everyday life situations.
Rosenthal, R., & Rubin, D. (1978). Interpersonal expectancy effects: The first 345 studies. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 3, 377–415.
Expecting the best for students: Teacher expectations and academic outcomes
This study aimed to explore differences in teachers’ expectations and judgments of student reading performance for Maori, Pacific Island, Asian and New Zealand European students. A further objective was to compare teacher expectations and judgments with actual student achievement.
Rubie‐Davies, C., Hattie, J., & Hamilton, R. (2006). Expecting the best for students: Teacher expectations and academic outcomes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(3), 429-444.
Improving Performance: How To Manage The White Space On The Chart
Improving Performance has been a pivotal book in the creation of the performance management movement by showing how to bridge the gap between organization strategy and the individual. It can be used as guide for principals to link planning to action, implementation of organization change, and offering ways to redesign processes to overcome obstacles that impede implementation.
Rummler, G. A., & Brache, A. P. (2012). Improving performance: How to manage the white space on the organization chart. John Wiley & Sons.
The Problem-Solving Power Of Teachers
This article examines practical strategies to address problems teacher are confronted with in the classroom.
Sacks, A. (2013). The problem-solving power of teachers. Educational Leadership, 71(2), 18-22.
Developing and enhancing teamwork in organizations: Evidence-based best practices and guidelines
This latest volume in the SIOP Professional Practice Series was inspired by a Leading Edge Conference sponsored by the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology to bring together leading-edge practitioners and academics to exchange views and knowledge about effective teams and help lead to better practice in that area.
Salas, E., Tannenbaum, S., Cohen, D., & Latham, G. (Eds.). (2013). Developing and enhancing teamwork in organizations: Evidence-based best practices and guidelines (Vol. 33). John Wiley & Sons.
Treatment integrity assessment within a problem-solving model
The purpose of this chapter is to explain the role of treatment integrity assessment within the “implementing solutions” stage of a problem-solving model.
Sanetti, L. H., & Kratochwill, T. R. (2005). Treatment integrity assessment within a problem-solving model. Assessment for intervention: A problem-solving approach, 314-325.
Interest as a predictor of academic achievement: A meta-analysis of research.
This paper provides an overview of previous research results pertaining to the relation between interest and academic achievement. focus on the conceptualization and operationalization of interest.
Schiefele, U., Krapp, A., & Winteler, A. (1992). Interest as a predictor of academic achievement: A meta-analysis of research.
A meta‐analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States
This project consisted of a meta-analysis of U.S. research published from 1980 to 2004 on the effect of specific science teaching strategies on student achievement. T
Schroeder, C. M., Scott, T. P., Tolson, H., Huang, T. Y., & Lee, Y. H. (2007). A meta‐analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 44(10), 1436-1460.
The importance of soft skills: Education beyond academic knowledge.
This paper makes a survey of the importance of soft skills in students’ lives both at college and after college. It discusses how soft skills complement hard skills, which are the technical requirements of a job the student is trained to do.
Schulz, B. (2008). The importance of soft skills: Education beyond academic knowledge.
Best Practices in Using Curriculum-Based Measurement in a Problem-Solving Model
This chapter provides a rationale for why school psychologists and other educators should be interested in the use of CBM, especially within a particular decision-making model, Problem Solving.
Shinn, M. R. (1995). Best practices in curriculum-based measurement and its use in a problem-solving model. Best practices in school psychology III, 547-567.
Teams in the Military: A Review and Emerging Challenges
the purpose of this chapter is to review the science of teams and their effectiveness, extrapolate critical lessons learned, and highlight several future challenges critical for military psychology to address in order to prepare future military teams for success.
Shuffler, M. L., Pavlas, D., & Salas, E. (2012). Teams in the military: A review and emerging challenges. In J. H. Laurence & M. D. Matthews (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of military psychology(pp. 282–310). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Interpersonal problem solving as a mediator of behavioral adjustment in preschool and kindergarten children.
This is an experimental test of the mediating function of interpersonal cognitive problem solving skills on behavioral adjustment in preschool and kindergarten children.
Shure, M. B., & Spivack, G. (1981). Interpersonal problem solving as a mediator of behavioral adjustment in preschool and kindergarten children. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 1(1), 29-44.
Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a systematic literature search to identify evidence-based classroom management practices.
Simonsen, B., Fairbanks, S., Briesch, A., Myers, D., & Sugai, G. (2008). Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice. Education and Treatment of Children, 31(3), 351-380.
Teacher job satisfaction and motivation to leave the teaching profession: Relations with school context, feeling of belonging, and emotional exhaustion.
This study examines the relations between school context variables and teachers’ feeling of belonging, emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction, and motivation to leave the teaching profession. Six aspects of the school context were measured: value consonance, supervisory support, relations with colleagues, relations with parents, time pressure, and discipline problems.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2011). Teacher job satisfaction and motivation to leave the teaching profession: Relations with school context, feeling of belonging, and emotional exhaustion. Teaching and teacher education, 27(6), 1029-1038.
Science and human behavior
The psychology classic—a detailed study of scientific theories of human nature and the possible ways in which human behavior can be predicted and controlled.
Skinner, B. F. (1965). Science and human behavior (No. 92904). Simon and Schuster.
Teacher expectations.
The purpose of this paper is to integrate statistically the results of the literature on teacher expectations.
Smith, M. L. (1980). Teacher expectations. Evaluation in Education, 4, 53-55.
Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Several barriers can impede critical thinking instruction. However, actively engaging students in project-based or collaborative activities can encourage students’ critical thinking development if instructors model the thinking process, use effective questioning techniques, and guide students’ critical thinking processes.
Snyder, L. G., & Snyder, M. J. (2008). Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills. The Journal of Research in Business Education, 50(2), 90.
Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Several barriers can impede critical thinking instruction. However, actively engaging students in project-based or collaborative activities can encourage students’ critical thinking development if instructors model the thinking process, use effective questioning techniques, and guide students’ critical thinking processes.
Snyder, L. G., & Snyder, M. J. (2008). Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills. The Journal of Research in Business Education, 50(2), 90.
Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness
The present study explores conflict management as a team phenomenon in schools. The author examined how the contextual variables (task interdependence, goal interdependence) are related to team conflict management style (integrating vs. dominating) and school team effectiveness (team performance).
Somech, A. (2008). Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness. Educational administration quarterly, 44(3), 359-390.
Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness
The present study explores conflict management as a team phenomenon in schools. The author examined how the contextual variables (task interdependence, goal interdependence) are related to team conflict management style (integrating vs. dominating) and school team effectiveness (team performance).
Somech, A. (2008). Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness. Educational administration quarterly, 44(3), 359-390.
Evidence-based Practice: A Framework for Making Effective Decisions.
Evidence-based practice is a decision-making framework. This paper describes the relationships among the three cornerstones of this framework.
Spencer, T. D., Detrich, R., & Slocum, T. A. (2012). Evidence-based Practice: A Framework for Making Effective Decisions. Education & Treatment of Children (West Virginia University Press), 35(2), 127-151.
Classroom Management
In this overview, classroom management strategies have been grouped into four essential areas: rules and procedures, proactive management, well-designed and delivered instruction, and disruptive behavior management. These strategies are devised for use at both school and classroom levels.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Overview of Classroom Management.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-classroom.
Effective Instruction Overview
A summary of the available studies accumulated over the past 40 years on a key education driver, teacher competencies offers practical strategies, practices, and rules to guide teachers in ways to improve instruction that improves student performance and the quality of the work experience.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Effective Instruction Overview. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-overview
Teacher Soft Skills Overview
This overview examines the available research on the topic of soft skills (personal competencies) and how these proficiencies support the technical competencies required for success in school
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2018). Overview of Teacher Soft Skills.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-compentencies-soft-skills.
Best Practices in Developing Local Norms for Academic Problem Solving.
Stewart, L. H., & Kaminski, R. (2002). Best Practices in Developing Local Norms for Academic Problem Solving.
A contextual consideration of culture and school-wide positive behavior support
This article considers culture within the context of School-wide Positive Behavior Support. The paper provides an overview of culture and working definitions to assist educators to more effectively implement evidence-based practices.
Sugai, G., O’Keeffe, B. V., & Fallon, L. M. (2012). A contextual consideration of culture and school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 14(4), 197-208. Can pd
Fidelity of problem-solving implementation and relationship to student performance
This study examined the fidelity of problem-solving implementation by multidisciplinary
teams (MDTs) in 227 schools and the relationship to student outcomes.
Telzrow, C. F., McNamara, K., & Hollinger, C. L. (2000). Fidelity of problem-solving implementation and relationship to student performance. School Psychology Review, 29(3), 443.
Best practices in school psychology III.
Increasingly, school services are being guided by a problem solving approach and are evaluated by the achievement of positive outcomes. This shift is explored here in 96 chapters and 11 appendices. The volume provides a comprehensive reference relating contemporary research and thought to quality professional services
Thomas, A., & Grimes, J. (Eds.). (1995). Best practices in school psychology III.Washington, DC: National Association of School Psychologists.
Best Practices in School Psychology as a Problem-Solving Enterprise.
This chapter presents the conceptual and operational underpinnings of a problem-solving special education system designed to improve educational results for students with disabilities.
Tilly III, W. D. (2002). Best Practices in School Psychology as a Problem-Solving Enterprise.
The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model.
This chapter chronicles some of the major steps school psychology has taken toward adopting science as the basis of practice. Each step has yielded benefits for students as well as practice challenges to be overcome.
Tilly, W. D. (2008). The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology–5(pp. 17–36). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model.
This chapter chronicles some of the major steps school psychology has taken toward adopting science as the basis of practice. Each step has yielded benefits for students as well as practice challenges to be overcome.
Tilly, W. D. (2008). The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology–5(pp. 17–36). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Two meta-analyses exploring the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning.
This article reports the findings of two meta-analyses that explored the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning. Combined, the results suggest that teacher clarity has a larger effect for student affective learning than for cognitive learning. However, neither the effects for cognitive learning nor affective learning were homogeneous.
Titsworth, S., Mazer, J. P., Goodboy, A. K., Bolkan, S., & Myers, S. A. (2015). Two meta-analyses exploring the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning. Communication Education, 64(4), 385-418.
Preservice teachers’ perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum.
This study investigated preservice teachers' perceived barriers for implementing multicultural curriculum with preservice teachers as they began their teacher education program.
Van Hook, C. W. (2002). Preservice teachers' perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(4), 254-265.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Using data to advance learning outcomes in schools
This article describes the emergence and influence of evidence-based practice and data-based decision making in educational systems. This article describes the ways in which evidence-based practice (EBP) and response to intervention (RtI) can be used to improve efficacy, efficiency, and equity of educational services.
VanDerHeyden, A., & Harvey, M. (2013). Using data to advance learning outcomes in schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 15(4), 205-213.
What Influences Learning? A Content Analysis Of Review Literature.
This is a meta-review and synthesis of the research on the variables related learning.
Wang, M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg, H. J. (1990). What influences learning? A content analysis of review literature. The Journal of Educational Research, 30-43.
Assessing cross-cultural sensitivity awareness: A basis for curriculum change
This study examined the social attitudes related to race, gender, age, and ability among senior level health education students at a mid-sized university in the southeast by means of a personally experienced critical incident involving a cross-cultural incident.
Wasson, D. H., & Jackson, M. H. (2002). Assessing cross-cultural sensitivity awareness: A basis for curriculum change. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(4), 265-277.
Leadership for data-based decision-making: Collaborative data teams, 2006
This article offers practical suggestions on how to build a data-based culture in schools.
Wayman, J. C., Midgley, S., & Stringfield, S. (2006). Leadership for data-based decision-making: Collaborative educator teams. Learner centered leadership: Research, policy, and practice, 189-206.
Impact of highly and less job-related diversity on work group cohesion and performance: A meta-analysis.
A meta-analysis of the data from empirical investigations of diversity in work groups was used to examine the impact of two types of diversity attributes, highly job-related and less-related, on work group cohesion and performance.
Webber, S. S., & Donahue, L. M. (2001). Impact of highly and less job-related diversity on work group cohesion and performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of management, 27(2), 141-162.
Intractable self-fulfilling prophecies fifty years after Brown v. Board of Education.
This journal discuss about inequality as a persistent problem in school. An educational system that sorts for differentiated pathways must be replaced with one that develops the talents of all. Psychology has a critical role to play in promoting a new understanding of malleable human capabilities and optimal conditions for their nurturance in schooling.
Weinstein, R. S., Gregory, A., & Strambler, M. J. (2004). Intractable self-fulfilling prophecies fifty years after Brown v. Board of Education. American Psychologist, 59(6), 511.
Hard Thinking on Soft Skill
A prudent way forward for educators given the many acknowledged unknowns in soft skills reform is to substantially enhance efforts that fall within traditional school practices and responsibilities rather than to boldly make risky bets on unproven programs and measures. This paper breakdown the steps for school and district administrators.
Whitehurst, G. J. (2016). Hard thinking on soft skills. Evidence Speaks Reports, 1(14), 1-10.
The effects of extrinsic rewards in intrinsic motivation: A meta‐analysis.
Results of this meta‐analysis research, testing for a moderator effect, show that support for the overjustification effect occurs only when intrinsic motivation is operationalized as task behaviour during a free‐time measure.
Wiersma, U. (1992). The effects of extrinsic rewards in intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis.
Scoping and sequencing educational resources and speech acts: A unified design framework for learning objects and educational discourse.
This paper looks at scope and sequence as essential to effective instruction Instructional.
Wiley, D., & Waters, S. (2005). Scoping and sequencing educational resources and speech acts: A unified design framework for learning objects and educational discourse. Interdisciplinary Journal of E-Learning and Learning Objects, 1(1), 143-150.
4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.
Help your students understand the perspectives of other people with these tried-and-tested methods.
Wilson, D., & Conyers, M. (2017). 4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.Edutopia. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/article/4-proven-strategies-teaching-empathy-donna-wilson-marcus-conyers
Troubleshooting Behavioral Interventions: A Systematic Process for Finding and Eliminating Problems
This article describes a systematic process for finding and resolving problems with classroom-based behavioral interventions in schools.
Witt, J. C., VanDerHeyden, A. M., & Gilbertson, D. (2004). Troubleshooting behavioral interventions: A systematic process for finding and eliminating problems. School Psychology Review, 33, 363-383.
Time management: An experimental investigation.
Four groups of preservice teachers participating in student teaching seminars were randomly assigned to one of three conditions to test the effectiveness of brief training in time-management techniques.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: An experimental investigation. Journal of school Psychology, 24(3), 267-275.
Failing Teachers?
This book describes the research undertaken during the Teaching Competence Project, a two-year research project funded by the Gatsby Charitable Foundation. There were five interlinked studies in the research.
Wragg, E. C., Chamberlin, R. P., & Haynes, G. S. (2005). Failing teachers?. Routledge.
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
LINK
Center for Teaching
Resources provided by the Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching provides resources to assist teachers become better problem solvers.
Center for Teaching Excellence
Resources provided by the University of Waterloo Centre for Teaching Excellence provides resources to assist teachers become better problem solvers.
Teaching Excellence & Educational Innovation: Solve a Teaching Problem
This site provides practical strategies to address teaching problems across the disciplines. These strategies are firmly grounded in educational research and learning principles.
